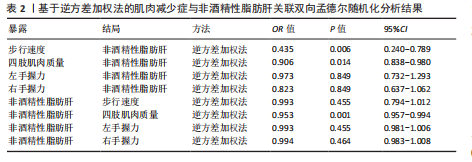
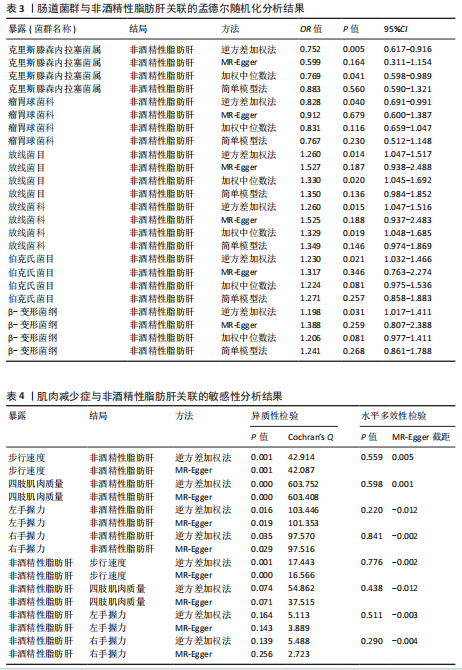
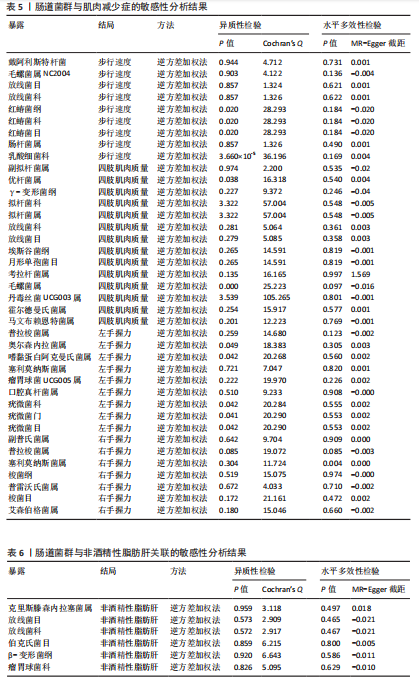
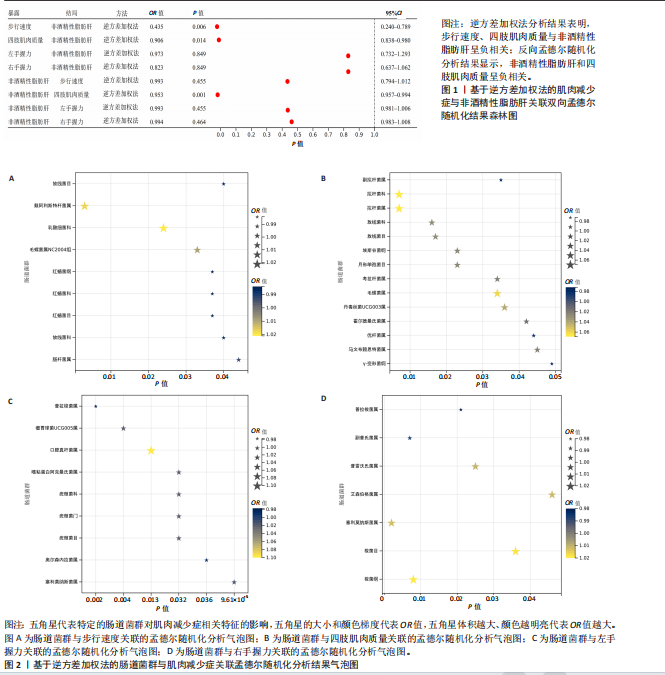
[1] DOS SANTOS ALS, ANASTÁCIO LR. The Impact of L-Branched-Chain Amino Acids and L-Leucine on Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Other Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Liver Disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(2):181-194.
[2] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, BALNTZI V, GRAY SR, et al. Global Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Severe Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86-99.
[3] HUANG DQ, EL-SERAG HB, LOOMBA R. Global Epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, Predictions, Risk Factors and Prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(4):223-238.
[4] ALSAQAL S, HOCKINGS P, AHLSTRÖM H, et al. The Combination of MR Elastography and Proton Density Fat Fraction Improves Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022;56(2):368-379.
[5] JEE JJ, LIM J, PARK S, et al. Gut Microbial Community Differentially Characterizes Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022; 37(9):1822-1832.
[6] HARRING M, GOLABI P, PAIK JM, et al. Sarcopenia Among Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is Associated with Advanced Fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21(11): 2876-2888.
[7] NICOLETTI A, PONZIANI FR, BIOLATO M, et al. Intestinal Permeability in the Pathogenesis of Liver Damage: From Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Liver Transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(33):4814-4834.
[8] DENG KQ, HUANG X, LEI F, et al. Role of Hepatic Lipid Species in the Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022;323(2):C630-C639.
[9] HU H, LIN A, KONG M, et al. Intestinal Microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Perspectives. J Gastroenterol. 2020;55(2):142-158.
[10] JENNISON E, BYRNE CD. The Role of the Gut Microbiome and Diet in the Pathogenesis of Non - alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021;27(1):22-43.
[11] GOMAA EZ. Human Gut Microbiota/Microbiome in Health and Diseases: A Review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020; 113(12):2019-2040.
[12] ALBILLOS A, DE GOTTARDI A, RESCIGNO M. The Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J Hepatol. 2020;72(3):558-577.
[13] HU H, LIN A, KONG M, et al. Intestinal Microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Perspectives. J Gastroenterol. 2020;55(2):142-158.
[14] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017; 318(19):1925-1926.
[15] XU HQ, SUN JQ, LIU Y, et al. Cutpoints for Muscle Mass and Strength Derived from Weakness or Mobility Impairment and Compared with Other Diagnostic Criteria in Community - Dwelling Elderly People. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;108(3):324-345.
[16] SKINNER J, SHEPSTONE L, HICKSON M, et al. Alcohol Consumption and Measures of Sarcopenic Muscle Risk: Cross - Sectional and Prospective Associations Within the UK Biobank Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023; 113(2):143-156.
[17] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31.
[18] SUDLOW C, GALLACHER J, ALLEN N, et al. UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age. PLoS Med. 2015;12(3):e1001779.
[19] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, GRAY SR, FORREST E, et al. Associations of Muscle Mass and Grip Strength With Severe NAFLD: A Prospective Study of 333,295 UK Biobank Participants . J Hepatol. 2022;76(5):1021-1029.
[20] KURILSHIKOV A, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, BACIGALUPE R, et al. Large-Scale Association Analyses Identify Host Factors Influencing Human Gut Microbiome Composition. Nat Genet. 2021;53(2):156-165.
[21] HARTWIG FP, DAVIES NM, HEMANI G, et al. Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization: Avoiding the Downsides of a Powerful, Widely Applicable but Potentially Fallible Technique. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1717-1726.
[22] ZHANG L, ZHANG C, ZHANG J, et al. A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study of Sarcopenia - Related Traits and Knee Osteoarthritis. Clin Interv Aging. 2023;18:1577-1586.
[23] JOO SK, KIM W. Interaction Between Sarcopenia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023;29(Suppl): S68-S78.
[24] DENG C, OU Q, OU X, et al. Association between Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2024;14(5): e78933.
[25] SAMUEL VT, SHULMAN GI. The Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance: Integrating Signaling Pathways and Substrate Flux. J Clin Invest. 2016;126 (1):12-22.
[26] JAMIALAHMADI T, NEMATY M, JANGJOO A, et al. The Predictive Role of Parathyroid Hormone for Non - alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Invasive and Non - invasive Findings in Candidates of Bariatric Surgery. Eat Weight Disord. 2022;27(2):693-700.
[27] NACHIT M, DE RUDDER M, THISSEN JP, et al. Myosteatosis Rather Than Sarcopenia Associates With Non - alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Non - alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Preclinical Models. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(1):144-158.
[28] YAMASANDHI PG, DHARMALINGAM M, BALEKUDURU A. Fetuin - A in Newly Detected Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus as a Marker of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2021;40(6):556 -562.
[29] CHADT A, AL-HASANI H. Glucose Transporters in Adipose Tissue, Liver, and Skeletal Muscle in Metabolic Health and Disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020;472(9):1273-1298.
[30] LIU L, HU R, YOU H, et al. Formononetin Ameliorates Muscle Atrophy by Regulating Myostatin -mediated PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a Pathway and Satellite Cell Function in Chronic Kidney Disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(3):1493-1506.
[31] OTA T. Molecular Mechanisms of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1261:223-229.
[32] ANAND AC. Nutrition and Muscle in Cirrhosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;7(4):340-357.
[33] KHAN S, BENJAMIN J, MAIWALL R, et al. Sarcopenia Is the Independent Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Cirrhosis. J Clin Transl Res. 2022;8(3):200-208.
[34] CHEN L, CHANG S, CHANG H, et al. Probiotic Supplementation Attenuates Age-Related Sarcopenia via the Gut-Muscle Axis in SAMP8 Mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):515-531.
[35] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, LANE NE, et al. Population-based Metagenomics Analysis Reveals Altered Gut Microbiome in Sarcopenia: Data from the Xiangya Sarcopenia Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(5):2340-2351.
[36] DAS S, PREETHI B, KUSHWAHA S, et al. Therapeutic Strategies to Modulate Gut Microbial Health: Approaches for Sarcopenia Management. Histol Histopathol. 2024; 39(11):1395-1425.
[37] VELÁZQUEZ KT, ENOS RT, BADER JE, et al. Prolonged High-Fat-Diet Feeding Promotes Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Alters Gut Microbiota in Mice. World J Hepatol. 2019;11(8):619-637.
[38] SUK KT, KIM DJ. Gut Microbiota: Novel Therapeutic Target for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13(3):193-204.
[39] ALIWA B, HORVATH A, TRAUB J, et al. Altered Gut Microbiome, Bile Acid Composition and Metabolome in Sarcopenia in Liver Cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14 (6):2676-2691.
[40] ŞANLIBABA P, TOPRAK ZTT, TEZEL BU. The Role of Probiotics on Slowing Down the Aging Process. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2022;21(1):53-66.
[41] YAN D, CAI X, XUE H, et al. Recent Advances in the Bioproduction of Mannitol. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024;40(8):2626-2643.
[42] DAHL WJ, HUNG WL, FORD AL, et al. In Older Women, a High-Protein Diet Including Animal-sourced Foods Did Not Impact Serum Levels and Urinary Excretion of Trimethylamine-N- oxide. Nutr Res. 2020; 78:72-81.
[43] ALIWA B, HORVATH A, TRAUB J, et al. Altered Gut Microbiome, Bile Acid Composition and Metabolome in Sarcopenia in Liver Cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(6):2676-2691.
[44] KRAUTKRAMER KA, FAN J, BÄCKHED F. Gut Microbial Metabolites as Multi-kingdom Intermediates. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(2):77-94.
[45] DODD D, SPITZER MH, VAN TREUREN W, et al. A Gut Bacterial Pathway Metabolizes Aromatic Amino Acids Into Nine Circulating Metabolites. Nature. 2017;551(7682):648-652.
[46] DELEAVAL P, LUAIRE B, LAFFAY P, et al. Short-Term Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids-Enriched Dialysis Fluid on Branched-Chain Amino Acids Plasma Level and Mass Balance: A Randomized Cross - Over Study. J Ren Nutr. 2020;30(1):61-68.
[47] 方志杰,马抢平,董万涛,等.肠道菌群与骨质疏松症的遗传关系:来自英国数据库211个肠道微生物群分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(18):3941-3947.
|