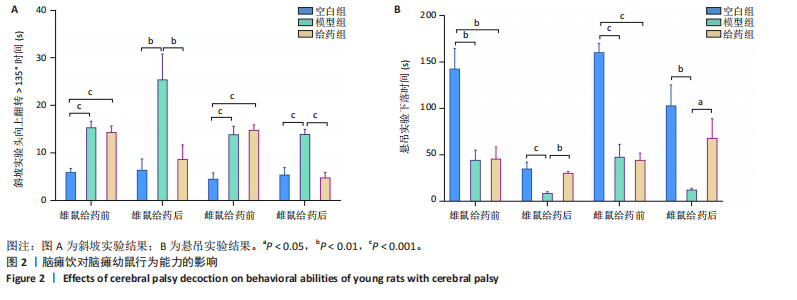
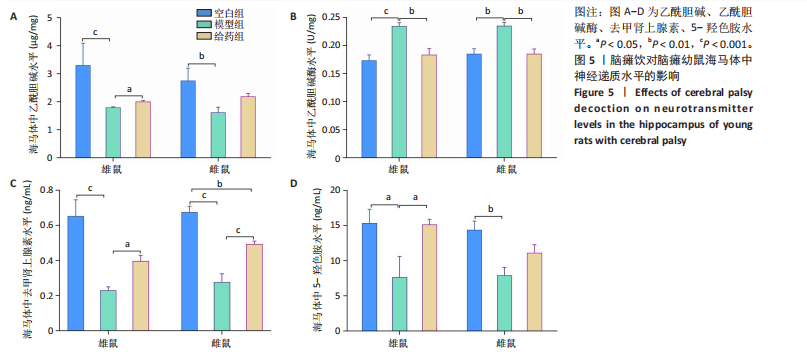
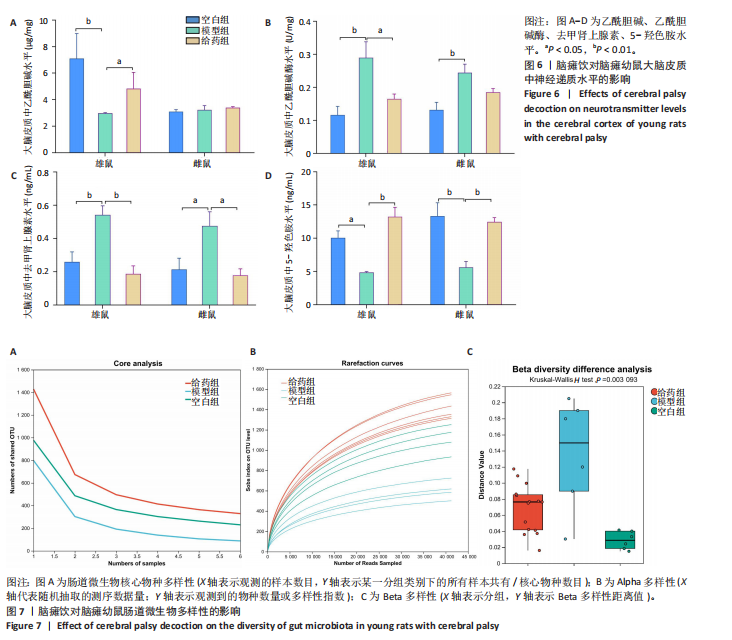
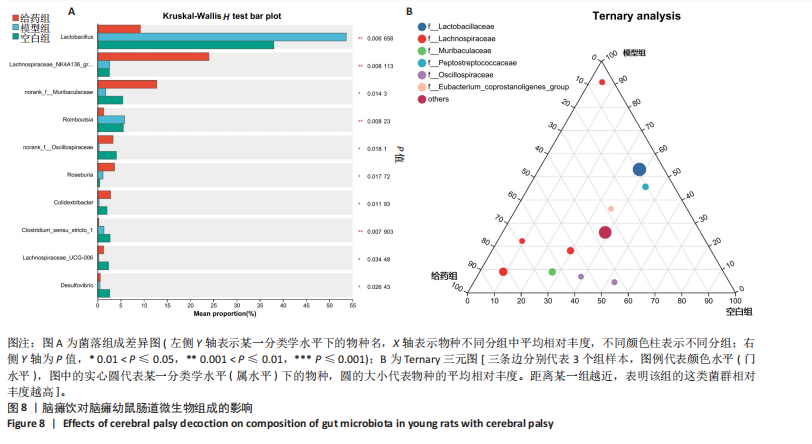
[1] GALEA C, MCINTYRE S, SMITHERS-SHEEDY H, et al. Cerebral palsy trends in Australia (1995-2009): a population-based observational study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019;61(2):186-193.
[2] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会,中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑性瘫痪康复专业委员会,中国医师协会康复医师分会儿童康复专业委员会,等.中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2022)第一章:概论[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2022,37(12):887-892.
[3] 王强力,吴梦婷,郑贺彬,等.针刺核心肌群联合康复训练治疗脑瘫的疗效观察及对运动能力和平衡能力的影响[J].上海针灸杂志, 2024,43(10):1128-1133.
[4] STIGGER F, FELIZZOLA AL, KRONBAUER GA, et al. Effects of fetal exposure to lipopolysaccharide, perinatal anoxia and sensorimotor restriction on motor skills and musculoskeletal tissue: implications for an animal model of cerebral palsy. Exp Neurol. 2011;228(2):183-191.
[5] CAVARSAN CF, GORASSINI MA, QUINLAN KA. Animal models of developmental motor disorders: parallels to human motor dysfunction in cerebral palsy. J Neurophysiol. 2019;122(3):1238-1253.
[6] STRATA F, COQ JO, BYL N, et al. Effects of sensorimotor restriction and anoxia on gait and motor cortex organization: implications for a rodent model of cerebral palsy. Neuroscience. 2004;129(1):141-156.
[7] BALDRICK P. Developing drugs for pediatric use: a role for juvenile animal studies? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004;39(3):381-389.
[8] 赵伟,孙国志.不同种实验动物间用药量换算[J].畜牧兽医科技信息,2010(5):52-53.
[9] 陈玥,苏丹,贵文娟,等.实验动物与人类年龄相关性研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(11):116-122.
[10] LISMAN J, BUZSÁKI G, EICHENBAUM H, et al. Viewpoints: how the hippocampus contributes to memory, navigation and cognition. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(11):1434-1447.
[11] 崔连旭,李昊旻,许峻荣,等.脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基对小型猪创伤性颅脑损伤组织修复的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2026,30(7):1730-1735.
[12] 李思宇,杨坤,宋常月,等.基于GRIN2A/PLCB1/PRKCG信号通路探讨白芍总苷减轻马钱子水提物神经损伤的作用机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(23):56-63.
[13] 张静雯,范琼尹,张苏素,等.新型5-羟色胺和去甲肾上腺素重摄取抑制剂ZBH2012001通过增强单胺系统功能和抑制神经免疫炎症发挥抗抑郁作用[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2024,38(5):321-334.
[14] 王其飞,杜兴彬,孔健达.中枢疲劳的神经生理基础及运动诱发机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(32):6979-6988.
[15] SMYTH R, REID SM, PATON K, et al. Causation in cerebral palsy: Parental beliefs and associated emotions. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024; 66(2):258-266.
[16] VILLAMOR E. Changing trends in cerebral palsy prevalence: an opportunity to consider etiological pathways. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022;64(9):1054-1055.
[17] CAESAR RA, BOYD RN, CIONI G, et al. Early detection of developmental delay in infants born very preterm or with very low birthweight. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2023;65(3):346-357.
[18] 刘浩哲,苗明三.基于中西医临床病症特点的脑性瘫痪动物模型分析[J].中药药理与临床,2021,37(5):189-194.
[19] 姜煜,徐林,赵亚林,等.舒筋健脑方对缺血缺氧脑瘫模型大鼠细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28):4477-4483.
[20] 刘港,曾杰,赵亚林,等.舒筋健脑方干预脑瘫模型大鼠减轻大脑皮质的组织炎症反应[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(23):3674-3679.
[21] 单海军,娄元俊,朱珊,等.补肾开窍祛痰方改善痉挛型脑瘫大鼠运动行为的效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(15):3731-3735.
[22] 罗石任,谢艳,张丽,等.酸枣仁提取物靶向调控促进骨骼增长的miRNA筛选[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(35):5658-5664.
[23] 许静,霍康,郭秦乐,等.地黄苷A对CLP诱导的脓毒症大鼠脑功能障碍和Nrf2/GPX4介导的铁死亡通路的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2024,24(14):2619-2625.
[24] 李朋月,景永帅,吴兰芳,等.山药多糖对脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用机制[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2021,35(9):675-676.
[25] 苗树船,夏勋,张列.茯苓酸抑制H2O2诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞凋亡及促进细胞存活[J].西部医学,2021,33(7):982-986.
[26] 齐梓彤,刘薇,雒慧钧,等.负载丹皮酚外泌体对缺血性脑卒中大鼠线粒体功能障碍的保护作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2023,39(4):615-621.
[27] 邓云飞,李惠红,魏伟,等.泽泻醇A保护血脑屏障改善脑缺血/再灌注损伤的作用和机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2024,40(1): 83-90.
[28] 赵晓华,田倩倩,薛伟,等.吴茱萸碱通过GSK-3β/β-catenin通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].南开大学学报(自然科学版),2023, 56(5):23-28.
[29] 丁蕊,袁永,贾亚泉,等.六味地黄丸介导RAGE抑制MMP-2/MMP-9对Aβ1-40损伤bEnd.3细胞紧密连接蛋白的影响[J].中成药,2024,46(2):424-430.
[30] 刘彦宏,武凤,于修芳,等.杜仲提取物通过HPG轴对APP/PS1小鼠学习认知功能的影响[J].中药材,2022,45(8):1964-1968.
[31] 谢万科,刘彦宁,李治延.柯诺辛碱对创伤性脑损伤大鼠线粒体自噬的影响[J].中医药导报,2024,30(5):7-12.
[32] 李雅茜.抑郁症中医辨证分型与脑功能S-ET特征、神经递质的关系分析[J].四川中医,2022,40(9):72-76.
[33] 袁丽君,涂星,李三宇,等.土家族麝针疗法对缺血性脑卒中大鼠下丘脑中DA、5-HT、ICAM-1和MCP-1含量的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(4):840-844.
[34] 王永为,李海艳,高亚贤,等.脊髓损伤后5-HT2A受体的变化与鼠尾痉挛关系的分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(1):83-86.
[35] 张易,郑素珍,杨丽薇,等.中度有氧运动对老年抑郁症病人5-羟色胺、去甲肾上腺素水平及自主神经功能的干预效果研究[J].实用老年医学,2023,37(6):595-598.
[36] 刘俊财,葛珍,江晓,等.蜂王浆肽对阿尔茨海默症模型斑马鱼运动能力与关键基因表达影响[J].食品工业科技,2023,44(21):395-401.
[37] 彭颖.辣木籽水提物对酒精诱导线虫运动功能障碍的影响[J].食品与机械,2020,36(10):149-152+158.
[38] 刘运琴,刘燕芹,戢汉斌,等.淫羊藿苷对精神分裂症模型大鼠认知功能的改善作用及机制[J].中国药房,2021,32(7):812-818.
[39] 殷铭,吕笑丽,王碧馨,等.shRNA干扰蓝斑核去甲肾上腺素转运体(NET)表达对大鼠抑郁样行为的改善作用[J].神经解剖学杂志, 2017,33(3):329-335.
[40] 申丽英,董雨,孔维,等.慢性睡眠剥夺对大鼠空间学习记忆、海马体齿状回区去甲肾上腺素水平及其受体表达的影响[J].职业与健康,2021,37(3):330-333.
[41] 孙道涵,李蜀平,廖磊,等.调和肝脾方改善睡眠的时效关系及作用机制的研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2019,28(27):2993-2996+3001.
[42] 王宏吉,曹波.基于脑肠轴探讨肠道菌群调控腹泻型肠易激综合征的研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药,2024,33(19):59-65.
[43] 顾富城,杨美鑫,吴伟欣,等.龟鹿二仙胶对膝骨关节炎大鼠肠道菌群的影响:机器学习与16SrDNA分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2026,30(4):1058-1072.
[44] THURSBY E, JUGE N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. 2017;474(11):1823-1836.
[45] 戎新倩,舒青龙.基于脑-肠-微生物轴的肠易激综合征机制与治疗研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2023,50(9):4190-4205.
[46] HUGON P, DUFOUR JC, COLSON P, et al. A comprehensive repertoire of prokaryotic species identified in human beings. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(10):1211-1219.
[47] 张静仪,郑泽荣,彭仕熙,等.基于脑肠轴理论探讨化痰开窍方治疗老年缺血性脑卒中的临床疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2024, 44(15):3602-3605.
[48] 周彦妮,陈敏,杨焱麟,等.基于脑肠轴的肠道菌群调控腹泻型肠易激综合征的研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(3):1582-1586.
[49] 王菲,辛凯,陈丽,等.基于TLR4/NF-κB信号通路探究涤浊汤对高尿酸血症大鼠肠道菌群紊乱的调节作用[J].中国微生态学杂志, 2024,36(1):10-17+28.
[50] 陈杰东.不同脂肪供能比饮食热量限制干预对肥胖大鼠糖脂代谢、肠道菌群和肝脏转录组的影响[D].福州:福建医科大学,2022.
[51] 谢佑红,周天宇,王金枝,等.马钱子苷通过肠道菌群和神经肽抑制OVX小鼠骨量丢失的机制探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024, 30(4):538-545.
[52] ZHANG Z, SHAO S, ZHANG Y, et al. Xiaoyaosan slows cancer progression and ameliorates gut dysbiosis in mice with chronic restraint stress and colorectal cancer xenografts. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110916.
[53] 魏巍,王世轩,战丽彬.肌少-骨质疏松症与肠道菌群相关性研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2024,26(9):2434-2443. |