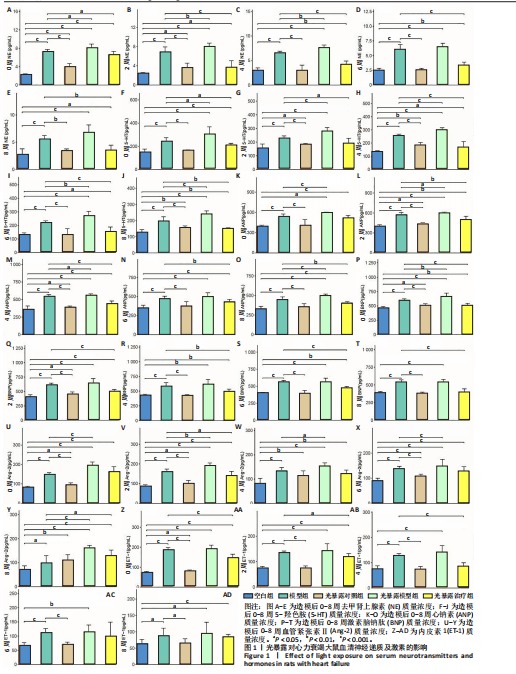
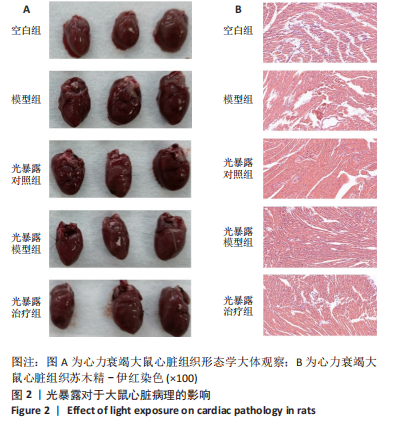
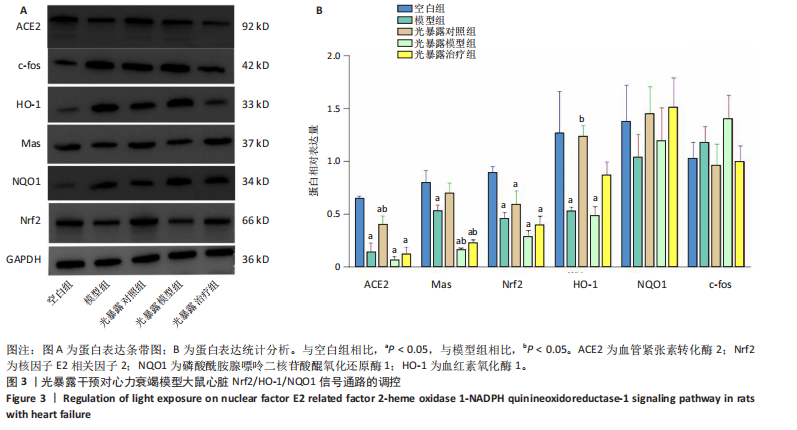
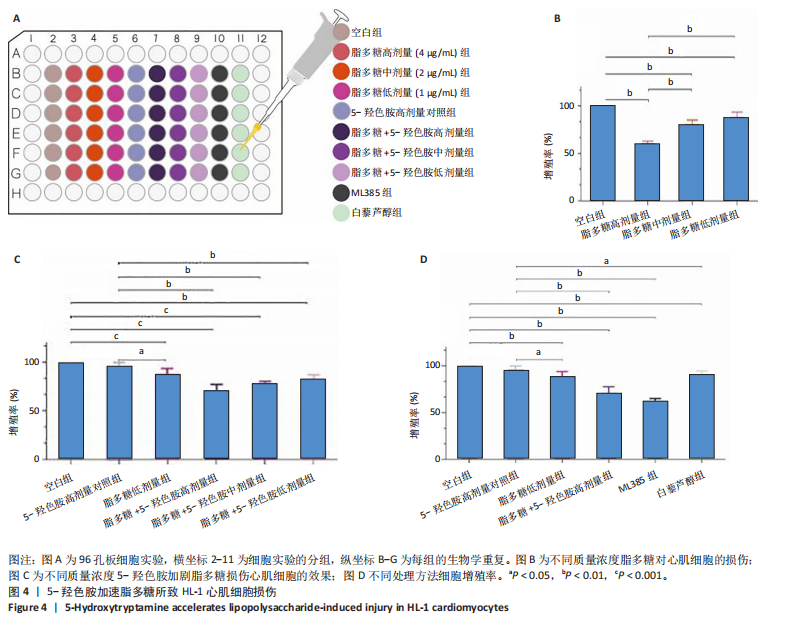
[1] 孙珂,王婷,李静颐,等. 心脏组织工程联合干细胞促进心肌修复的研究进展[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2024,16(2):237-240.
[2] 董国菊,刘思雨. 射血分数保留心力衰竭中西医病证结合的分期诊断专家共识[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2023,41(5):254-258.
[3] 张倩,卫晓红,陈洁,等. 慢性心力衰竭常用动物模型的研究进展及其在中医药研究中的应用[J]. 中国中药杂志,2023,48(3):614-624.
[4] MENG D, LI HQ, DEISSEROTH K, et al. Neuronal activity regulates neurotransmitter switching in the adult brain following light-induced stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(20):5064-5071.
[5] MADDALONI G, CHANG YJ, SENFT RA, et al. Adaptation to photoperiod via dynamic neurotransmitter segregation. Nature. 2024;632(8023): 147-156.
[6] TEKIYEH MAROOF N, MEHRZADI S, NASEROLESLAMI M, et al. Apelin13 Loaded Nano-Niosomes Confer Cardioprotection in a Rat Model of Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion by Targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025;18(3):529-543.
[7] 张榕,刘春华,胡爽,等. 夜间光暴露小鼠肝脏非靶向代谢组学研究[J].预防医学,2021,33(2):130-134.
[8] 李玮,郝翠芳.夜间光污染对雌性大鼠生殖功能的影响[J].中国妇幼保健,2021,36(6):1379-1381.
[9] 刘鑫,朱浩彦,吴嘉贺,等. 基于生物信息学分析预测和验证实验性自身免疫性心肌炎的关键基因[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2025, 46(1):27-35.
[10] 徐建军.内质网应激介导自吞噬对脂多糖诱导HL-1心肌细胞损伤保护机制的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
[11] 曹红,张小萌,许琮.镍纹蛋白样β对脂多糖诱导心肌细胞损伤的抑制作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2023,63(23):1-4.
[12] 李凡凡,徐阳,王晓旭.紫草素调节Nrf2/HO-1信号通路对实验性大鼠肉芽肿性小叶性乳腺炎的治疗作用研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2024,42(1):26-32.
[13] 姚宁丰,佘仁夏,舒艺璇,等.白藜芦醇对脑出血后小胶质细胞功能的影响及其机制[J].解放军医学杂志,2023,48(4):420-430.
[14] 曾佑成.基于铁死亡探讨白藜芦醇对脓毒症大鼠心肌损伤的作用机制的研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2023.
[15] 中华中医药学会慢性心力衰竭中医诊疗指南项目组.慢性心力衰竭中医诊疗指南(2022年)[J].中医杂志,2023,64(7):743-756.
[16] CHICOS AB, KANNANKERIL PJ, KADISH AH, et al.Parasympathetic effects on cardiac electrophysiology during exercise and recovery in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;297(2):H743-H749.
[17] HEIDENREICH PA, BOZKURT B, AGUILAR D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145(18): e895-e1032.
[18] MARYAM, VARGHESE TP, B T.Unraveling the complex pathophysiology of heart failure: insights into the role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024;49(4):102411.
[19] SAYER G, BHAT G.The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Heart Failure. Cardiol Clin. 2014;32(1):21-32.
[20] MÖLLER PETRUN A, MARKOTA A.Angiotensin II-Real-Life Use and Literature Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(9):1483.
[21] YANG P, WU Y, LI F, et al. Activation of ETAR and ETBR in myocardial tissue characterizes heart failure induced by experimental autoimmune myocarditis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024;24(1):11.
[22] 柯元南,Manthey J.慢性充血性心衰的血液动力学和儿茶酚胺,肾素活性及抗利尿激素的变化[J].中华内科杂志,1987,26(1):16-19.
[23] 张浩华.精氨酸血管加压素受体拮抗剂在心力衰竭患者中应用效果的研究进展[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2018,26(7): 9-13.
[24] SHAO L, SHEN Y, REN C, et al. Inflammation in myocardial infarction: roles of mesenchymal stem cells and their secretome. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):452.
[25] ZHANG DY, ANDERSON AS.The Sympathetic Nervous System and Heart Failure. Cardiol Clin. 2014;32(1):33-45,
[26] 郭艳琳.下丘脑室旁核CRH神经元激活在慢性充血性心力衰竭中的交感兴奋作用及机制研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2011.
[27] KANG YM, HE RL, YANG LM, et al. Brain tumour necrosis factor-α modulates neurotransmitters in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;83(4):737-746.
[28] BO W, CAI M, MA Y, et al. Manipulation of Glutamatergic Neuronal Activity in the Primary Motor Cortex Regulates Cardiac Function in Normal and Myocardial Infarction Mice. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024; 11(20):e2305581.
[29] TÄHKÄMÖ L, PARTONEN T, PESONEN AK.Systematic review of light exposure impact on human circadian rhythm.Chronobiol Int. 2019;36(2):151-170.
[30] AN K, ZHAO H, MIAO Y, et al.A circadian rhythm-gated subcortical pathway for nighttime-light-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23(7):869-880.
[31] HAGE B, BRITTON B, DANIELS D, et al. Diminution of Heart Rate Variability in Bipolar Depression. Front Public Health. 2017;5:312.
[32] MASON IC, GRIMALDI D, REID KJ,et al.Light exposure during sleep impairs cardiometabolic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022; 119(12):e2113290119.
[33] HUYNH P, HOFFMANN JD, GERHARDT T, et al. Myocardial infarction augments sleep to limit cardiac inflammation and damage. Nature. 2024;635(8037):168-177.
[34] 闫赛强,王朝,张珣,等.疏肝健脾中药联合益生菌治疗失眠的临床疗效及对血清5-羟色胺,褪黑素,血管活性肠肽水平的影响[J].天津中医药,2024,41(3):287-293.
[35] BRINDLEY RL, BAUER MB, BLAKELY RD, et al. Serotonin and Serotonin Transporters in the Adrenal Medulla: A Potential Hub for Modulation of the Sympathetic Stress Response. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017;8(5): 943-954.
[36] HWANG YK, OH JS. Interaction of the Vagus Nerve and Serotonin in the Gut–Brain Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26(3):1160.
[37] 闻松,杨长坤.5-羟色胺及其受体拮抗剂在心血管疾病中的研究现状[J].河北医科大学学报,2021,42(12):1475-1481.
[38] 杨荣军,史钰芳,王庆海.慢性心力衰竭与抑郁症共同发病机制及药物治疗的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(5):625-630.
[39] 刘倩,黄勇祥,郑昌博.5-羟色胺受体在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2022,36(7):521-528.
[40] ZHANG Q, WANG L, WANG S, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapy for myocardial infarction.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022; 7(1):78.
[41] YU C, XIAO JH. The Keap1-Nrf2 System: A Mediator between Oxidative Stress and Aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6635460.
[42] 胡流芳,王迎,任汝静,等.Keap1-Nrf2/ARE信号通路的抗氧化应激作用及其调控机制[J].国际药学研究杂志,2016,43(1):146-152+166.
[43] 陶卉,段晓宇,刘筱,等.Nrf2/HO-1通路通过调控内质网应激改善小鼠心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤的作用研究[J].蚌埠医学院学报, 2023,48(3):296-300.
[44] 罗星,徐长庆.PTH,细胞内钙和CaSR在心肌损伤中的“三角关系”[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(1):179-183.
[45] KIM HJ, ZHENG M, KIM SK, et al. CO/HO-1 Induces NQO-1 Expression via Nrf2 Activation. Immune Netw. 2011;11(6):376-382.
[46] 张玉琴,李鸷,李煌,等. 栝楼桂枝颗粒激活Nrf2信号通路减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠氧化应激损伤作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017,23(21):112-116.
[47] 卢志刚,黄家彬,徐忠诚,等.醒脑静注射液对急性脑梗死外周血单个核细胞Nrf2、HO-1、NQO1表达及临床疗效的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2016,32(5):98-101.
[48] 纪新博,顾申红,麦华德,等. Prdx1过表达通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制氧化应激减轻自发性高血压大鼠心肌肥厚和纤维化[J].安徽医科大学学报,2023,58(2):196-201.
[49] 张轶斐,白雪慧,曹梓静,等. 基于Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1信号通路探讨益肾通络方改善糖尿病肾脏病小鼠氧化应激损伤的机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2025,31(5):41-51.
[50] 唐玲,唐荣伟,赵臻怡,等.金丝桃苷调控Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1通路减轻大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2024,43(4): 285-290.
[51] 郭君婷,赵婷婷,叶斯木·塔拉甫别克,等.基于Nrf2/HO-1信号通路调控的恰玛古多糖抗多柔比星心肌毒性的机制研究[J].药学学报,2024,59(4):930-938.
[52] 刘金江,赵径,王娇,等.胺碘酮通过激活Keap1/Nrf2通路减轻大鼠心脏缺血再灌注损伤[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2024,30(3):316-322.
[53] 陈伟,王海英,徐鹏,等.缺血后处理激活大鼠心肌缺血再灌注时Nrf2-ARE信号通路的机制:与ROS的关系[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2015,35(8):998-1002.
[54] 姚琪,唐关敏.虾青素调控Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1通路减轻心肌缺血再灌注大鼠氧化应激损伤[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2023,43(8):1953-1957.
[55] 于馨雅,申元英,郭乐. Nrf2/HO-1通路在氧化应激和炎性反应中的作用[J].医学研究杂志,2023,52(7):19-22.
[56] CHEN Y, ZHANG P, CHEN W, et al. Ferroptosis mediated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis associated with Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunol Lett. 2020;225:9-15.
[57] LIU N, SUN S, WANG P, et al.The Mechanism of Secretion and Metabolism of Gut-Derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(15):7931.
[58] 成龙,党正中,刘春亮,等. 5-羟基色氨酸生产、测定和代谢途径及其应用研究进展[J].经济动物学报,2024,28(1): 50-56.
[59] PAQUELET GE, CARRION K, LACEFIELD CO, et al. Single-cell activity and network properties of dorsal raphe nucleus serotonin neurons during emotionally salient behaviors. Neuron. 2022;110(16):2664-2679.e8.
[60] 田志锋,曾璇,严子涵,等. 5-羟色胺与缝隙连接的交互作用与抑郁症发病的关系及中药干预研究进展[J].中草药,2024,55(21): 7539-7546.
[61] 李仲文,诸毅晖,宋孝军,等. 针刺通过调节睡眠结构改善失眠的神经递质机制研究进展[J]. 针刺研究,2023,48(6): 618-624.
[62] 鲁楠,迟云鹏,陶淑慧,等. 5-羟色胺在心血管疾病中的研究进展[J].中华心血管病杂志,2023,51(2):208-214.
[63] 闻松,杨长坤,江平. 5-羟色胺及其受体拮抗剂在心血管疾病中的研究现状[J].河北医科大学学报,2021,42(12):1475-1481.
[64] BRATTELID T, QVIGSTAD E, BIRKELAND JA, et al.Serotonin responsiveness through 5-HT2A and 5-HT4 receptors is differentially regulated in hypertrophic and failing rat cardiac ventricle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43(6):767-779.
[65] BIRKELAND JA, SWIFT F, TOVSRUD N, et al. Serotonin increases L-type Ca2+ current and SR Ca2+ content through 5-HT4 receptors in failing rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007; 293(4):H2367-H2376.
[66] 刘敏科,金华.心血管疾病与肠道菌群和5-羟色胺信号系统关系的研究现状[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(23):3943-3946.
[67] 彭仁聪,马培荣,伍崇信,等.参麦注射液联合新活素对缺血性心肌病患者神经内分泌激素与心肺运动功能的影响[J].吉林医学, 2024,45(9):2195-2199.
[68] XU YX, ZHOU Y, HUANG Y, et al. Physical activity alleviates negative effects of bedroom light pollution on blood pressure and hypertension in Chinese young adults. Environ Pollut. 2022;313:120117.
[69] XU YX, YU Y, HUANG Y,et al. Exposure to bedroom light pollution and cardiometabolic risk: A cohort study from Chinese young adults. Environ Pollut. 2022;294:118628.
[70] 郭益雯,齐进,胡可嘉.室内外夜间灯光暴露的健康效应研究进展[J].环境与职业医学,2023,40(9):1102-1108.
[71] OBAYASHI K, YAMAGAMI Y, TATSUMI S, et al. Indoor light pollution and progression of carotid atherosclerosis: A longitudinal study of the HEIJO-KYO cohort. Environ Int. 2019;133(Pt B):105184.
[72] OBAYASHI K, SAEKI K, KURUMATANI N.et al.Light exposure at night is associated with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in the general elderly population: The HEIJO-KYO cohort. Chronobiol Int. 2015;32(3):310-317.
|