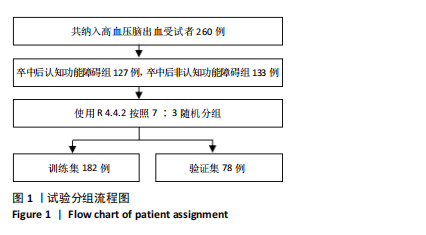
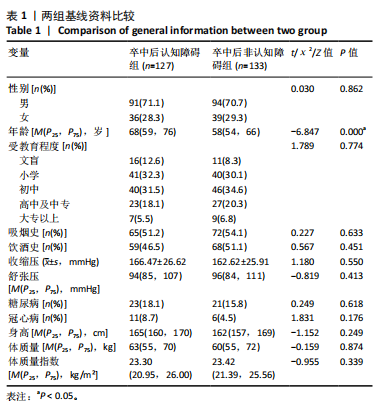
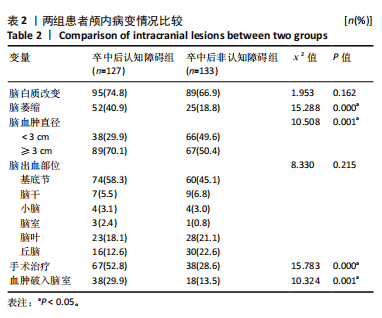
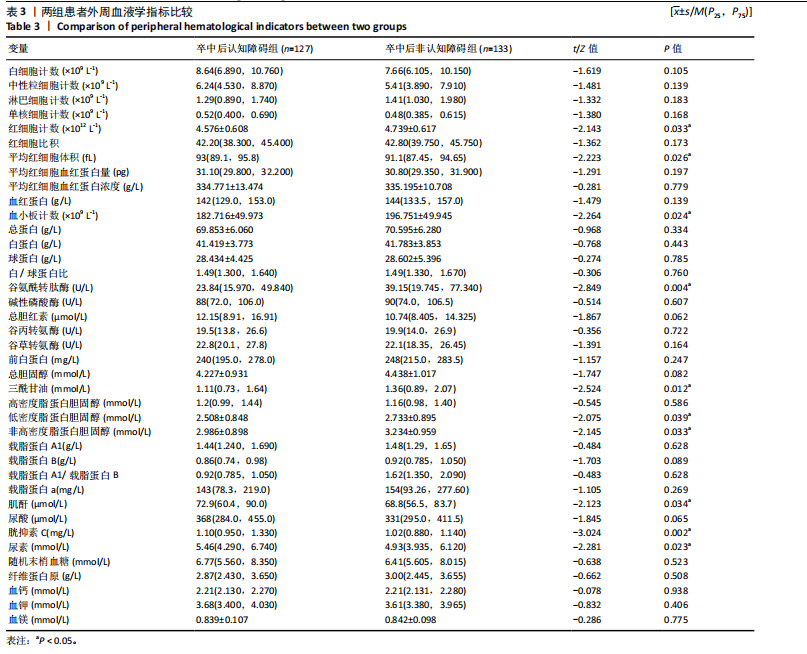
[1] TU WJ, WANG LD. China stroke surveillance report 2021. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):33.
[2] AN SJ, KIM TJ, YOON BW. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Clinical Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update. J Stroke. 2017; 19(1):3-10.
[3] FEIGIN VL, LAWES CM, BENNETT DA, et al. Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2(1):43-53.
[4] SEIFFGE DJ, FANDLER-HÖFLER S, DU Y, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage - mechanisms, diagnosis and prospects for treatment and prevention. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024;20(12):708-723.
[5] LEKOUBOU A, NGUYEN C, KWON M, et al. Post-stroke Everything. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023;23(11):785-800.
[6] EL HUSSEINI N, KATZAN IL, ROST NS, et al. Cognitive Impairment After Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023;54(6):e272-e291.
[7] 邓里娜,吴波.《中国脑出血诊治指南2019》更新要点及解读[J].心脑血管病防治,2021,21(1):13-17+34.
[8] 汪凯,董强,郁金泰,等.卒中后认知障碍管理专家共识2021[J].中国卒中杂志,2021,16(4):376-389.
[9] 曲艳吉,卓琳,詹思延.中国脑卒中后认知障碍流行病学特征的系统评价[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2013,15(12):1294-1301.
[10] ROST NS, BRODTMANN A, PASE MP, et al. Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1252-1271.
[11] ZHOU W, FENG H, TAO H, et al. Factors Influencing Poststroke Cognitive Dysfunction: Cross-Sectional Analysis. JMIR Form Res. 2024;8:e59572.
[12] MA Y, HE X, YANG T, et al. Cognitive function in older adults with stroke: A latent profile analysis. Geriatr Nurs. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2024.10.053.
[13] SPRINGER MV, CHEN B, WHITNEY RT, et al. Age differences in the change in cognition after stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024; 33(12):108087.
[14] QUINN TJ, RICHARD E, TEUSCHL Y, et al. European Stroke Organisation and European Academy of Neurology joint guidelines on post-stroke cognitive impairment. Eur Stroke J. 2021;6(3):I-XXXVIII.
[15] BRITO DV, NÓBREGA C. Making bridges between preclinical and clinical insights into age-related cognitive decline. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(8):2321-2322.
[16] CHAU JPC, LO SHS, ZHAO J, et al. Apathy mediates the association between age and cognition after stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2024;46(21): 5038-5043.
[17] PLUTA R, JABŁOŃSKI M, JANUSZEWSKI S, et al. Crosstalk between the aging intestinal microflora and the brain in ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:998049.
[18] DONNELLAN C, WERRING D. Cognitive impairment before and after intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review. Neurol Sci. 2020; 41(3):509-527.
[19] GU Y, WANG F, GONG L, et al. A nomogram incorporating red blood cell indices to predict post-stroke cognitive impairment in the intracerebral hemorrhage population. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:985386.
[20] XIONG L, REIJMER YD, CHARIDIMOU A, et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage and cognitive impairment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(5):939-944.
[21] ZHANG Z, GUO P, HUANG S, et al. Inhibiting Microglia-Derived NLRP3 Alleviates Subependymal Edema and Cognitive Dysfunction in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus after Intracerebral Hemorrhage via AMPK/Beclin-1 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4177317.
[22] LIU DZ, WALDAU B, ANDER BP, et al. Inhibition of Src family kinases improves cognitive function after intraventricular hemorrhage or intraventricular thrombin. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(7): 2359-2367.
[23] JIANG C, ZOU X, ZHU R, et al. The correlation between accumulation of amyloid beta with enhanced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment after intraventricular hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2019; 131(1):54-63.
[24] MAGID-BERNSTEIN J, GIRARD R, POLSTER S, et al. Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions. Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1204-1229.
[25] DE OLIVEIRA MANOEL AL. Surgery for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):45.
[26] IBRAHIM A, ARIFIANTO MR, AL FAUZI A. Minimally Invasive Neuroendoscopic Surgery for Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Review of the Rationale and Associated Complications. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2023;130:103-108.
[27] MA Y, CHEN Y, YANG T, et al. Blood biomarkers for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024;33(8):107632.
[28] OH YS, KIM JS, PARK JW, et al. Arterial stiffness and impaired renal function in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci. 2016;37(3): 451-457.
[29] IGARASHI K, YOSHIDA M, WARAGAI M, et al. Evaluation of dementia by acrolein, amyloid-β and creatinine. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;450:56-63.
[30] AURIEL E, KLIPER E, SHENHAR-TSARFATY S, et al. Renal Function, MRI Brain Changes and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment. Stroke. 2015; 46(suppl_1):A47.
[31] AURIEL E, KLIPER E, SHENHAR-TSARFATY S, et al. Impaired renal function is associated with brain atrophy and poststroke cognitive decline. Neurology. 2016;86(21):1996-2005.
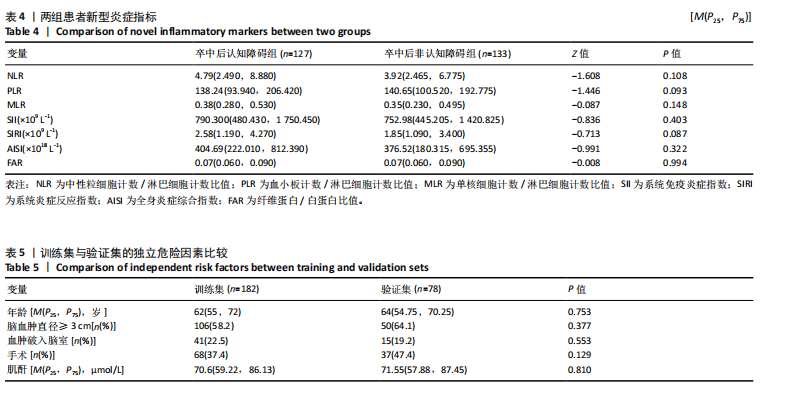
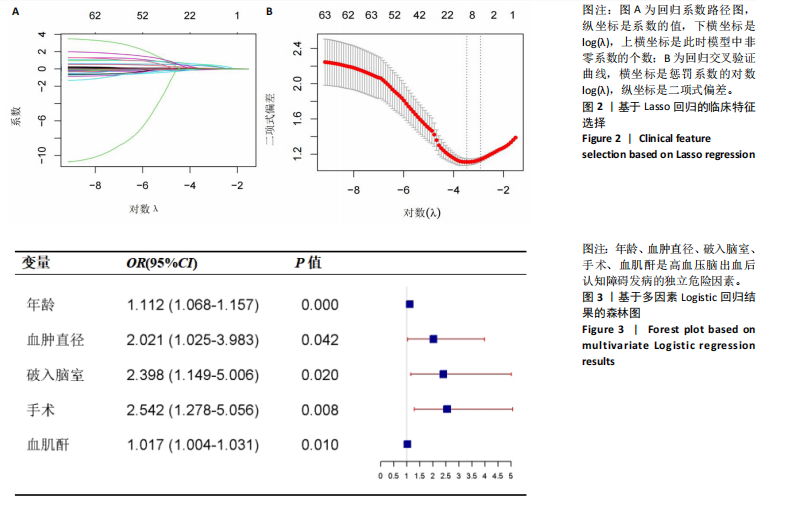
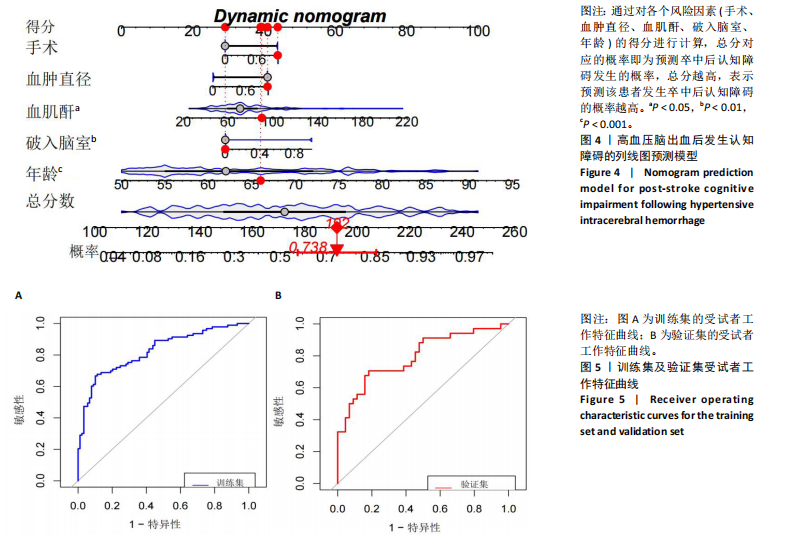
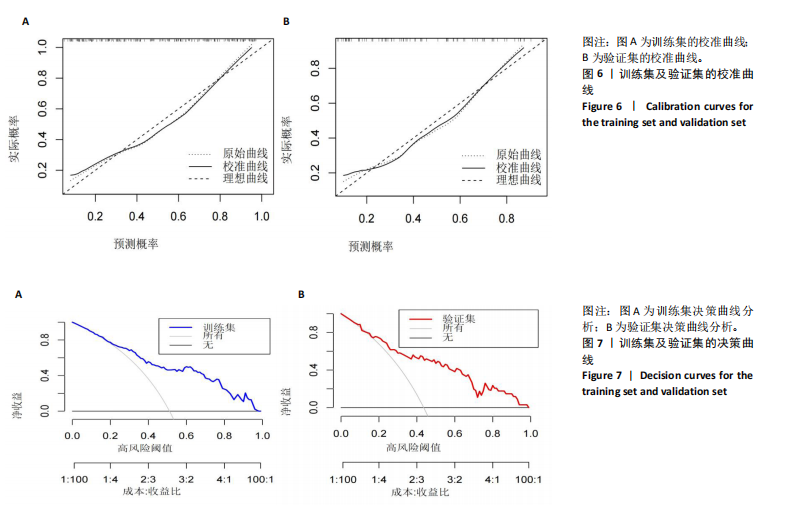
[32] BALACHANDRAN VP, GONEN M, SMITH JJ, et al. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4): e173-e180.
|