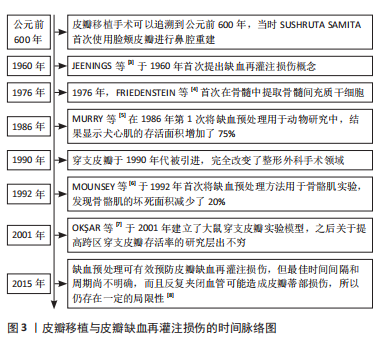
2.1 皮瓣移植与皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤治疗的时间脉络 皮瓣移植的历史非常悠久,最早可以追溯到公元前600年,经过2 000多年的研究、实践和发展,关于皮瓣移植的技术和皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的治疗不断提升,皮瓣移植和皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的治疗时间脉络图见图3。
2.2 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的病理机制十分复杂,缺血时,由于血流的断供氧气无法运输,造成缺氧;再灌注后,机体产生的大量活性氧破坏抗氧化防御,产生氧化应激。缺血再灌注损伤组织器官中Ca2+平衡发生紊乱,而细胞内Ca2+超载又通过促进活性氧等有害物质的再次释放加剧氧化应激;同时,中性粒细胞的大量涌入会介导炎症反应发生,引起细胞凋亡,促使血管损伤和微循环障碍,最终导致皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。
2.2.1 炎性损伤 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的炎性损伤是由中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞、巨噬细胞等炎性细胞与核转录因子κB、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等多种炎性细胞与细胞因子共同作用的结果[9]。核转录因子κB是一种已知的调控人体免疫应答、细胞周期以及内环境稳态的转录因子,与组织细胞的炎性损伤密切相关。生理状态下,核转录因子κB以RelA/P50二聚体的形式与核转录因子κB抑制因子α(IκBα)结合,或以RelB/P100(P52前体)二聚体的形式存在,从而限制核转录因子κB的活化与下游相关基因的转录;在细胞内外应激源的刺激下,IκB 激酶被激活,活化的IκB 激酶可将IκB蛋白磷酸化,后者最终被蛋白酶体水解,失去IκB蛋白抑制的核转录因子κB二聚体(RelA/P50)可被激活并进入细胞核,从而进行下游相关炎性因子(如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、单核细胞趋化蛋白1等)的转录调控,加重组织细胞的炎性损伤。肿瘤坏死因子α是炎症损伤过程中最早出现的炎性递质,不仅可通过激活中心粒细胞、淋巴细胞等炎性细胞合成并分泌白细胞介素6等炎性因子,还可进一步激活核转录因子κB信号通路,从而导致机体内发生“炎症级联反应”,进一步加重缺血再灌注损伤组织细胞的炎性损伤。白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6是白细胞家族中主要的促炎递质,在缺血再灌注损伤组织细胞中大量产生,加剧炎症反应。
氧化损伤、缺血缺氧等外源性刺激会导致血管内皮细胞中Toll样受体4、核转录因子κB的表达升高,加重血管炎性损伤[10]。皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤后释放的活性氧以及炎性因子等内源性刺激物也会进一步促进Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB信号通路的表达,造成皮瓣组织的进一步损伤,加速皮瓣的坏死。同时,活化的核转录因子κB还可促进细胞间黏附分子1和血管细胞黏附因子1等黏附分子的表达,介导炎性细胞在血管内皮细胞中的黏附,加重血管炎性损伤和血栓的形成。
2.2.2 活性氧的大量产生 在皮瓣移植过程中,血栓形成、中性粒细胞浸润、毛细血管狭窄、内皮功能障碍、细胞因子和促炎物质的释放通过再灌注触发活性氧产生。活性氧主要来源于线粒体,包括氧自由基(如超氧阴离子自由基、羟基自由基)以及非自由基氧化剂(如过氧化氢、一氧化氮、脂质氢过氧化物、过氧基自由基),上述这些自由基与活性氧结合,形成了一大群重要的活性氧化还原剂,在许多细胞内外的生物过程中发挥着关键作用,参与了与细胞损伤相关的多个生命过程。近些年的研究发现,邻近线粒体释放活性氧触发活性氧诱导活性氧释放是一种新的机制[11],这一过程可能导致线粒体功能障碍和细胞死亡的增加;同时,活性氧的产生还涉及黄嘌呤氧化酶和烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶系统,这些系统表现出复杂的串扰机制,一个系统的激活会导致其他系统的激活,导致生物体内活性氧水平的进一步升高。黄嘌呤氧化酶的活性提升伴随着活性氧的产生。在组织灌注不足状态下,黄嘌呤脱氢酶由于较低水平的ATP而转换为黄嘌呤氧化还原酶,组织血流灌注恢复后,黄嘌呤氧化酶与O2反应后,介导细胞内次黄嘌呤转化为黄嘌呤和尿酸[12-13],引起更激烈的氧化应激反应。烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶系统在缺血再灌注损伤中产生大量活性氧。再灌注后,组织释放多种化学递质(如磷脂酶A2、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和血管紧张素Ⅱ)来激活烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶[14],加重缺血再灌注损伤组织细胞的氧化应激。再灌注阶段,活性氧造成灌注不足的组织氧化损伤,导致血管内皮细胞功能障碍、DNA损伤、局部氧化应激和炎症反应。
皮瓣移植后,缺血缺氧会导致线粒体功能障碍并释放出大量的活性氧[15],再灌注同样也会造成大量活性氧的堆积,这会引起皮瓣内活性氧积聚并产生大量的丙二醛等氧化产物,而细胞中的超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽以及血红素加氧酶1等抗氧化物质无法消除如此多的活性氧,进一步破坏组织细胞结构和功能,最终引起皮瓣组织的氧化损伤。
2.2.3 钙超载 皮瓣移植术后,细胞或细胞器内Ca2+超载也是引起缺血再灌注损伤皮瓣坏死的重要原因之一。Ca2+作为一种信号转导分子参与细胞内的能量代谢、蛋白合成等生物过程。生理状态下,细胞内外的Ca2+通过细胞膜与细胞器膜中的Ca2+相关通道、Ca2+-ATP 酶(Ca2+-ATPase)、Na+-Ca2+交换等维持细胞内外Ca2+的稳定。在缺血再灌注损伤出现后,由于缺氧/缺血的组织细胞腺嘌呤核苷三磷酸主要来源于细胞内的无氧酵解并同时伴有大量H+的释放,为维持细胞内环境的稳态,细胞将会进行Na+-H+交换、Na+-Ca2+交换,从而将细胞外Ca2+转移到细胞内;此外,缺血再灌注损伤会造成内质网Ca2+-ATP 酶等功能的下降,抑制内质网对细胞内Ca2+的处理能力,导致细胞内处于高Ca2+状态,引起细胞内Ca2+超载,造成细胞损伤[16]。缺血再灌注损伤组织器官中Ca2+平衡发生紊乱,而细胞内Ca2+超载又通过促进活性氧等有害物质的再次释放,进一步加重组织器官缺血再灌注损伤。
2.2.4 细胞凋亡 细胞凋亡也被称为“程序性细胞死亡”。生理状态下的细胞凋亡有利于维持细胞内环境的稳态,但过度的细胞凋亡会加剧细胞死亡。既往研究发现,细胞凋亡会导致缺血缺氧皮瓣组织血管容量、血流速率以及皮瓣活力下降,从而引起皮瓣坏死[17]。细胞凋亡依赖于Bcl-2家族与Caspase家族等凋亡因子的调控。Bcl-2家族包含Bax、Bak等促凋亡蛋白以及Bcl-2、Bcl-XL等抗凋亡蛋白,Bax等促凋亡蛋白参与线粒体外膜渗透,从而促进凋亡小体的形成,而Bcl-2等抗凋亡蛋白通过同源结构域(BH3)与促凋亡蛋白结合,抑制细胞凋亡。在线粒体外膜渗透发生后,线粒体内的细胞色素C被释放到细胞质中,促进凋亡蛋白酶激活因子1寡聚并募集Pro-Caspase9,形成凋亡小体。当细胞发生损伤时,作为凋亡启动子的Caspase8、Caspase9被激活,并且激活凋亡执行子Caspase3、Caspase7或Caspase9,执行细胞死亡[18]。移植皮瓣发生缺血再灌注损伤并发症后,炎性因子与活性氧的释放、中心粒细胞的聚集、Ca2+超载等致病因素可引起皮瓣血管内皮细胞的凋亡,从而引起皮瓣血管萎缩,导致皮瓣坏死。
2.2.5 血管损伤与微循环障碍 血管损伤是引起皮瓣缺血缺氧的主要原因,而血管重建后的再灌注会引起皮瓣内炎性物质、活性氧等有害物质的进一步释放,加重血管损伤以及血栓的形成,从而导致皮瓣组织微循环障碍,发生血管危象[19]。皮瓣组织的血运主要来源于肌皮动脉、直接皮动脉和中皮动脉在皮下所构成的网状真皮层,拥有可以将血液及其营养物质传输到皮肤的毛细血管网;而回流过程中主要依赖于乳头状真皮中的环状动静脉分流网络[20]。在皮瓣移植过程中,由于破坏了皮瓣组织局部的动静脉循环,因此在局部建立新的动静脉循环是防止坏死的关键。
新生血管的形成机制较为复杂,主要有2个来源:一是从已有的毛细血管中萌发的新生微血管,二是骨髓来源的内皮祖细胞形成的新生血管。对于这一过程研究较深入的是与血管内皮生长因子相关的血管内皮生长因子/Notch/Delta样配体4信号通路以及血管内皮生长因子/AMP依赖的蛋白激酶信号通路。血管内皮生长因子是血管生成的关键因子,同时也是新生血管萌发的“启动子”,通过多个途径参与血管的生成。Notch/Delta样配体4通路是形成功能性血管的基础,在血管生成过程中,血管内皮生长因子表达上调的同时DLL4的表达也将上调,并且激活Notch通路释放Notch胞内结构域,而Notch胞内结构域反馈性下调内皮细胞对血管内皮生长因子反应性,促进具有良好功能的血管网的形成。
血管内血栓的形成也是皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤后的主要病理产物之一。课题组前期研究发现,皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤后并发静脉危象(静脉瘀血)是引起皮瓣坏死的关键因素之一,而静脉危象的主要原因是炎性因子、活性氧等有害物质的损害以及新生血管的损伤[21]。新生血管内血栓的形成对于皮瓣的存活是致命的,活化的核转录因子κB可促进纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1抑制循环系统中纤溶系统的活性,增加血栓形成的风险[22]。缺血再灌注损伤后,白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性因子产生聚集,引起单核巨噬细胞、中心粒细胞等炎性细胞在血管周围聚集,细胞间黏附分子1和血管细胞黏附因子1等黏附分子介导上述炎性细胞在血管内皮细胞中的黏附,加重血管炎性损伤并导致血管腔狭窄,进一步加重血栓的形成[23]。
2.3 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的治疗
2.3.1 间充质干细胞移植 间充质干细胞是一类起源于中胚层的成体干细胞,具有多向分化潜能、复杂分泌活性以及低免疫原性等独特的生物学特性[24],拥有抗氧化、抑制炎症反应、诱导血管新生以及调控细胞增殖、分化、迁移等作用,可以通过抗氧化、抑制炎症反应及诱导血管新生等作用有效减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高移植皮瓣的存活率。
在抗氧化应激方面,间充质干细胞对活性氧水平和抗氧化酶活性具有显著的调节作用。杨志宏等[25]在大鼠皮下移植骨髓间充质干细胞的研究中发现,骨髓间充质干细胞不仅可以增强超氧化物歧化酶活性,还可以降低丙二醛含量和乳酸脱氢酶活性。MOUSAVI等[26]也发现骨髓间充质干细胞可以显著降低皮瓣组织中丙二醛含量并提高超氧化物歧化酶的活性,减少皮瓣坏死面积。以上研究结果表明,间充质干细胞能够通过提高抗氧化酶的活性或(和)清除过多的活性氧来减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高皮瓣的成活率。
在抑制炎症反应方面,NIU等[27]在大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤模型中发现,间充质干细胞来源外泌体降低了丙二醛含量并提高了超氧化物歧化酶活性,显著降低炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的表达水平;并且与对照组相比,静脉注射外泌体的炎症细胞浸润减轻、皮瓣坏死率更低,表明骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过缓解缺血再灌注损伤过程中的氧化应激和炎症反应降低缓解皮瓣坏死率。张赛圣等[28]在皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤模型中发现,注射骨髓间充质干细胞来源miR-126能够通过下调肿瘤坏死因子α、血管细胞黏附分子1及巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α的表达来抑制炎症反应。DENG等[29]在在大鼠皮下移植骨髓间充质干细胞的研究中发现,骨髓间充质干细胞移植降低了白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平,并且减少了氧化应激损伤和细胞凋亡,显著促进了缺血再灌注损伤皮瓣的存活,在体内外都能保护血管内皮细胞免受缺血再灌注损伤。
在诱导血管新生方面,血管新生和血管生成是缺血组织血管修复的主要机制,而皮瓣移植后的存活主要依赖于血管新生。间充质干细胞能够旁分泌各种促血管新生因子促进血管新生,改善微循环。NIU等[30]通过在大鼠尾静脉注射外泌体的研究中发现,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体显著提高了血管内皮生长因子表达水平,促进了缺血再灌注损伤皮瓣中新血管的形成;此外,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体显著增加了人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖和迁移并在体外促进了血管生成,减少了皮瓣的坏死面积。CHEHELCHERAGHI等[31]的研究发现,骨髓间充质干细胞抑制不仅可以显著增加血管内皮生长因子表达,还能增加胶原束的密度。SHI等[32]的研究发现,人牙髓干细胞来源外泌体通过PI3K/AKT信号通路促进静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和小管形成,并且呈剂量依赖性。
2.3.2 富血小板血浆治疗 富血小板血浆是通过全血离心获得的第一代血小板浓缩物,含有大量的血小板,而血小板中含有很多生长因子,包括表皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、胶质细胞生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β以及血管内皮生长因子等,这些细胞因子和生长因子可促进预制皮瓣血管化,减轻缺血再灌注损伤[33],提高皮瓣存活率。既往研究也表明,富血小板血浆在缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤、提高皮瓣存活率方面的作用非常显著[34-35]。刘建疆[36]研究发现,术后注射富血小板血浆可以有效提高缺血皮瓣组织中血管内皮生长因子和转化生长因子β的表达,诱导血管新生,减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。富血小板血浆注射还可以显著提高皮瓣组织中血管内皮生长因子和血管内皮生长因子受体2的表达,增加毛细血管的数量和密度,提高皮瓣存活率[37]。TIAN等[38]的研究发现,富血小板血浆可以显著提高皮瓣组织中血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子AA和血小板衍生生长因子BB的mRNA表达,促进血管新生,提高皮瓣存活率。
富血小板血浆不仅可以促进血管生成,还可以通过抑制氧化应激来减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。王彦进等[39]的研究发现,富血小板血浆可以有效降低皮瓣组织中丙二醛水平、减少氧自由基生成,提高血管内皮生长因子表达,通过促进血管生成和抑制氧化应激反应来减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高移植皮瓣的存活率。为了进一步研究富血小板血浆的治疗效果,ZHANG等[40]通过在术前、术中和术后3个时期分别注射同等剂量的富血小板血浆,结果发现3个时期的富血小板血浆注射均可以通过提高缺血皮瓣组织中血管内皮生长因子和血管内皮生长因子受体2的表达,增加微血管密度,提高皮瓣存活率,并且术中注射效果最好。后来随着富血小板血浆治疗效果的下降以及临床治疗的需要,一些学者尝试用富血小板血浆与其他药物或者疗法联用以期提高富血小板血浆的治疗效果。龙照忠等[41]在富血小板血浆与封闭负压引流设备序贯结合的研究中发现,富血小板血浆与封闭负压引流设备序贯结合可以显著促进创面愈合,提高皮瓣存活率。杨东升等[42]的研究发现,富血小板血浆和前列地尔联用可以显著减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤、降低缺血皮瓣的坏死面积,并且富血小板血浆和前列地尔联用的治疗效果明显优于单独使用。
2.3.3 信号通路调节剂 信号通路是指可以把细胞外的细胞因子、激素、神经递质、生长因子以及小分子化合物等分子信号,通过细胞膜传入细胞内发挥效应的一系列酶促反应通路[43]。
缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路:血管生成受多种分子途径的调控,包括缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子途径。缺氧诱导因子1是调节氧稳态的关键分子,是促进血管生成的重要核转录调节因子。血管内皮生长因子是最关键的促血管生成调节因子之一,它可以促进内皮细胞的表达、分裂和迁移,从而增加血管生成[44]。血管内皮生长因子还可以改善血管的通透性,增加血流量。LIU等[45]的研究发现,利伐西明不仅可以调控缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路,还可以上调缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子和CD34的表达,增加微血管密度,表明利伐他明通过促进远端皮瓣血管生成、增加血液灌注、改善血液循环、缩短建立血液循环所需时间来增加皮瓣远端充血量,提高皮瓣存活率。
干扰素基因刺激因子-干扰素调节因子3信号通路:中性粒细胞的大量聚集是导致并加剧皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的重要原因[46]。缺血时,皮瓣组织缺氧容易导致血管内皮细胞损伤,再灌注后,内皮细胞表面有黏附分子的表达,造成白细胞黏附到血管内皮增加和炎症递质的释放,进一步加剧血管内皮细胞损伤,加重皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。干扰素基因刺激因子蛋白是一种重要的炎症信号分子,棕榈酸可以激活干扰素基因刺激因子,其核周易位并与干扰素调节因子3 结合,导致干扰素调节因子3磷酸化和核易位。LI等[47]的研究发现,干扰素基因刺激因子-干扰素调节因子3可以直接与p-选择素启动子结合并增强p-选择素的表达,从而触发氧化应激诱导的内皮细胞活化。人参皂苷Rb3可以抑制干扰素调节因子3的磷酸化和核易位,进而抑制p-选择素介导的白细胞-内皮细胞的黏附[48],因此,人参皂苷Rb3可通过抑制干扰素基因刺激因子-干扰素调节因子3信号通路、调节黏附分子表达、改善微循环等途径有效缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。
Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB信号通路:Toll样受体4是Toll样受体家族成员,以往的研究表明,Toll样受体4的激活可以释放炎症递质[49],引起炎症反应,导致缺血再灌注损伤,因此在各种缺血再灌注损伤中被广泛研究。核转录因子κB是由Toll样受体4募集的一种转录调节因子,能够在各种细胞病理状况下刺激白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎因子的产生[50],因此通过调节Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB信号通路可以缓解缺血再灌注损伤。王飞等[51]在动物研究中发现,黄芪甲苷可以显著提高皮瓣组织中超氧化物歧化酶活性,降低血清白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平;降低皮瓣组织中核转录因子κB p65 mRNA和Toll样受体4表达水平以及全蛋白MyD88、Toll样受体4和核蛋白核转录因子κB p65表达水平、丙二醛含量,表明黄芪甲苷通过抑制Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB信号通路介导的氧化损伤和炎症反应来减轻大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。陈烨文[52]的研究发现,党参多糖通过显著增加超氧化物歧化酶活性、降低丙二醛含量、降低血清肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β表达水平、降低皮瓣核转录因子κB和Toll样受体4的蛋白表达水平提高皮瓣存活率,表明党参多糖能够调控Toll样受体4信号通路减轻氧化应激和炎症反应,减轻大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高皮瓣存活率。陈浩等[53]在大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的研究中发现,托里消毒散灌胃治疗可降低p-p65和p-IκBα蛋白表达和血清中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、细胞介素6炎性因子水平,提高大鼠皮瓣成活率并减少皮瓣坏死面积,表明托里消毒散通过调控核转录因子κB信号通路抑制炎症反应,进而减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。
2.3.4 体外冲击波治疗 冲击波是由电液压产生的双相高能声波,体外冲击波治疗是一种简单、节省时间和廉价的方法,因在泌尿外科领域的碎石应用而闻名,过去的半个世纪已经在临床医学得到广泛应用,目前的数据支持它在复杂的软组织伤口特别是缺血性组织中的应用。研究表明,各种生长因子在冲击波反应中过度表达,包括促血管生成因子(如血管内皮生长因子和一氧化氮合酶)[54],重要的是创伤早期促炎免疫反应被证明在冲击波治疗中持续被抑制[55]。REICHENBERGER等[56]的研究发现,经体外冲击波治疗后,缺血皮瓣组织促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α显著下调,而促血管生成功能相关的基因血管内皮生长因子a和血管细胞黏附因子1显著上调,表明体外冲击波通过促进血管生成和抑制组织炎症来改善缺血再灌注损伤皮瓣的存活。除单独冲击波治疗外,ZHANG等[57]利用体外冲击波联合内皮祖细胞移植治疗大鼠缺血皮瓣,结果发现冲击波组、内皮祖细胞组以及联合治疗组趋化因子和血管生成因子的表达均提高,缺血大鼠皮瓣存活率也均明显提高,并且联合治疗的存活率最高,表明联合治疗在提高大鼠缺血皮瓣存活率方面优于冲击波和内皮祖细胞单独治疗。
2.3.5 预处理
(1)缺血预处理:是指通过利用短暂反复的缺血而随后再灌注的方法,提前使组织对缺血、缺氧状态进行预适应,用来提高组织对缺血的耐受性,从而在手术期间及手术后减少细胞凋亡和坏死,进而缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高皮瓣移植术后的存活率。
缺血预处理于1986年第一次用于动物研究中,使犬心肌的存活面积增加了75%;在1992年首次用于骨骼肌实验,结果骨骼肌的坏死面积减少了20%。尽管缺血预处理在减轻组织缺血再灌注损伤以及提高皮瓣的存活率方面效果显著,但其具体机制尚未完全阐明,大量研究表明一般与氧化应激、炎症反应以及血管新生等有关。首先,在正常的代谢过程中细胞会产生一定量的内源性抗氧化物,如过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶等,这些抗氧化物能够及时有效地清除体内的过氧化物和自由基,避免组织细胞受到损伤,因此,提高抗氧化物活性可以有效保护组织受免缺血再灌注损伤。TUNCER等[58]的研究报道,缺血预处理能够通过降低黏膜损伤提高超氧化物歧化酶水平,抑制氧化应激反应,进而缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。张延琴[59]总结了20例游离皮瓣移植患者的术后表现,发现缺血预处理能够通过改善微循环来提高抗氧应激能力,降低移植皮瓣的坏死面积。MASA等[60]的研究发现,对照组和缺血治疗组皮瓣存活率大致相等,而缺血预处理组与缺血再灌注损伤组相比新生血管明显增多、组织水肿明显减少,表明缺血预处理促进了血管新生,缓解了皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。PAK等[61]的研究发现,远端缺血预处理可以直接或间接激活血管生成促进因子,从而促进血管生成,缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。DEMIR?Z等[62]在研究中发现,缺血预处理组髓过氧化物酶活性均显著低于缺血再灌注组,急性炎症细胞反应少于缺血再灌注组,说明缺血预处理能够通过抑制炎症反应,缓解皮瓣皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。KRAG等[63]在研究中发现,缺血预处理减弱了缺血再灌注损伤后肌皮瓣中促炎因子白细胞介素6的分泌,有效缓解了皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。
(2)高压氧预处理:大量文献已证明,高压氧对皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤中的中性粒细胞、白细胞、炎症递质、脂质过氧化以及微血管血流等具有显著的调节作用。SONG等[64]的研究证实,高压氧预处理可降低大鼠腹部皮瓣模型缺血再灌注损伤过程中细胞间黏附分子1、血管细胞黏附因子1的表达,进而提高皮瓣存活率,这些表明高压氧预处理的作用机制与炎症反应有关。门泉仓[65]的研究发现,高压氧预处理不仅可以提高皮瓣组织中连接蛋白43的表达,还调节了细胞间黏附分子1和血管细胞黏附因子1、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9和核转录因子κB的表达,还可抑制白细胞趋化,提高皮瓣组织对缺血再灌注损伤的耐受力。朱江英等[66]的研究发现,高压氧预处理可以提高皮瓣组织中血管内皮生长因子和转化生长因子β的表达,诱导血管新生、增加毛细血管数量、改善微循环,进而预防皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高移植皮瓣的存活率。
高压氧预处理作用显著,那高压氧预处理的频次与皮瓣存活率应在必然也存在一定关系。崔佳等[67]在动物实验中发现,高压氧预处理能够降低皮瓣组织中丙二醛水平并提高超氧化物歧化酶的含量,进而通过抑制氧化应激反应来预防皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高移植皮瓣的存活率。后来崔佳等[68]进行了进一步实验,术前予以高压氧0,2,4,6 d 4种不同频次的高压氧预处理,结果发现术前每日1次、连续4 d的高压氧预处理对于减轻皮瓣组织缺血再灌注损伤的效果最好,皮瓣存活率最高。
(3)冲击波预处理:体外冲击波治疗可以有效减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。Keil等[69]的研究发现,术前冲击波治疗7 d后,缺血皮瓣组织中的血管内皮生长因子的表达明显上调,血流和新生血管明显增多,皮瓣存活率显著提高,表明冲击波预处理通过促进血管新生来改善缺血组织微循环,进而减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤。MITTERMAY等[70]的研究也发现,冲击波治疗可以显著提高缺血动物的血管内皮生长因子受体2水平,表明冲击波预处理治疗可通过促进新生血管的形成和血管生成相关生长因子的表达来改善缺血损伤后皮瓣的存活。不仅如此,REICHENBERGER等[71]还进行了术前和术后冲击波治疗对比研究,发现术前和术后联合应用冲击波治疗后血管密度和皮瓣灌注量均明显增加,皮瓣存活率显著提高,并且术后单次应用的方案最有效。
(4)其他预处理:经皮神经电刺激预处理不仅可以将带蒂岛状穿支皮瓣中choke区的扼流吻合转化为真正的吻合,还可以诱导具有抑制炎症反应、抗氧化应激、促进血管新生及抗细胞凋亡等作用的血红素加氧酶1产生,减轻皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤[72]。高浓度氢预处理不仅可以显著下调与细胞坏死性凋亡有关的相关因子受体相互作用蛋白1、受体相互作用蛋白3和线粒体动力相关蛋白的表达,还能抑制皮瓣组织炎性浸润,进而缓解皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤[73]。术前供区拔罐负压吸引可以提高血管内皮生长因子的表达、促进血管新生、增加毛细血管数量,改善局部皮瓣组织微循环,进而提高移植皮瓣的存活率[74]。
抗氧化剂(如臭氧)已被用作一种治疗因素,它的有益作用已在实验和临床水平上用于不同疾病的治疗[75-76]。小剂量的臭氧通过减少自由基及其影响来防止组织损伤;除了作为抗氧化剂外,臭氧还通过其外周血管扩张作用和超氧化物歧化酶的激活来改善缺氧,从而降低氧化应激。医用臭氧预处理具有抗氧化和促血管生成的特性,可提高皮瓣存活率。?KSüZ等[77]术前腹腔给予臭氧1 mg/kg,连续7 d,结果发现臭氧通过抗氧化、促血管生成和血管扩张作用对皮瓣存活有积极作用。


