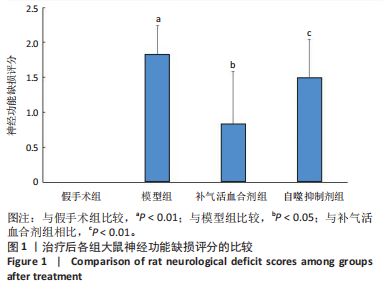
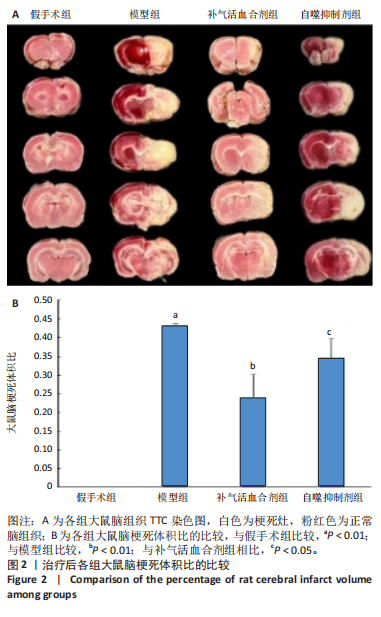
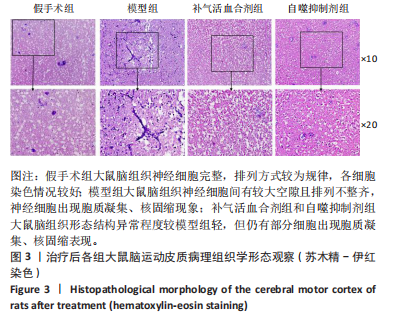
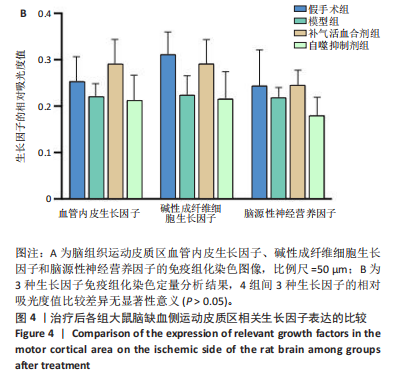
[1] World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2020. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
[2] LAVER KE, LANGE B, GEORGE S, et al. Virtual reality for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;11(11):CD008349.
[3] YANG YR, CHEN YH, CHANG HC, et al. Effects of interactive visual feedback training on post-stroke pusher syndrome: a pilot randomized controlled study. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(10):987-993.
[4] 刘悦,卢阳佳,邝伟川,等.中风复元口服液治疗气虚痰浊内阻型中风60例临床疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2012,14(12):18-20.
[5] 周嘉澄,刘悦,林延.中风复元汤治疗脑梗死恢复期60例总结[J].湖南中医杂志,2009,25(5):14+91.
[6] ZHAO L, DING LD, XIA ZH, et al. A Network-Based Approach to Investigate the Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Huangqi-Chuanxiong and Sanleng-Ezhu Herb Pairs in the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:844186.
[7] DU X, AMIN N, XU L, et al. Pharmacological intervention of curcumin via the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1249644.
[8] LONG J, GU C, ZHANG Q, et al. Extracellular vesicles from medicated plasma of Buyang Huanwu decoction-preconditioned neural stem cells accelerate neurological recovery following ischemic stroke. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1096329.
[9] LONG EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1): 84-91.
[10] 黄柳,贾妍,郭炳彦,等. RhoA激酶信号通路介导的自噬障碍在2型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化中的作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2019,11(12):1446-1450.
[11] SPORNS PB, FULLERTON HJ, LEE S, et al. Current treatment for childhood arterial ischaemic stroke. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021; 5(11):825-836.
[12] AJOOLABADY A, WANG S, KROEMER G, et al. Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;225:107848.
[13] LEES KR, BLUHMKI E, VON KUMMER R, et al. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHET trials. Lancet. 2010; 375(9727):1695-1703.
[14] PEÑA ID, BORLONGAN C, SHEN G, et al. Strategies to Extend Thrombolytic Time Window for Ischemic Stroke Treatment: An Unmet Clinical Need. J Stroke. 2017;19(1):50-60.
[15] NITZSCHE A, POITTEVIN M, BENARAB A, et al. Endothelial S1P1 Signaling Counteracts Infarct Expansion in Ischemic Stroke. Circ Res. 2021;128(3):363-382.
[16] TAO T, LIU M, CHEN M, et al. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Challenges and prospective. Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 216:107695.
[17] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022; 42(1):259-305.
[18] JIANG HJ, HUANG XL, XIAN B, et al. Chinese herbal injection for cardio-cerebrovascular disease: Overview and challenges. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1038906.
[19] DUAN H, ZHANG Q, LIU J, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell, the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;168:105599.
[20] 陈少茹,李智勇.中风复元合剂中芍药苷和橙皮苷的含量测定[J].今日药学,2020,30(1):15-18.
[21] 刘通,廖翔宇,陈玉宁,等.补气活血合剂对脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠血清外泌体及Nestin, GFAP蛋白表达的影响[J].中医康复,2024, 1(2):8-13.
[22] FU C, ZHANG X, LU Y, et al. Geniposide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation via autophagy in BV-2 microglial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106547.
[23] WU C, YANG M, LIU R, et al. Nicotine Reduces Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Response to Escherichia coli K1 Infection by Inhibiting Autophagy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:484.
[24] HOU K, XU D, LI F, et al. The progress of neuronal autophagy in cerebral ischemia stroke: Mechanisms, roles and research methods. J Neurol Sci. 2019;400:72-82.
[25] WU S, YIN Y, DU L. FUS aggregation following ischemic stroke favors brain astrocyte activation through inducing excessive autophagy. Exp Neurol. 2022;355:114144.
[26] LI H, PENG D, ZHANG SJ, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes neurogenesis via sirtuin 1/autophagy pathway in a cerebral ischemia model. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(5):791.
[27] HE Q, LIU Q, CHEN Y, et al. Long-Zhi Decoction Medicated Serum Promotes Angiogenesis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Based on Autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018: 6857398. doi: 10.1155/2018/6857398.
[28] ZHANG W, HAN L, WEN Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2912.
[29] LU WH, SHI YX, MA ZL, et al. Proper autophagy is indispensable for angiogenesis during chick embryo development. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1742-1754.
[30] TUWAR MN, CHEN WH, CHIWAYA AM, et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Translocator Protein (TSPO) as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(13):2298.
[31] MARTINELLI S, ANDERZHANOVA EA, BAJAJ T, et al. Stress-primed secretory autophagy promotes extracellular BDNF maturation by enhancing MMP9 secretion. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4643.
[32] LAN W, LI Z, LI YH, et al. Acupuncture combined with exercise training at different time points on nerve repair of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its effects on the expressions of Nestin, bFGF and EGF. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(1):38-45.
[33] ZHANG R, XIE L, WU F, et al. ALG-bFGF Hydrogel Inhibiting Autophagy Contributes to Protection of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity viaPI3K/Akt/FOXO1/KLF4 Pathway After SCI. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:828896. |