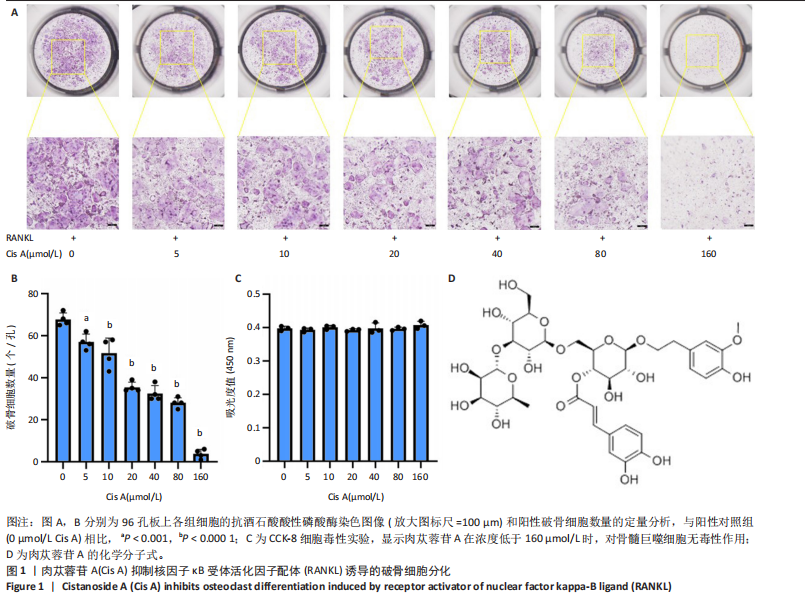
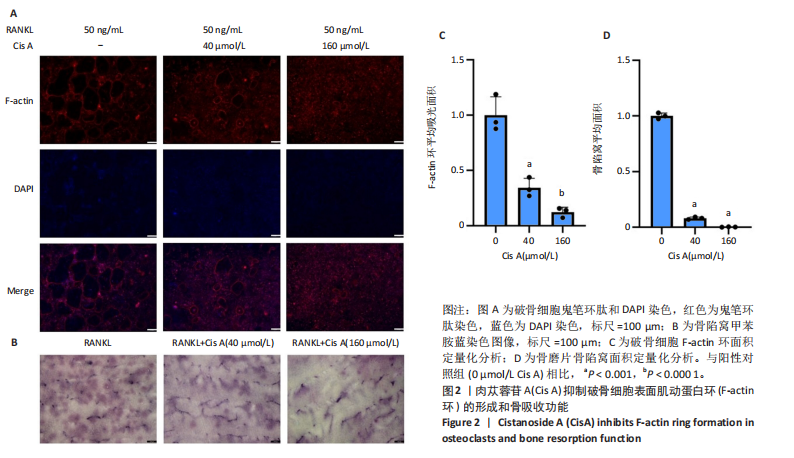
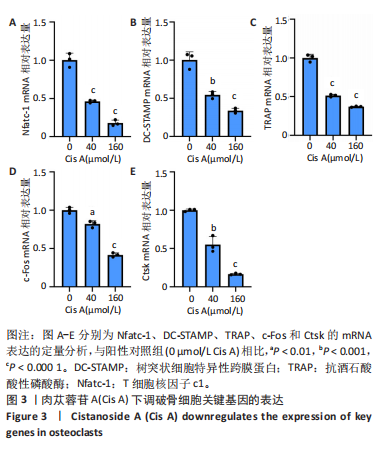
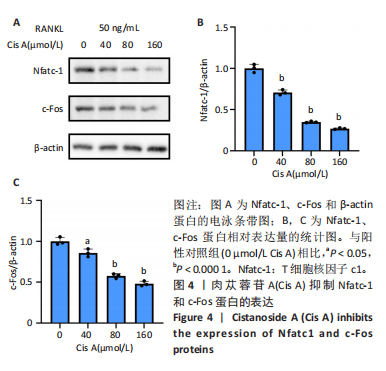
[1] SONG J, ZHAO J, LIU T, et al.Prevalence and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis in a Chinese Population: A Cross-Sectional Study in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e942346.
[2] BARTELT A, BEHLER-JANBECK F, BEIL F, et al.Lrp1 in osteoblasts controls osteoclast activity and protects against osteoporosis by limiting PDGF-RANKL signaling. Bone Res. 2018;26:6:4.
[3] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17(12):1726-1733.
[4] TU KN, LIE JD, WAN CKV, et al. Osteoporosis: A Review of Treatment Options.P T. 2018;43(2):92-104.
[5] ZUR Y, ROSENFELD L, KESHELMAN CA, et al. A dual-specific macrophage colony-stimulating factor antagonist of c-FMS and αvβ3 integrin for osteoporosis therapy. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(8):e2002979.
[6] ARAI F, MIYAMOTO T, OHNEDA O, et al.Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 1999;190(12):1741-1754.
[7] JEEVARATNAM K, SALVAGE SC, LI M, et al.Regulatory actions of 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on osteoclast function: possible roles of Epac-mediated signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1433(1):18-28.
[8] LUO J, YANG Z, MA Y, et al. LGR4 is a receptor for RANKL and negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):539-546.
[9] XIAO L, ZHONG M, HUANG Y, et al.Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21706-21729.
[10] 姚辛敏,周晓洁,周妍妍. 肉苁蓉化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中医药学报,2021,49(2):93-97.
[11] BETH-TASDOGAN NH, MAYER, B, HUSSEIN, H, et al.Interventions for managing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;7(7):CD012432.
[12] NAN ZD, ZENG KW, SHI SP, et al.Phenylethanoid glycosides with anti-inflammatory activities from the stems of Cistanche deserticola cultured in Tarim desert. Fitoterapia. 2013:89:167-174.
[13] XIONG Q, KADOTA S, TANI T, et al.Antioxidative effects of phenylethanoids from Cistanche deserticola. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996; 19(12):1580-1585.
[14] XIONG Q, TEZUKA Y, KANEKO T, et al.Inhibition of nitric oxide by phenylethanoids in activated macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 400(1):137-144.
[15] LUO H, CAO R, WANG L, et al. Protective effect of Cistanchis A on ethanol-induced damage in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016:83:1071-1079.
[16] XU X, ZHANG Z, WANG W, et al.Therapeutic Effect of Cistanoside A on Bone Metabolism of Ovariectomized Mice. Molecules. 2017;22(2):197.
[17] 王代荣. 藁本内酯对RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成和钛颗粒诱导的颅骨骨溶解的作用机制研究[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2019.
[18] 中国老年学和老年医学学会骨质疏松分会中医药专家委员会,葛继荣, 王和鸣, 等. 中医药防治原发性骨质疏松症专家共识(2020)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(12):1717-1725.
[19] WEIVODA MM, BRADLEY EW.Macrophages and Bone Remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(3):359-369.
[20] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL.Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342.
[21] VEIS DJ, O’BRIEN CA.Osteoclasts, Master Sculptors of Bone. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:257-281.
[22] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, GREENBLATT MB, et al.Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. 2020;9(9):2073.
[23] ANASTASILAKIS AD, MAKRAS P, POLYZOS SA, et al.The Five-Year Effect of a Single Zoledronate Infusion on Bone Mineral Density Following Denosumab Discontinuation in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113(4):469-473.
[24] MURDOCH R, MELLAR A, HORNE AM., et al.Effect of a Three-Day Course of Dexamethasone on Acute Phase Response Following Treatment With Zoledronate: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(5):631-638.
[25] MOON JK, PARK J, YOO Y, et al. The efficacy of Denosumab in the treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: a retrospective comparative study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):4140.
[26] EBSTEIN E, BROCARD P, SOUSSI G, et al. Burden of comorbidities: Osteoporotic vertebral fracture during non-small cell lung cancer - the BONE study.Eur J Cancer. 2024:200:113604.
[27] 冯朵,王靖,蒋勇军,等. 肉苁蓉总苷对HepG2肝癌荷瘤小鼠的影响 [J]. 食品科学,2024,45(6):120-129.
[28] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: The Conceptual Framework Unifying the Immune and Skeletal Systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349.
[29] WEI CM, LIU Q, SONG FM, et al. Artesunate inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and prevents LPS-induced bone loss in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):476-485.
[30] SHARMA N, WEIVODA MM, SØE K.Functional Heterogeneity Within Osteoclast Populations-a Critical Review of Four Key Publications that May Change the Paradigm of Osteoclasts. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022;20(5):344-355.
[31] VÄÄNÄNEN HK, ZHAO H, MULARI M; et al.The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci.2000;113(Pt 3):377-381.
[32] SALTEL F, DESTAING O, BARD F, et al. Apatite-mediated actin dynamics in resorbing osteoclasts.Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(12):5231-5241.
[33] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26.
[34] CHANG EJ, HA J, HUANG H, et al.The JNK-dependent CaMK pathway restrains the reversion of committed cells during osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 15):2555-2564.
[35] BARDWELL AJ, ABDOLLAHI M, BARDWELL L. Docking sites on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases, MAPK phosphatases and the Elk-1 transcription factor compete for MAPK binding and are crucial for enzymic activity. Biochem J. 2003;370(Pt 3):1077-1085.
[36] GRIGORIADIS AE, WANG ZQ, CECCHINI MG, et al.c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science. 1994;266(5184):443-448.
[37] TAKAYANAGI H.The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1116:227-237.
[38] 党祎,姚红林,袁能华. NFATc1在骨质疏松症中的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(2):257-262+274.
[39] KIVIRANTA R, MORKO J, ALATALO SL, et al.Impaired bone resorption in cathepsin K-deficient mice is partially compensated for by enhanced osteoclastogenesis and increased expression of other proteases via an increased RANKL/OPG ratio. Bone. 2005;36(1):159-172.
[40] TAKAGI T, INOUE H, TAKAHASHI, N, et al.Sulforaphene attenuates multinucleation of pre-osteoclasts by suppressing expression of cell-cell fusion-associated genes DC-STAMP, OC-STAMP, and Atp6v0d2. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017;81(6):1220-1223.
[41] JIANG T, GU H, WEI J.Echinacoside Inhibits Osteoclast Function by Down-Regulating PI3K/Akt/C-Fos to Alleviate Osteolysis Caused by Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:930053.
|