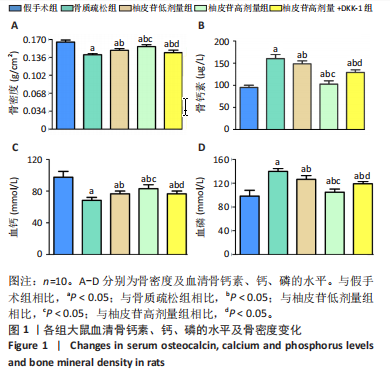
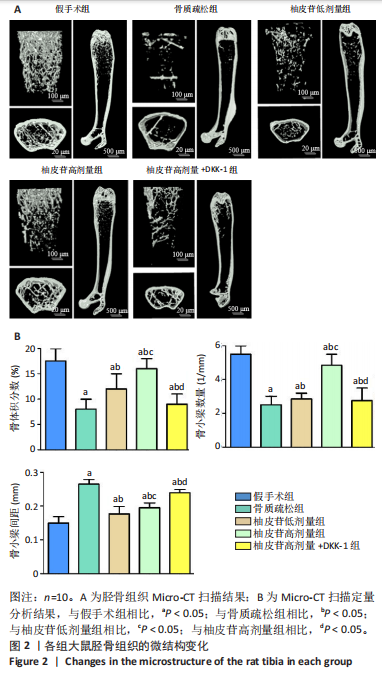
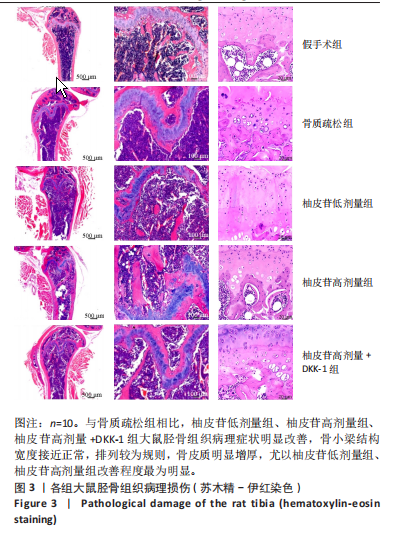
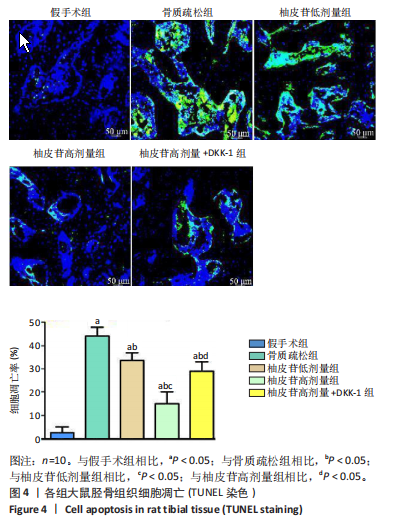
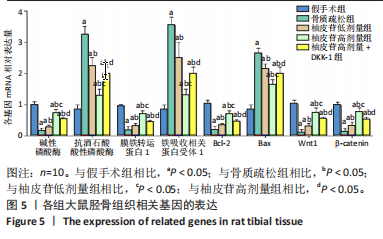
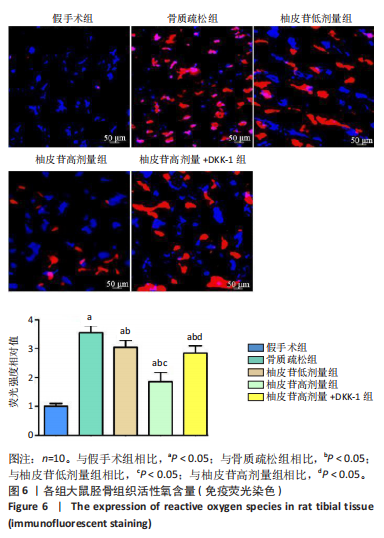
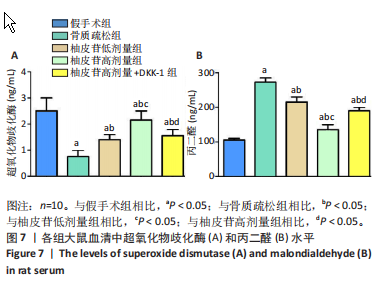
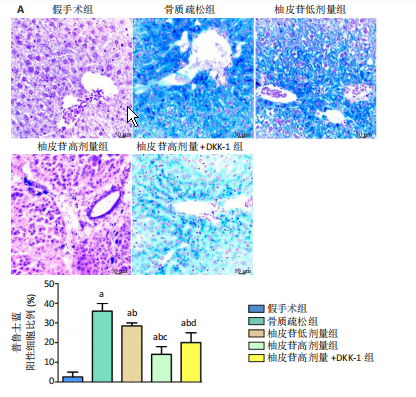
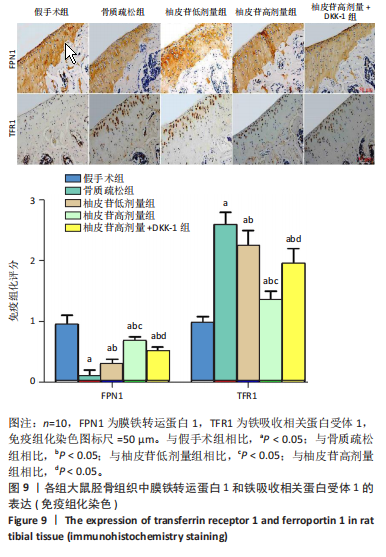
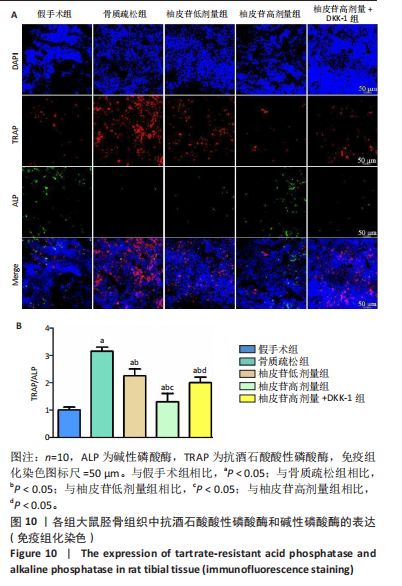
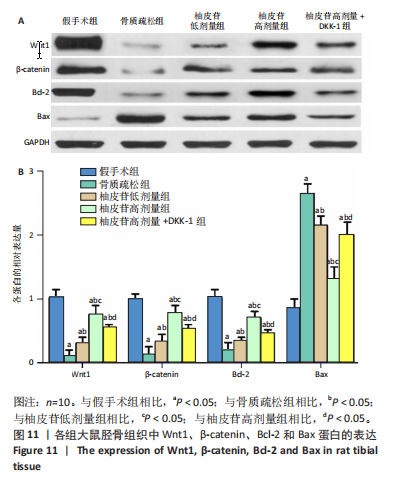
[1] PATEL D, WAIRKAR S. Bone regeneration in osteoporosis: opportunities and challenges. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023;13(2):419-432.
[2] LAIRD C, BENSON H, WILLIAMS KA. Pharmacist interventions in osteoporosis management: a systematic review. Osteoporos Int. 2023; 34(2):239-254.
[3] CHAKRABARTI K, MCCUNE WJ. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in premenopausal women: management for the rheumatologist. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2023;35(3):161-169.
[4] ZHANG G, ZHEN C, YANG J, et al. 1-2 T static magnetic field combined with Ferumoxytol prevent unloading-induced bone loss by regulating iron metabolism in osteoclastogenesis. J Orthop Translat. 2022;38(11):126-140.
[5] VASIKARAN SD, MIURA M, PIKNER R, et al. Practical Considerations for the Clinical Application of Bone Turnover Markers in Osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;112(2):148-157.
[6] LI J, SONG J, MENG D, et al. Electrospun naringin-loaded microsphere/sucrose acetate isobutyrate system promotes macrophage polarization toward M2 and facilitates osteoporotic bone defect repair. Regen Biomater. 2023;2(10):1-16.
[7] HU J, LIN X, GAO P, et al. Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum and pathogenesis of WNT1 variants in a large cohort of patients with OI/osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;3(1):1-11.
[8] MOUSAVI S, VAKILI S, ZAL F, et al. Quercetin potentiates the anti-osteoporotic effects of alendronate through modulation of autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms in ovariectomy-induced bone loss rat model. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(4):3693-3703.
[9] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355(3):184-198.
[10] CHEN M, FU W, XU H, et al. Pathogenic mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;70(4):54-66.
[11] ZHANG K, QIU W, LI H, et al. MACF1 overexpression in BMSCs alleviates senile osteoporosis in mice through TCF4/miR-335-5p signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2023;39(3):177-190.
[12] ZHUANG Q, CHEN S, ZHANG W, et al. Avicularin Alleviates Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Mice by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB Pathway Inhibition. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(1):411-420.
[13] XIE H, CAO L, YE L, et al. microRNA-29b-3p/sirtuin-1/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ suppress osteogenic differentiation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2023;59(2):109-120.
[14] LEE AS, SUNG MJ, SON SJ, et al. Effect of Menaquinone-4 on Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor κB Ligand-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation and Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss. J Med Food. 2023;26(2):128-134.
[15] ZENG C, WANG S, CHEN F, et al. Alpinetin alleviates osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation in BMSCs by triggering autophagy via PKA/mTOR/ULK1 signaling. Phytother Res. 2023;37(1):252-270.
[16] BEEKMAN KM, DUQUE G, CORSI A, et al. Osteoporosis and Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(1):45-55.
[17] QASEEM A, HICKS LA, ETXEANDIA-IKOBALTZETA I, et al. Pharmacologic Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis or Low Bone Mass to Prevent Fractures in Adults: A Living Clinical Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(2):224-238.
[18] GE X, JIANG F, WANG M, et al. Naringin@Metal-Organic Framework as a Multifunctional Bioplatform. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(1):677-683.
[19] CHENG C, PENG X, XI L, et al. Feasibility study of oxidized naringin as a novel crosslinking agent for crosslinking decellularized porcine Achilles tendon and its potential application for anterior cruciate ligament repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(2):170-184.
[20] ZHENG L, SHEN X, XIE Y, et al. Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and prevents hyperglycaemia-induced osteoporosis by suppressing PPARγ expression. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023;55(3):394-403.
[21] WANG M, LI H, TANG J, et al. Effect of simvastatin on osteogenesis of the extremity bones in aging rats. Connect Tissue Res. 2023;64(1):
64-74.
[22] WU H, ZHANG D, XIA H, et al. SDH5 down-regulation mitigates the damage of osteoporosis via inhibiting the MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023;45(3):317-327.
[23] WAWRZYNIAK N, GRAMAZA-MICHALOWSKA A, KURZAWA P, et al.
Calcium carbonate-enriched pumpkin affects calcium status in ovariectomized rats. J Food Sci Technol. 2023;60(4):1402-1413.
[24] 张敏,张晓明,刘童斌.柚皮苷在骨组织再生领域的应用潜力[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(5):787-792.
[25] GAN J, DENG X, LE Y, et al. The Development of Naringin for Use against Bone and Cartilage Disorders. Molecules. 2023;28(9):3716-3736.
[26] LIU Y, ZHU S, LIU J, et al. Vitexin Regulates Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis of Rats via the VDR/PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2023; 71(1):546-556.
[27] SUN H, XU J, WANG Y, et al. Bone microenvironment regulative hydrogels with ROS scavenging and prolonged oxygen-generating for enhancing bone repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;24(1):477-496.
[28] HE Q, YANG J, PAN Z, et al. Biochanin A protects against iron overload associated knee osteoarthritis via regulating iron levels and NRF2/System xc-/GPX4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;157:113915-113930.
[29] FENG M, LIU L, WANG J, et al. The Molecular Mechanisms Study of Engeletin Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Inhibits Ovariectomized Murine Model Bone Loss. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16(5):2255-2270.
[30] NOONAN ML, NI P, SOLIS E, et al. Osteocyte Egln1/Phd2 links oxygen sensing and biomineralization via FGF23. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):7-23.
[31] JIN C, TAN K, YAO Z, et al. A Novel Anti-Osteoporosis Mechanism of VK2: Interfering with Ferroptosis via AMPK/SIRT1 Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(6):2745-2761.
[32] MENG D, SONG J, YI Y, et al. Controlled released naringin-loaded liposome/sucrose acetate isobutyrate hybrid depot for osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;10(1):1097178-1097190.
[33] ZHANG H, WANG A, LI G, et al. Osteoporotic bone loss from excess iron accumulation is driven by NOX4-triggered ferroptosis in osteoblasts. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;198(3):123-136.
[34] BAE S, KIM K, KANG K, et al. RANKL-responsive epigenetic mechanism reprograms macrophages into bone-resorbing osteoclasts. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(1):94-109
[35] CHEN R, WANG M, QI Q, et al. Sequential anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of a dual drug delivery scaffold loaded with parthenolide and naringin in periodontitis. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2023;53(1):20-37.
[36] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, HOU W, et al. Reversing the imbalance in bone homeostasis via sustained release of SIRT-1 agonist to promote bone healing under osteoporotic condition. Bioact Mater. 2022;19(5): 429-443.
[37] AYERS C, KANGSAGARA D, LAZUR B, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments to Prevent Fractures in People With Low Bone Mass or Primary Osteoporosis: A Living Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis for the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(2):182-195.
[38] OH WT, YANG YS, XIE J, et al. WNT-modulating gene silencers as a gene therapy for osteoporosis, bone fracture, and critical-sized bone defects. Mol Ther. 2023; 31(2):435-453.
[39] WANG X, MA Y, CHEN J, et al. A novel decellularized matrix of Wnt signaling-activated osteocytes accelerates the repair of critical-sized parietal bone defects with osteoclastogenesis, angiogenesis, and neurogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022; 21(8):110-128.
[40] FU M, TIAN Y, ZHANG T, et al. Comparative study of DHA-enriched phosphatidylcholine and EPA-enriched phosphatidylcholine on ameliorating high bone turnover via regulation of the osteogenesis-related Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovariectomized mice. Food Funct. 2020;11(11):10094-10104. |