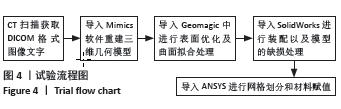
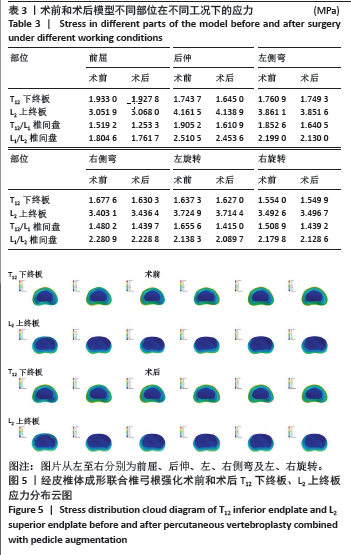
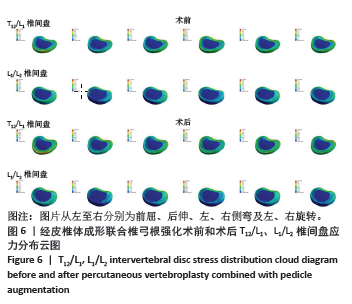
[1] 张坤,王敏,龙海涛,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后再发骨折预防措施研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2023,43(5): 1041-1050.
[2] BEALL DP, PHILLIPS TR. Vertebral augmentation: an overview. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(10):1911-1920.
[3] DENIS F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine. 1983;8(8): 817-831.
[4] LEE HM, PARK SY, LEE SH, et al. Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures(OVCFs):conservative treatment versus balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2012;12(11):998-1005.
[5] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.
[6] GENANT HK, WU CY, VAN KUIJK C, et al. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8(9): 1137-1148.
[7] VAN DER SCHAAF I, FRANSEN H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as treatment for Kummell’s disease. JBR-BTR. 2009;92(2):83-85.
[8] 姚汝斌,王仕永,杨开舜.椎弓根内骨水泥灌注联合椎体后凸成形治疗Kummell病:增强椎体内骨水泥团块稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(28):4435-4440.
[9] 罗培杰,袁凯,李大星,等. 长、短节段椎弓根螺钉并骨水泥强化治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段椎体骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):342-347.
[10] 费琦,李秋军,李东,等.椎体后凸成形术后骨水泥椎间盘渗漏对邻近节段力学影响的有限元分析[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(1): 51-55.
[11] 徐建彪,张伟学,王鸿晨,等.骨水泥注入量对经皮椎体后凸成形术后相邻椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(3): 177-181.
[12] 陈伟健,谢炜星,晋大祥,等.胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折有限元模型的建立[J].山东医药,2018,58(32):55-58.
[13] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. [Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty]. Neurochirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.
[14] LI K, JI C, LUO D, et al. Role of percutaneous vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement in the treatment of severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4602.
[15] DISTEFANO D, SCARONE P, ISALBERTI M, et al. The ‘armed concrete’ approach: stent-screw-assisted internal fixation (SAIF) reconstructs and internally fixates the most severe osteoporotic vertebral fractures. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021;13(1):63-68.
[16] 陈小平,宋宇,全小安,等. 三种防止骨水泥渗漏椎体增强术比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(15):1434-1437.
[17] 张熙辉,李峥嵘,李仕能,等. 胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折术后再骨折风险模型[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2023,40(9):1859-1862.
[18] 王翀妍,单治,陈欢欢,等. 椎基静脉孔与椎体内裂隙相通可能是后凸成形术骨水泥渗漏的危险因素[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,34(4): 373-379.
[19] EYHEREMENDY EP, DE LUCA SE, SANABRIA E. Percutaneous pediculoplasty in osteoporotic compression fractures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;15(8):869-874.
[20] 程明,彭诗语,江娇,等. 不同治疗方法对骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体力学稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(12):1519-1523.
[21] 秦大平,张晓刚,权祯,等. 不同方法治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体力学稳定性变化差异的有限元分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021,36(8):4886-4895.
[22] WICZENBACH T, PACHOCKI L, DASZKIEWICZ K, et al. Development and validation of lumbar spine finite element model. Peer J. 2023;11: e15805.
[23] 王一丹,许阳阳,王海燕,等. 青少年正常腰椎与腰椎间盘突出症关节突关节有限元分析[J]. 解剖学报,2022,53(6):776-784.
[24] GOEL VK, NYMAN E. Computational Modeling and Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 7:S6-S7.
[25] WANG MC, KIAPOUR A, MASSAAD E, et al. A guide to finite element analysis models of the spine for clinicians. J Neurosurg Spine. 2023; 40(1):38-44.
[26] BORENSZTEIN M, CAMINO WILLHUBER GO, POSADAS MARTINEZ ML, et al. Analysis of Risk Factors for New Vertebral Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty. Global Spine J. 2018;8(5):446-452.
[27] 张坤,王敏,龙海涛,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后再发骨折预防措施研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2023,43(5): 1041-1050.
[28] 唐本强,王彦辉,许崧杰,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体强化术后椎体内骨水泥分布类型的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2022,42(5):320-330.
[29] 刘成洲,贾宝欣,任聪慧,等. OVCFs患者经椎体成形术治疗后邻近椎体骨折相关因素分析[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志,2023,27(4): 312-317.
[30] 赵研,宋启春,李东,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折不同骨水泥分布的临床观察及生物力学的有限元分析[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2022, 24(11):818-824,836.
[31] SHI S, KANG XJ, ZHOU Z, et al. Excessive mechanical stress-induced intervertebral disc degeneration is related to Piezo1 overexpression triggering the imbalance of autophagy/apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):119.
[32] HAIBIER A, YUSUFU A, LIN H, et al. Effect of different cement distribution in bilateral and unilateral Percutaneous vertebro plasty on the clinical efficacy of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):908.
[33] 李晖,孟祥翔,张超远. 三种穿刺经皮椎体成形术的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(15):1363-1367. |