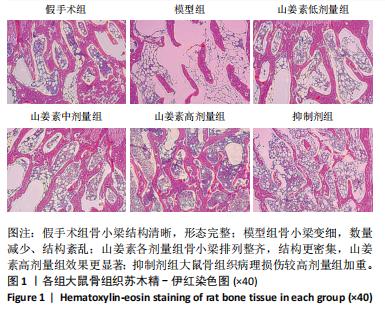
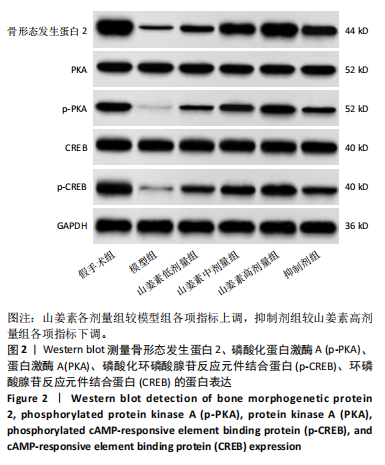
[1] PEREZ MO, PEDRO PPA, LYRIO AM, et al. Osteoporosis and fracture risk assessment: improving outcomes in postmenopausal women. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2023;69(suppl 1):e2023S130.
[2] HE X, WANG Y, LIU Z, et al. Osteoporosis treatment using stem cell-derived exosomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):72.
[3] ZHAO G, TONG Y, LUAN F, et al. Alpinetin: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:814370.
[4] 代万武,黄祖权,张波,等.山姜素对脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞损伤的保护作用研究[J].天津医药,2020,48(12):1137-1141.
[5] ZENG C, WANG S, CHEN F, et al. Alpinetin alleviates osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation in BMSCs by triggering autophagy via PKA/mTOR/ULK1 signaling. Phytother Res. 2023;37(1):252-270.
[6] JIANG X, CHEN W, SHEN F, et al. Pinoresinol promotes MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and differentiation via the cyclic AMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(3):2143-2150.
[7] XIE W, LI F, HAN Y, et al. Neuropeptide Y1 receptor antagonist promotes osteoporosis and microdamage repair and enhances osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells via cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(9):8120-8136.
[8] LV Q, SHI C, QIAO S, et al. Alpinetin exerts anti-colitis efficacy by activating AhR, regulating miR-302/DNMT-1/CREB signals, and therefore promoting Treg differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):890.
[9] 李明哲,罗国厂,张仲博,等.虎杖苷促进大鼠骨质疏松性骨折的作用及对SIRT1/FoxO1信号通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2023,29(8):1154-1159.
[10] 崇显瑾, 杨历新.利拉鲁肽通过cAMP/PKA/CREB通路干预2型糖尿病大鼠骨质疏松的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(11): 1949-1956.
[11] YANG Z, FENG L, WANG M, et al. Sesamin Promotes Osteoporotic Fracture Healing by Activating Chondrogenesis and Angiogenesis Pathways. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):2106-2121.
[12] GORTER EA, REINDERS CR, KRIJNEN P, et al. The effect of osteoporosis and its treatment on fracture healing a systematic review of animal and clinical studies. Bone Rep. 2021;15:101117.
[13] BASTAWY EM, AHMED RR, ABD EL-HAFEEZ AA, et al. Grapefruit juice exerts anti-osteoporotic activities in a prednisolone-induced osteoporosis rat femoral fracture model, possibly via the RANKL/OPG axis. Cytotechnology. 2019;71(4):769-783.
[14] MOUSAVI S, VAKILI S, ZAL F, et al. Quercetin potentiates the anti-osteoporotic effects of alendronate through modulation of autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms in ovariectomy-induced bone loss rat model. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(4):3693-3703.
[15] WEI L, CHEN W, HUANG L, et al. Alpinetin ameliorates bone loss in LPS-induced inflammation osteolysis via ROS mediated P38/PI3K signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2022;184(1):106400-106413.
[16] TANG BM, LI ZW, WANG ZY. PERK activator CCT020312 prevents inflammation-mediated osteoporosis in the ovariectomized rats. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2021;37(4):342-348.
[17] INGWERSEN LC, FRANK M, NAUJOKAT H, et al. BMP-2 Long-Term Stimulation of Human Pre-Osteoblasts Induces Osteogenic Differentiation and Promotes Transdifferentiation and Bone Remodeling Processes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3077-3094.
[18] WANG L, HAN L, XUE P, et al. Dopamine suppresses osteoclast differentiation via cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. Cell Signal. 2021;78(1): 109847-109865.
[19] CHEN T, WANG Y, HAO Z, et al. Parathyroid hormone and its related peptides in bone metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;192:114669.
[20] ZHOU W, YU L, FAN J, et al. Endogenous Parathyroid Hormone Promotes Fracture Healing by Increasing Expression of BMPR2 through cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway in Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):551-563.
[21] CHEN M, CUI Y, LI H, et al. Icariin Promotes the Osteogenic Action of BMP2 by Activating the cAMP Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3875-3890.
[22] MRAK E, CASATI L, PAGANI F, et al. Ghrelin Increases Beta-Catenin Level through Protein Kinase A Activation and Regulates OPG Expression in Rat Primary Osteoblasts. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:547473.
[23] 胡锐,万兰婷,安颖,等.虫草素通过调节COX-2/PGE2信号通路促进骨质疏松大鼠的骨折愈合[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(9): 1340-1345.
[24] CHEN QC, PU YL, BI J, et al. Protective effects of berberine on senile osteoporosis in mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(5):748-756. |