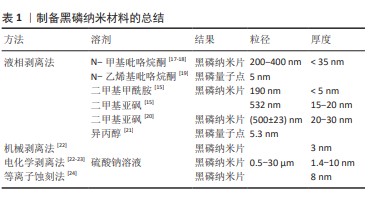
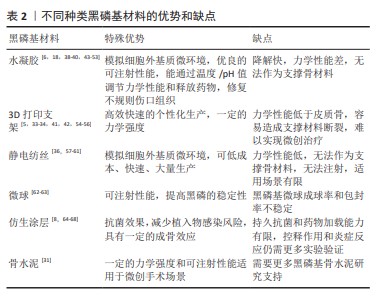
[1] CALVO MS, LAMBERG-ALLARDT CJ. Phosphorus. Adv Nutr. 2015;6(6): 860-862.
[2] SUN Z, XIE H, TANG S, et al. Ultrasmall Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots: Synthesis and Use as Photothermal Agents. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(39):11526-11530.
[3] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY, et al. Black Phosphorus and its Biomedical Applications. Theranostics. 2018;8(4):1005-1026.
[4] WU Y, LIAO Q, WU L, et al. ZnL2-BPs Integrated Bone Scaffold under Sequential Photothermal Mediation: A Win-Win Strategy Delivering Antibacterial Therapy and Fostering Osteogenesis Thereafter. ACS Nano. 2021;15(11):17854-17869.
[5] WANG C, YE X, ZHAO Y, et al. Cryogenic 3D printing of porous scaffolds for in situ delivery of 2D black phosphorus nanosheets, doxorubicin hydrochloride and osteogenic peptide for treating tumor resection-induced bone defects. Biofabrication. 2020;12(3):035004.
[6] PAN W, DAI C, LI Y, et al. PRP-chitosan thermoresponsive hydrogel combined with black phosphorus nanosheets as injectable biomaterial for biotherapy and phototherapy treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. 2020;239:119851.
[7] ZHAO Y, PENG X, XU X, et al. Chitosan based photothermal scaffold fighting against bone tumor-related complications: Recurrence, infection, and defects. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;300:120264.
[8] JEON S, LEE JH, JANG HJ, et al. Spontaneously promoted osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts on ultrathin layers of black phosphorus. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;128:112309.
[9] GUSMÃO R, SOFER Z, PUMERA M. Black Phosphorus Rediscovered: From Bulk Material to Monolayers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017; 56(28):8052-8072.
[10] LIU H, NEAL AT, ZHU Z, et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano. 2014;8(4): 4033-4041.
[11] YASAEI P, KUMAR B, FOROOZAN T, et al. High-quality black phosphorus atomic layers by liquid-phase exfoliation. Adv Mater. 2015;27(11): 1887-1892.
[12] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY, et al. Black Phosphorus and its Biomedical Applications. Theranostics. 2018;8(4):1005-1026.
[13] GUO Z, ZHANG H, LU S, et al. From Black Phosphorus to Phosphorene: Basic Solvent Exfoliation, Evolution of Raman Scattering, and Applications to Ultrafast Photonics. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;25(45): 6996-7002.
[14] GUO Z, CHEN S, WANG Z, et al. Metal-Ion-Modified Black Phosphorus with Enhanced Stability and Transistor Performance. Adv Mater. 2017; 29(42). doi: 10.1002/adma.201703811.
[15] YASAEI P, KUMAR B, FOROOZAN T, et al. High-quality black phosphorus atomic layers by liquid-phase exfoliation. Adv Mater. 2015;27(11): 1887-1892.
[16] ZHANG Y, RUI X, TANG Y, et al. Wet-Chemical Processing of Phosphorus Composite Nanosheets for High-Rate and High-Capacity Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2016;6(10):1502409.
[17] 张一弛,祁成创,黄泳糠,等.钆基水凝胶微球在光热抗肿瘤和骨修复中的应用研究[J].中国稀土学报,2023,41(1):159-167.
[18] LI S, QING Y, LOU Y, et al. Injectable thermosensitive black phosphorus nanosheet- and doxorubicin-loaded hydrogel for synergistic bone tumor photothermal-chemotherapy and osteogenesis enhancement. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;239:124209.
[19] WANG W, NIU X, QIAN H, et al. Surface charge transfer doping of monolayer molybdenum disulfide by black phosphorus quantum dots. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(50):505204.
[20] PASSAGLIA E, CICOGNA F, COSTANTINO F, et al. Polymer-Based Black Phosphorus (bP) Hybrid Materials by in Situ Radical Polymerization: An Effective Tool To Exfoliate bP and Stabilize bP Nanoflakes. Chem Mater. 2018;30(6):2036-2048.
[21] CHEN W, LI K, WANG Y, et al. Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Hole Extraction of Typical Planar Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells. J Phys Chem Lett. 2017;8(3):591-598.
[22] GUAN L, XING B, NIU X, et al. Metal-assisted exfoliation of few-layer black phosphorus with high yield. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018;54(6): 595-598.
[23] ERANDE MB, PAWAR MS, LATE DJ. Humidity Sensing and Photodetection Behavior of Electrochemically Exfoliated Atomically Thin-Layered Black Phosphorus Nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(18):11548-11556.
[24] JIA J, JANG SK, LAI S, et al. Plasma-Treated Thickness-Controlled Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Its Electronic Transport Properties. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):8729-8736.
[25] LI W, WU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Self-healing hydrogels for bone defect repair. RSC Adv. 2023;13(25):16773-16788.
[26] WANG S, ZHAO S, YU J, et al. Advances in Translational 3D Printing for Cartilage, Bone, and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering. Small. 2022;18(36):e2201869.
[27] VERMEULEN S, TAHMASEBI BIRGANI Z, HABIBOVIC P. Biomaterial-induced pathway modulation for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121431.
[28] AMIRYAGHOUBI N, FATHI M, PESYAN NN, et al. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for osteogenic repair and bone regenerative medicine. Med Res Rev. 2020;40(5):1833-1870.
[29] MISHCHENKO O, YANOVSKA A, KOSINOV O, et al. Synthetic Calcium-Phosphate Materials for Bone Grafting. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(18): 3822.
[30] GAHARWAR AK, CROSS LM, PEAK CW, et al. 2D Nanoclay for Biomedical Applications: Regenerative Medicine, Therapeutic Delivery, and Additive Manufacturing. Adv Mater. 2019;31(23):e1900332.
[31] MA S, WEI Y, SUN R, et al. Calcium Phosphate Bone Cements Incorporated with Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Enhanced Osteogenesis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(1):292-302.
[32] PENG G, FADEEL B. Understanding the bidirectional interactions between two-dimensional materials, microorganisms, and the immune system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;188:114422.
[33] WANG X, YU Y, YANG C, et al. Microfluidic 3D Printing Responsive Scaffolds with Biomimetic Enrichment Channels for Bone Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2105190.
[34] LIU X, MILLER AL 2ND, PARK S, et al. Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Synergistically Enhance Cell Proliferation and Osteogenesis on 3D Printed Scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(26):23558-23572.
[35] TONG L, LIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Near-infrared light control of bone regeneration with biodegradable photothermal osteoimplant. Biomaterials. 2019;193:1-11.
[36] LI Z, ZHANG X, OUYANG J, et al. Ca(2+)-supplying black phosphorus-based scaffolds fabricated with microfluidic technology for osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):4053-4064.
[37] QIAN Y, YUAN WE, CHENG Y, et al. Concentrically Integrative Bioassembly of a Three-Dimensional Black Phosphorus Nanoscaffold for Restoring Neurogenesis, Angiogenesis, and Immune Homeostasis. Nano Lett. 2019;19(12):8990-9001.
[38] XU Y, XU C, HE L, et al. Stratified-structural hydrogel incorporated with magnesium-ion-modified black phosphorus nanosheets for promoting neuro-vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:271-284.
[39] JING X, XU C, SU W, et al. Photosensitive and Conductive Hydrogel Induced Innerved Bone Regeneration for Infected Bone Defect Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(3):e2201349.
[40] WU M, LIU H, LI D, et al. Smart-Responsive Multifunctional Therapeutic System for Improved Regenerative Microenvironment and Accelerated Bone Regeneration via Mild Photothermal Therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(2):e2304641.
[41] QIU M, TULUFU N, TANG G, et al. Black Phosphorus Accelerates Bone Regeneration Based on Immunoregulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024; 11(1):e2304824.
[42] LONG J, YAO Z, ZHANG W, et al. Regulation of Osteoimmune Microenvironment and Osteogenesis by 3D-Printed PLAG/black Phosphorus Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(28):e2302539.
[43] QING Y, WANG H, LOU Y. Chemotactic ion-releasing hydrogel for synergistic antibacterial and bone regeneration. Mater Today Chem. 2022;24:24.
[44] WANG Z, ZHAO J, TANG W, et al. Multifunctional Nanoengineered Hydrogels Consisting of Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Upregulate Bone Formation. Small. 2019;15(41):e1901560.
[45] GAIHRE B, LIU X, LU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell spheroids incorporated with collagen and black phosphorus promote osteogenesis of biodegradable hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;121:111812.
[46] LIU X, GEORGE MN, LI L, et al. Injectable Electrical Conductive and Phosphate Releasing Gel with Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Carbon Nanotubes for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(8):4653-4665.
[47] TAN L, HU Y, LI M. Remotely-activatable extracellular matrix-mimetic hydrogel promotes physiological bone mineralization for enhanced cranial defect healing. Chem Eng J. 2022:431P4. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.133382
[48] HUANG K, WU J, GU Z. Black Phosphorus Hydrogel Scaffolds Enhance Bone Regeneration via a Sustained Supply of Calcium-Free Phosphorus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(3):2908-2916.
[49] MIAO Y, SHI X, LI Q, et al. Engineering natural matrices with black phosphorus nanosheets to generate multi-functional therapeutic nanocomposite hydrogels. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10):4046-4059.
[50] XU D, GAN K, WANG Y, et al. A Composite Deferoxamine/Black Phosphorus Nanosheet/Gelatin Hydrogel Scaffold for Ischemic Tibial Bone Repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1015-1030.
[51] XU H, LIU X, GEORGE MN, et al. Black phosphorus incorporation modulates nanocomposite hydrogel properties and subsequent MC3T3 cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(9):1633-1645.
[52] XU H, LIU X, PARK S, et al. Size-dependent osteogenesis of black phosphorus in nanocomposite hydrogel scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(8):1488-1498.
[53] MIAO Y, LIU X, LUO J, et al. Double-Network DNA Macroporous Hydrogel Enables Aptamer-Directed Cell Recruitment to Accelerate Bone Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(1):e2303637.
[54] WANG C, YUE H, LIU J, et al. Advanced Reconfigurable Scaffolds Fabricated by 4D Printing for Treating Critical-size Bone Defects of Irregular Shapes. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045025.
[55] YANG B, YIN J, CHEN Y, et al. 2D-Black-Phosphorus-Reinforced 3D-Printed Scaffolds: A Stepwise Countermeasure for Osteosarcoma. Adv Mater. 2018;30(10). doi: 10.1002/adma.201705611.
[56] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, LUO J, et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets-enabled DNA hydrogel integrating 3D-printed scaffold for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;21:97-109.
[57] LEE YB, SONG SJ, SHIN YC, et al. Ternary nanofiber matrices composed of PCL/black phosphorus/collagen to enhance osteodifferentiation.J Ind Eng Chem. 2019;80:802-810.
[58] WANG J, WANG J, QIU S, et al. Biodegradable L-lysine-modified amino black phosphorus/poly(l-lactide-coε-caprolactone) nanofibers with enhancements in hydrophilicity, shape recovery and osteodifferentiation properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022; 209(Pt 2):112209.
[59] ZHANG X, LI Q, LI L, et al. Bioinspired Mild Photothermal Effect-Reinforced Multifunctional Fiber Scaffolds Promote Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2023;17(7):6466-6479.
[60] SU Y, ZENG L, DENG R, et al. Endogenous Electric Field-Coupled PD@BP Biomimetic Periosteum Promotes Bone Regeneration through Sensory Nerve via Fanconi Anemia Signaling Pathway. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(12):e2203027.
[61] 王文博,徐敬之,吴亮,等.复合纳米纤维骨膜促进血管化和成骨矿化的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4028-4037.
[62] WANG X, SHAO J, ABD EL RAOUF M, et al. Near-infrared light-triggered drug delivery system based on black phosphorus for in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;179:164-174.
[63] XIN S, CHIMENE D, GARZA JE, et al. Clickable PEG hydrogel microspheres as building blocks for 3D bioprinting. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):1179-1187.
[64] LEE JH, BAEK SM, LEE G, et al. Biocompatible Magnesium Implant Double-Coated with Dexamethasone-Loaded Black Phosphorus and Poly(lactide- co -glycolide). ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2020;3(12): 8879-8889.
[65] YUAN B, ZHOU X, LI Y, et al. Black-Phosphorus-Nanosheet-Reinforced Coating of Implants for Sequential Biofilm Ablation and Bone Fracture Healing Acceleration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(41): 47036-47051.
[66] BOSE S, SURENDHIRAN D, CHUN BS, et al. Facile synthesis of black phosphorus-zinc oxide nanohybrids for antibacterial coating of titanium surface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;219:112807.
[67] ZENG J, GU C, GENG X, et al. Combined photothermal and sonodynamic therapy using a 2D black phosphorus nanosheets loaded coating for efficient bacterial inhibition and bone-implant integration. Biomaterials. 2023;297:122122.
[68] MA Y, JIANG L, HU J, et al. Developing a Versatile Multiscale Therapeutic Platform for Osteosarcoma Synergistic Photothermo-Chemotherapy with Effective Osteogenicity and Antibacterial Capability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(39):44065-44083.
[69] WANG Z, WEI H, HUANG Y, et al. Naturally sourced hydrogels: emerging fundamental materials for next-generation healthcare sensing. Chem Soc Rev. 2023;52(9):2992-3034.
[70] ZHOU B, JIANG X, ZHOU X, et al. GelMA-based bioactive hydrogel scaffolds with multiple bone defect repair functions: therapeutic strategies and recent advances. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):86.
[71] LIM DJ. Cross-Linking Agents for Electrospinning-Based Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5444.
[72] WANG Z, WANG Y, YAN J, et al. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;174:504-534.
[73] HU L, ZHANG H, SONG W. An overview of preparation and evaluation sustained-release injectable microspheres. J Microencapsul. 2013; 30(4):369-382.
[74] WONG CY, AL-SALAMI H, DASS CR. Microparticles, microcapsules and microspheres: A review of recent developments and prospects for oral delivery of insulin. Int J Pharm. 2018;537(1-2):223-244.
[75] WANG Y, HU X, ZHANG L, et al. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2829.
[76] ZHANG W, WANG X, LI X, et al. A 3D porous microsphere with multistage structure and component based on bacterial cellulose and collagen for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydrate Polymers: Scientific and Technological Aspects of Industrially Important Polysaccharides. 2020;236:116043.
[77] KRIEGEL C, ATTARWALA H, AMIJI M. Multi-compartmental oral delivery systems for nucleic acid therapy in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(6):891-901.
[78] KOO H, ALLAN RN, HOWLIN RP, et al. Targeting microbial biofilms: current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(12):740-755.
[79] LIU Y, SHI L, SU L, et al. Nanotechnology-based antimicrobials and delivery systems for biofilm-infection control. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(2):428-446.
[80] XIONG Z, ZHANG X, ZHANG S, et al. Bacterial toxicity of exfoliated black phosphorus nanosheets. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;161:507-514.
[81] LI B, LAI C, ZENG G, et al. Black Phosphorus, a Rising Star 2D Nanomaterial in the Post-Graphene Era: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Photocatalysis Applications. Small. 2019;15(8): e1804565.
[82] LYKISSAS MG, GIANNOULIS D. Minimally invasive spine surgery for degenerative spine disease and deformity correction: a literature review. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(6):99.
[83] JAHANGIRI M, HUSSAIN A, AKOWUAH E. Minimally invasive surgical aortic valve replacement. Heart. 2019;105(Suppl 2):s10-s15.
[84] MOUNIKA C, TADGE T, KEERTHANA M, et al. Advancements in poly(methyl Methacrylate) bone cement for enhanced osteoconductivity and mechanical properties in vertebroplasty: A comprehensive review. Med Eng Phys. 2023;120:104049.
[85] GHASEMI F, JAHANI A, MORADI A, et al. Different Modification Methods of Poly Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA) Bone Cement for Orthopedic Surgery Applications. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023;11(8):485-492.
[86] QUAN Q, GONGPING X, RUISI N, et al. New Research Progress of Modified Bone Cement Applied to Vertebroplasty. World Neurosurg. 2023;176:10-18.
[87] 栾伟,陈家瀚,滕勇,等.新型可吸收骨水泥的制备及其应用于小牛椎体标本压缩性骨折椎体成形术的生物力学研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2022,27(10):721-728.
[88] MU X, WANG JY, BAI X, et al. Black Phosphorus Quantum Dot Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity in Living Cells and Mice. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(24):20399-20409.
[89] FADEEL B, GARCIA-BENNETT AE. Better safe than sorry: Understanding the toxicological properties of inorganic nanoparticles manufactured for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(3):362-374.
[90] PARK EJ, PARK K. Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2009; 184(1):18-25.
[91] LIU X, CHEN K, LI X, et al. Electron Matters: Recent Advances in Passivation and Applications of Black Phosphorus. Adv Mater. 2021; 33(50):e2005924.
[92] ESWARAIAH V, ZENG Q, LONG Y, et al. Black Phosphorus Nanosheets: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications. Small. 2016;12(26): 3480-3502.
[93] QIU M, WANG D, LIANG W, et al. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light-controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(3):501-506.
[94] OLEFSKY JM, GLASS CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;72:219-246.
[95] VI L, BAHT GS, WHETSTONE H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1090-1102.
[96] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969.
|