中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 136-146.doi: 10.12307/2024.722
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
哺乳动物多能干细胞:在创建疾病模型、发病机制、药物发现和个性化治疗中的作用
许文强1,2,陈浩林3,颜 昌1,徐 涛1,谢雅彬1,李雪玲2
- 1内蒙古自治区低氧转化医学重点实验室,医学技术与麻醉学院,基础医学与法医学院,包头医学院,内蒙古自治区包头市 014060;2草原家畜生殖调控与繁育国家重点实验室,内蒙古大学,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010010;3大连医科大学附属第一医院,大连医科大学,辽宁省大连市 116000
-
收稿日期:2023-08-22接受日期:2023-10-14出版日期:2025-01-08发布日期:2024-05-18 -
通讯作者:谢雅彬,副教授,硕士生导师,内蒙古自治区低氧转化医学重点实验室,医学技术与麻醉学院,基础医学与法医学院,包头医学院,内蒙古自治区包头市 014060 并列通讯作者:李雪玲,教授,博士生导师,硕士生导师,内蒙古大学生命科学学院,草原家畜生殖调控与繁育国家重点实验室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010010 -
作者简介:许文强,男,1985年生,汉族, 2022年内蒙古大学毕业,动物学博士,讲师,硕士生导师,主要从事动物胚胎干细胞和低氧神经保护研究。 -
基金资助:包头医学院科学研究基金项目(BYJJ-ZRQM 202215),项目负责人:许文强;包头医学院“花蕾计划”项目(HLJH202312),项目指导人:许文强;包头医学院“花蕾计划”项目(HLJH202320),项目指导人:谢雅彬;包头医学院科学研究基金项目(BBJJ201804),项目负责人:谢雅彬;内蒙古自然科学基金项目(2021LHMS08022),项目负责人:谢雅彬;内蒙古自治区高等学校科学研究项目(NJZZ19189),项目负责人:谢雅彬
Mammalian pluripotent stem cells: effects on creating disease models, pathogenesis, drug discovery and personalized treatment
Xu Wenqiang1, 2, Chen Haolin3, Yan Chang1, Xu Tao1, Xie Yabin1, Li Xueling2
- 1Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Hypoxic Translational Medicine, School of Medical Technology and Anesthesia, School of Basic Medicine and Forensic Medicine, Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014060, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Regulation and Breeding of Grassland Livestock, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 3First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-22Accepted:2023-10-14Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-18 -
Contact:Xie Yabin, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Hypoxic Translational Medicine, School of Medical Technology and Anesthesia, School of Basic Medicine and Forensic Medicine, Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014060, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Li Xueling, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Master’s supervisor, State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Regulation and Breeding of Grassland Livestock, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xu Wenqiang, PhD, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Hypoxic Translational Medicine, School of Medical Technology and Anesthesia, School of Basic Medicine and Forensic Medicine, Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014060, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Regulation and Breeding of Grassland Livestock, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Foundation Project of Baotou Medical College, No. BYJJ-ZRQM 202215, (to XWQ); Baotou Medical College “Bud Plan Project”, No. HLJH202312 (to XWQ), HLJH202320 (to XYB); Scientific Research Foundation Project of Baotou Medical College, No. BBJJ201804 (to XYB); Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2021LHMS08022 (to XYB); Inner Mongolia University Scientific Research Project, No. NJZZ19189 (to XYB)
摘要:
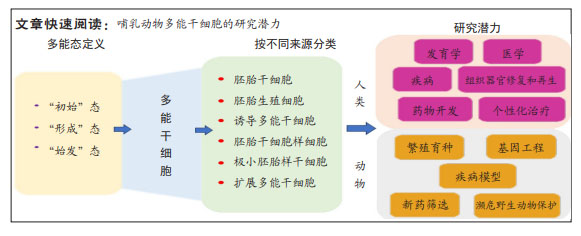
文题释义:
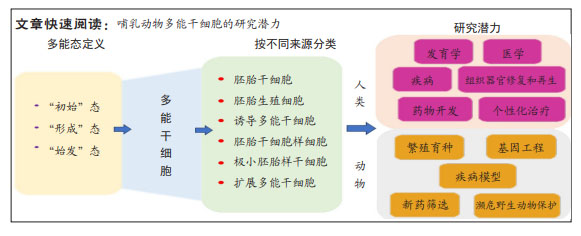
多能干细胞:具有自我复制和多向分化潜能的未分化细胞,其主要特征类似于胚胎早期发育的围着床期,体外培养的多能干细胞可以长期保持自我更新,在特定的信号刺激下分化为具备所有细胞系分化潜能的3个原始胚层。多能干细胞为研究细胞命运转换、阐明发育和分化相关的重要机制,以及探索再生药物提供了宝贵的资源。
胚胎干细胞:一类经典的多能干细胞,来源于胚胎发育早期的囊胚内细胞团,可在体外无限扩增并具有分化为各种体细胞类型的潜能,在发育研究和潜在的医学应用方面具有不可估量的价值。
背景:多能干细胞的自我更新和多向分化的特征有可能彻底改变人们对生物学、医学、发育和疾病的理解。干细胞在胚胎发育的早期发挥着重要作用,研究干细胞可以深入理解生物体发育和组织器官形成的基本原理,探索各种疾病的潜在机制,研究受损组织和器官的修复和再生,以及推动药物发现和个性化治疗。
目的:回顾多能干细胞的研究历程,并对多能干细胞的基本类别进行归纳总结,同时阐述常见哺乳动物中各类多能干细胞的建系情况。
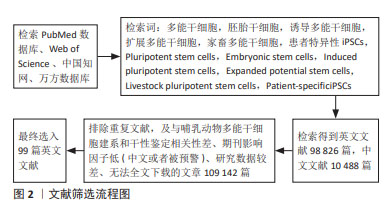
方法:应用计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网和万方数据库,检索词为“多能干细胞,胚胎干细胞,诱导多能干细胞,扩展多能干细胞,家畜多能干细胞,Pluripotent stem cells,Embryonic stem cells,Induced pluripotent stem cells,Expanded potential stem cells,Livestock pluripotent stem cells等”,根据纳入标准和排除标准系统地筛选与哺乳动物多能干细胞相关的文献99篇进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①小鼠胚胎干细胞经典理论认为,干细胞的多能态分为“初始”(naïve)态和“始发”(primed)态两种,naïve态对应于早期胚胎未植入子宫壁前的囊胚内细胞团;primed态对应于植入后的上胚层,二者在表观遗传特征、转录活性、外部信号依赖性和代谢表型等方面存在显著的特征差异;后来研究发现在初始态和始发态之间,还存在一个过渡状态——“形成态”(formative态);事实上,胚胎干细胞的多能性属于连续阶段的发展进程,而不是某种独立的细胞状态。②除了从囊胚内细胞团获得多能干细胞之外,还有多种多能干细胞获得方式和建系方法:如利用来源于小鼠胎儿原始生殖细胞所建立的胚胎生殖干细胞;利用Oct3/4,Sox2,c-Myc和Klf4因子诱导成年小鼠和人的成纤维细胞去分化所建立的诱导多能干细胞;体细胞核移植,孤雌激活,以及从新生或成体睾丸组织或卵巢组织中分离并进行类胚胎干细胞培养所建立的胚胎干细胞样细胞系;来源于多种成体组织的极小胚胎样干细胞和来源于前囊胚期的扩展多能干细胞,这些多能干细胞的共同特征为不断自我更新,表达核心多能因子,并具备原始三胚层分化能力。③目前,多能干细胞正在被用于疾病建模,以便研究不同疾病的机制并开发新的药物。同时,科学家正在尝试用多能干细胞培养各种组织和器官,为再生医学和移植提供新的可能性。然而,多能干细胞的临床应用面临着安全性挑战,包括细胞畸变和免疫排斥问题。不断改进多能干细胞的产生方法,将使其更安全、高效地适用于临床。④借鉴小鼠和人多能干细胞的获得方式和建系方法,研究者们已经在家畜中建立了各类多能干细胞,包括胚胎干细胞、诱导性多能干细胞、生殖细胞谱系的多能干细胞和扩展多能干细胞,这将为动物繁殖育种、基因工程、疾病模型、新药筛选和野生濒危动物保护提供新的途径。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5835-0116 (许文强);https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7489-9002 (谢雅彬); https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7995-0452 (李雪玲)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
许文强, 陈浩林, 颜 昌, 徐 涛, 谢雅彬, 李雪玲. 哺乳动物多能干细胞:在创建疾病模型、发病机制、药物发现和个性化治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(1): 136-146.
Xu Wenqiang, Chen Haolin, Yan Chang, Xu Tao, Xie Yabin, Li Xueling. Mammalian pluripotent stem cells: effects on creating disease models, pathogenesis, drug discovery and personalized treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 136-146.
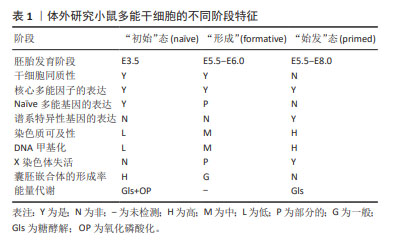
大量的研究证据表明,多能干细胞的多能性不是一种独特的细胞状态,而是连续阶段的发展进程,所有这些细胞都能够进行自我更新和分化,与体内发育的妊娠阶段相对应,且具有不同的代谢、线粒体和表观遗传特征[9-10]。表1总结了体外培养的小鼠多能干细胞不同阶段的特征。
2.2 多能干细胞的研究进展 数十年来,干细胞技术不断推陈出新,为生命科学研究打开了崭新的局面。随着不断扩展和深入研究,多能干细胞分类也在发生变化。到目前为止,在文章对干细胞研究进行系统回顾后,总结出了6种基本的多能干细胞。
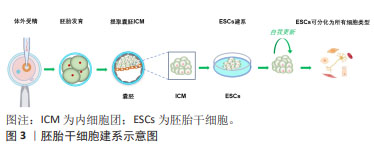
2.2.1 胚胎干细胞 胚胎干细胞来源于胚胎着床前胚泡期(囊胚)的内细胞团,它们具有分化成身体所有细胞类型的能力,见图3。1981年,胚胎干细胞第一次成功地从小鼠囊胚的内细胞团获得,并可在体外培养并长期保持多能性[2-3]。小鼠胚胎干细胞被定义为“na?ve”多能性,具有无偏分化和嵌合体贡献潜力[5]。体外培养所需的特定条件,如饲养层的共培养以及后来的化学成分确定的无饲养层培养体系,使胚胎干细胞表现出无限的增殖能力和未分化的潜能状态。
1998年是生命科学研究历史上具有划时代意义的一年,THOMSON等[1]从人类囊胚的内细胞团获得并建立人胚胎干细胞系,这些人胚胎干细胞具备正常核型,并表达高水平端粒酶活性,和灵长类胚胎干细胞特征的细胞表面标记物,但不表征早期谱系分化标记物,长期体外培养的人胚胎干细胞仍具备形成滋养层和三胚层衍生物的潜能[5]。然而,与小鼠内细胞团来源的胚胎干细胞不同的是,人类或灵长类动物胚胎干细胞特征相当于小鼠上胚层干细胞,属于“primed”多能态,具有偏分化能力和有限的嵌合体贡献潜力[5]。人胚胎干细胞的应用价值在于为基础研究和再生医学领域提供重要的细胞工具,具体包括:用于探究胚胎正常的发育机制,并揭示出生缺陷和疾病的原因;研究胚胎发育早期细胞凋亡、分化、诱变、免疫排斥和细胞衰老的理想模型材料;用于治疗药物的疗效和毒性检测;诱导形成人类脏器、软骨组织、神经元和血管等组织;定向分化为特定细胞类型,为疾病和残疾的治疗提供可再生的替代细胞和组织。但同时,人胚胎干细胞细胞也有诱发畸胎瘤和免疫排斥的风险,这是必须面对和解决的问题。
2.2.2 胚胎生殖细胞 除囊胚内细胞团之外,胚胎的原始生殖细胞(primordial germ cells,PGCs)同样可以用于多能干细胞的建立[11-12],见图4。早在1992年,MATSUI等[11]从E10.5-E12.5的小鼠胚胎中分离原始生殖细胞,在添加了膜相关铁因子(steel factor,SF)、白血病抑制因子(leukemia inhibitory factor,LIF)和碱性成纤维生长因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF)的培养体系中,实现了原始生殖细胞在体外的连续增殖;胚胎干细胞的各项检测标准表明原始生殖细胞符合胚胎干细胞的基本特征。原始生殖细胞的长期培养及其重编程为多能的胚胎干细胞对生殖细胞生物学和畸胎瘤的诱导具有重要意义。
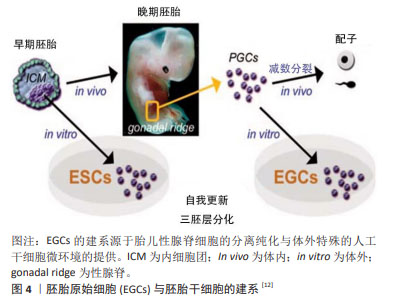
来源于原始生殖细胞的人胚胎干细胞被称为人胚胎生殖细胞(human embryonic germ cells,hEGCs)。SHAMBLOTT等[13]于1998年首次建立了人胚胎生殖细胞细胞系,即从受精后5-9周的人胎儿分离得到含有原始生殖细胞的性腺脊和肠系膜,利用添加了重组的人碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor,rhbFGF)、重组人白血病抑制因子(recombinant human
leukemia inhibitory factor,rhLIF)及毛喉素的培养基,在小鼠STO成纤维细胞饲养层上进行培养,从而建立了最早的人胚胎生殖干细胞系。随后,有3个科研团队相继报道获得可以在体外自我更新、保持未分化状态,并可分化为三胚层衍生物的人胚胎生殖细胞[14-16]。这些人类原始生殖细胞来源的培养物符合多潜能干细胞的标准,与胚胎生殖细胞非常相似,它们与人胚胎干细胞细胞一起丰富了人类多能干细胞的定义。人胚胎生殖细胞在细胞分化和细胞移植研究中具有潜在的应用前景,已成为生命科学和医学研究的前沿热点[13,17]。
2.2.3 诱导多能干细胞(induced pluripotent stem cells,iPSCs) 来源于哺乳动物囊胚内细胞团或胚胎原始生殖细胞的胚胎干细胞,在保持多能性的同时具有无限生长的能力[2-3,13]。人胚胎干细胞的这些特性给疾病机制的研究、有效且安全药物的筛选以及各种疾病和损伤患者的治疗带来了希望。然而,人类胚胎的使用却面临着阻碍人胚胎干细胞应用的伦理争议,而且,可有效应用的患者或疾病特异性的胚胎干细胞的获得难度极大。因此,规避这些问题的一种方法是通过重编程诱导体细胞发生去分化,从而产生干细胞多能性。在2012年,诺贝尔生理学或医学奖授予TAKAHASHI的诱导性多能干细胞,其团队建立了在Oct3/4,Sox2,Klf4和c-Myc四因子作用下将成年小鼠和人的成纤维细胞重新编程为类胚胎干细胞的方案[4],机制如图5所示[18]。他们最初利用反转录病毒转导技术将24个候选基因用于重新编程小鼠成纤维细胞,随后这些候选基因逐渐被精确到Oct4,Sox2,c-Myc和Klf4等4个转录因子[4]。紧接着,这项技术被成功地应用于人成纤维细胞诱导产生诱导性多能干细胞[19]。与此同时,YU等[20]研究发现Oct4,Sox2,Nanog和Lin28足以重新编程人类细胞,其中Oct4和Sox2似乎是必不可少的,另外两个基因强烈(Nanog)或适度(Lin28)的影响重新编程的效率。
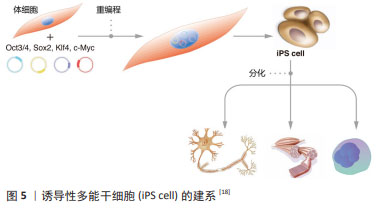
由于可以从患者自身采集体细胞,所以诱导性多能干细胞克服了胚胎干细胞的免疫排斥和伦理限制的缺点。更重要的是,诱导性多能干细胞表现出许多胚胎干细胞类似的特征,包括细胞表型、多能marker表达、染色体端粒特征以及形成拟胚体、嵌合体或畸胎瘤等能力[21]。然而,诱导性多能干细胞的缺点也逐渐引起了人们的担忧,这在一定程度上限制了诱导性多能干细胞的应用开发。首先,基因传递所用到的病毒载体可能导致多种病毒整合到受体细胞的基因组中,引起细胞的遗传异常乃至肿瘤发生;其次,由人成纤维细胞重编程为诱导性多能干细胞的效率极低( < 0.02%);再次,癌基因Myc作为重编程因子,激活沉默的Myc基因容易诱导诱导性多能干细胞成为癌细胞[22];最后,诱导性多能干细胞的重编程过程和随后的长期体外培养容易导致这些细胞的遗传不稳定和表观遗传异常。这些弊端引起了人们对诱导性多能干细胞未来应用的担忧,因此有必要进行更深入的研究,以了解重新编程过程,并需要深入研究这些基因组和表观基因组变化的生物学结构。
2.2.4 胚胎干细胞样细胞 胚胎干细胞样细胞是指能够表现出与胚胎干细胞相似的特性,但不是来自胚胎的细胞,胚胎干细胞样细胞制备方法主要包括体细胞核移植(somatic cell nuclear transfer,SCNT),孤雌生殖,以及新生或成体生殖细胞来源的干细胞系,见图6。它们通常与胚胎干细胞具有相同的关键特征,如自我更新和分化成多种细胞类型的能力。
SCNT是指将体细胞的细胞核移植到去核的卵母细胞中形成重构的受精卵,后者被激活并培养至囊胚期可用于干细胞建系,或者通过胚胎移植技术移植到母体子宫进行动物克隆。除受精之外,SCNT或称为克隆技术,也可以赋予体细胞全能性。GURDON博士[23]最早于1962年首次证明可以通过SCNT从分化的青蛙体细胞中克隆动物。30多年后,第一只克隆哺乳动物多利羊诞生了[24]。在SCNT过程中,受体卵母细胞的胞质中遗留的因子可对供体细胞核进行重编程,从而使其重新获得多能性和多向分化潜能。此外,基因编辑技术也被运用与SCNT-胚胎干细胞建系,LEE等[25]使用CRISPR/cas9介导的基因靶向产生了B2M纯合子敲除体细胞核移植诱导胚胎干细胞(SCNT-ESC)系。B2MKO细胞株在细胞表面不表达hla-1分子,而具有多能性和向三胚层分化的能力。
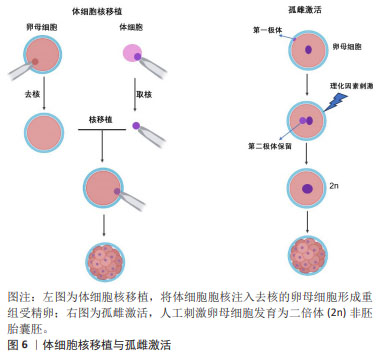
孤雌生殖是指在没有受精的情况下激活卵子的胚胎发育。哺乳动物卵母细胞可通过人工刺激发育为二倍体非胚胎囊胚,并可从囊胚内细胞团中获得孤雌生殖干细胞。JU等[26]利用从同一小鼠卵母细胞供体分离的体细胞核进行核移植和孤雌激活,建立了符合胚胎干细胞标准的多能干细胞系。在灵长类动物中,由于遗传缺陷影响了正常的胎盘形成,孤雌生殖无法长成可存活的胎儿[27]。然而,孤雌生殖干细胞仍具备一定的多能性,可发育为视网膜色素上皮样细胞、肌样和骨样细胞、神经元细胞和肝细胞。
从新生或成体睾丸组织或卵巢组织中分离并进行类胚胎干细胞的培养,可建立符合干细胞标准的胚胎干细胞样细胞系。研究发现新生和成年小鼠睾丸中的精原干细胞或雄性生殖系干细胞表型上与胚胎干细胞相似,同时具备体外三胚层分化和畸胎瘤形成能力,并且显示出生殖系贡献与传递[28]。GUAN等[28]从成年小鼠睾丸中分离精原干细胞,在体外的特殊培养条件下获得胚胎干细胞的特性。这些细胞能够在体外自发分化为三胚层的衍生物,并在免疫缺陷小鼠中产生畸胎瘤。当注入早期囊胚时,精原干细胞有助于各种器官的发育,并表现出种系传播[29]。
存在于卵巢中的雌性生殖系干细胞,早先被认为可能保留了产生多能干细胞的能力,如WANG等[30]从卵巢中提取的雌性生殖干细胞(female germline stem cells,FGSCs)在干细胞多能基因表达和分化潜力方面表现出胚胎干细胞类似的特性。GONG等[31]通过培养10周龄B6D2F1 (C57BL/6×DBA2)雌性小鼠卵巢细胞,建立了符合干细胞标准的胚胎干细胞样细胞细胞系。然而,近年来关于卵巢干细胞的多能特性出现了很大争议,甚至有新的证据表明FGSCs并不存在。尽管如此,这些新技术为研究生殖细胞生物学提供了可能性,并为个性化的再生应用夯实了基础。最近,利用非生殖系干细胞生产人工生殖细胞的研究为不孕不育症的治疗开辟了新的途径。
GOLESTANEH等[32]首次报道了通过成人睾丸细胞建立的人胚胎干细胞样细胞,他们从人类器官供体获得睾丸组织,并将其从干细胞龛中移至添加有适当的生长因子和试剂的胚胎干细胞培养基,发现持续的培养可使睾丸生殖细胞重编程为多能干细胞。人胚胎干细胞样细胞的建立为成人自体干细胞治愈疾病和干细胞生物技术与医学的应用提供了可能性。
此外,从成年生物体的骨髓中分离出的间充质干细胞或多能基质细胞是人体内分布最广泛的细胞之一[33],由于具备骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞和其他细胞系的分化潜能,被认为具有多能干细胞特征[34]。间充质干细胞不仅具有产生异位骨组织的能力,而且可以转分化为上皮细胞和神经外胚层的谱系,更重要的是,间充质干细胞具备通过分泌可溶性因子改变组织微环境的能力,为间充质干细胞的广泛治疗功效提供了基础。
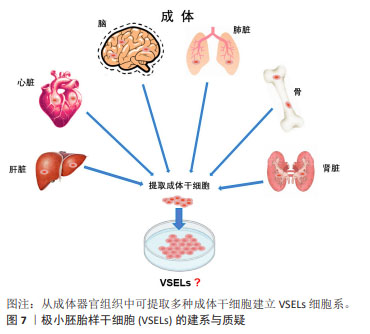
2.2.5 极小胚胎样干细胞 在再生医学领域,成体干细胞尽管克服了胚胎干细胞的伦理问题和其他技术问题,在某些方面可能成为胚胎干细胞的潜在替代者,然而有研究表明,成体干细胞具有多能干细胞部分属性,可能的机制包括干细胞的转分化或去分化,或者干细胞与不同谱系细胞的融合[35]。大量研究表明,在成人组织中存在多潜能干细胞,包括极小胚胎样干细胞、多能成体干细胞、间充质干细胞和骨髓分离的成人多系诱导细胞等[36-37]。
在这些细胞中,最具特征的是在成体器官,如成人性腺、脐带血/组织和骨髓中被分离和鉴定的极小胚胎样干细胞[38]。极小胚胎样干细胞为成体器官组织来源的干细胞,在器官发生的早期沉积,并可作为组织定向干细胞的来源,见图7。尽管目前没有被广泛接受,甚至后来有人对极小胚胎样干细胞的客观存在及其多能性提出质疑,但是已有研究揭示了极小胚胎样干细胞在再生医学和细胞治疗中的巨大潜力:极小胚胎样干细胞与胚胎干细胞相同的多能性特征,包括Oct4和Nanog启动子区域开放的染色质结构和体外的三胚层分化能力[39]。不同的是,极小胚胎样干细胞的嵌合体和畸胎瘤形成能力不足,致瘤风险较低,而且一般情况下极小胚胎样干细胞处于静息状态,代谢活性较低,可作为组织定向干细胞的备份,在受伤发生时进入细胞周期,为组织再生和动态平衡做出贡献[40]。极小胚胎样干细胞的缺点是体外培养不像胚胎干细胞那样容易,这可能与一些发育关键基因的甲基化修饰有关。
值得注意的是,关于极小胚胎样干细胞的真实性和分化能力曾遭受怀疑。有研究报道称在小鼠骨髓中并不能找到任何已经报道的具备干细胞潜能,特别是造血潜能的极小胚胎样干细胞,他们发现“极小胚胎样干细胞”并不表达Oct4,而且不能分化为血细胞[41]。然而,面对质疑,KUCIA等[37]指出该研究团队没有遵循先前发表在Current Cytometry Protocols上的极小胚胎样干细胞分离详细方案,从而导致极小胚胎样干细胞没有得到充分的分离和纯化。
2.2.6 扩展多能干细胞 胚胎干细胞和诱导性多能干细胞由于具备分化为机体所有类型细胞的潜能被认为具有多能性,而且在过去的数十年,它们在胚胎早期发育机制的研究和干细胞治疗的探索与应用方面发挥着积极的作用。然而,胚胎干细胞和诱导性多能干细胞并不具备原始受精卵的“全能性”特征,即同时形成胚胎组织和胚外组织[42]。人胚胎干细胞的研究一直致力于模拟体内胚胎的发生过程,然而,之前所用primed态人胚胎干细胞相当于小鼠早期植入后的上胚层干细胞[43],并且缺乏类似滋养外胚(trophectoderm,TE)和原始内胚层(primitive endoderm,PE)的细胞。因此,他们不能完全概括人类早期胚胎发育的谱系相互作用。
从早期植入前胚胎(4细胞-8细胞)提取干细胞,通过抑制植入前胚胎中运行的谱系分化相关途径,可建立扩展多能干细胞系,见图8。扩展多能干细胞具有强大的自我更新能力,并在体外培养或嵌合体实验中产生胚胎和胚胎外细胞系[44-45]。扩展多能干细胞由于具备全能多能性,又被称为全能干细胞。小鼠来源的扩展多能干细胞的建立是从早期植入前胚胎提取干细胞,通过抑制在植入前囊胚胚胎中运行的分子信号途径,如促进卵裂球分化的关键分子通路而建立的[46]。

值得注意的是,一些重要的化学小分子也被用于扩展多能干细胞的体外制备。SHEN等[47]利用剪接体抑制剂Pladienolide B成功驱动体外培养的小鼠胚胎干细胞从多能态向全能态的转变,并实现了全能干细胞产生胚胎和胚外细胞系的双向发育潜力的长期保持。HU等[48]利用维甲酸类似物TTNPB、1-氮杂苯丙酮和激酶阻滞剂WS6共3个小分子的组合成功实现了体外培养的小鼠全能干细胞的化学诱导和长期维持。XU等[49]发现一种化学“鸡尾酒”能够从小鼠2-细胞胚胎和扩展多能干细胞中衍生出全能样干细胞,这些细胞表现出与2-细胞小鼠胚胎相同的特征,并在单细胞水平上具备胚胎和胚胎外发育潜力。YANG等[50]则通过化学诱导着丝粒周围异染色质的重塑以及全能特异性的宽H3K4me3结构域的重建,从表观遗传角度促进了小鼠胚胎干细胞从多能到全能的转变。
扩展多能干细胞的建系方法相对降低了从囊胚期胚胎中建立干细胞的异质性。更重要的是,扩展多能干细胞允许高效的基因组编辑,这使其具备很好的发展潜力,为其在广泛的生物技术应用和农业研究领域提供了重要基础。
2.3 家畜多能干细胞的研究进展与应用 回顾多能干细胞的研究史和发展过程,容易发现各种类型多能干细胞的建立基本上都会经历从小鼠或大鼠等模型动物开始,继而推广到人和其他哺乳动物。从家畜中已获得的多能干细胞,包括胚胎干细胞、诱导性多能干细胞、生殖细胞谱系的多能干细胞和扩展多能干细胞,为动物繁殖育种、基因工程、疾病模型、新药筛选和野生濒危动物保护开辟了新的途径,具有发展畜牧业和创造人类福利的巨大潜力。
2.3.1 胚胎干细胞 小鼠胚胎干细胞成功获得之后,研究者尝试在猪、牛、羊、兔子等家畜动物中建立囊胚内细胞团来源的干细胞系[51-53]。然而,在家畜物种建立胚胎干细胞的进程是极其缓慢的。从20世纪80年代开始,经过数十年的努力,绵羊、猪和牛等家畜物种来源的早期胚胎类胚胎干细胞才被陆续报道;然而,具体的多能干细胞多能特征表明,这些细胞多数处于primed状态,且在体外只能维持数十代,猪、牛、绵羊、水牛的类胚胎干细胞[54-55],不能保持强大的自我更新能力,而且通常在畸胎瘤和嵌合体试验中无法完成3个胚层的分化。这可能源于家畜物种和啮齿类在细胞谱系形成的个体发育方面的差异,以及控制多能性的分子途径的差异。直到2008年,3i方法首次被成功用于大鼠真正胚胎干细胞的分离和培养,从而为家畜多能干细胞的建立提供了有价值的参考[56]。3i法是一种添加与胚胎干细胞诱导分化信号通路相关的3种抑制剂的培养方案,即通过在培养基微环境中添加CHIR99021(GSK3激酶抑制剂)、PD184352(ERK1/2激酶抑制剂)和SU5402(成纤维细胞生长因子酪氨酸激酶受体抑制剂)3种小分子,促进符合干细胞特征的家畜多能干细胞的成功建系[57]。
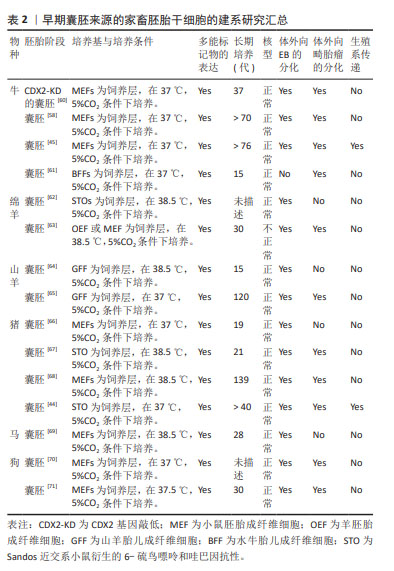
牛胚胎干细胞的研究始于1996年,为了获得牛胚胎干细胞,已经进行了大量的研究。然而,所获得的这些干细胞难以满足多能干细胞的全部标准,体外长期培养中多能性难以保持;三胚层衍生效率低下;体外和体内实验中发育潜力有限。直到2018年,BOGLIOTTI等[58]首次报道了基本符合干细胞标准的牛胚胎干细胞的成功建立。他们在MEF饲养层上,利用特定的mTeSR1基础培养基(不含生长因子)、经典的WNT信号通路抑制剂IWR1和bFGF组成的CTFR培养体系,在体外成功地实现了符合干细胞特征的牛胚胎干细胞长期培养;而且这些干细胞可作为核移植供体产生正常的囊胚,为基因组选择和基因组编辑提供了可能性。HAN等[59]研究发现组蛋白甲基化修饰酶抑制剂MLL1与PD0325901和CHIR99021(2i)相结合,可促进IVF来源的牛囊胚的发育。文章总结了早期囊胚来源的家畜胚胎干细胞最新研究成果[44-45,58,60-71],并展示在表2中。
2.3.2 胚胎干细胞样细胞 从核移植(nuclear transfer,NT)来源的囊胚中获得内细胞团用于NT-胚胎干细胞样细胞的建立,已经在牛和水牛中实现[72-73]。WANG等[72]报告了来自核移植胚胎的牛胚胎干细胞系,这些细胞表现出与之前的牛胚胎干细胞不同的特征,其染色模式与牛囊胚相似,克隆表型与小鼠胚胎干细胞和胚胎生殖细胞相同,并呈现碱性磷酸酶阳性和SSEA4、OCT4阳性,长期培养之后仍保持胚状体和3个胚胎生殖层的分化能力。GEORGE等[73]利用水牛成纤维细胞建立了NT-胚胎干细胞样细胞,这些细胞的克隆呈经典的圆顶状,多能性标记基因与体外受精的胚胎干细胞样细胞中表达模式相似。家畜的NT-胚胎干细胞样细胞可以从基因选择的高价值动物中获得,这些动物可能用于克隆。
从小鼠建立了第一个孤雌生殖胚胎来源的胚胎干细胞系之后,已在猪、马、羊、牛和水牛中建立了该干细胞系[74-75]。MUZAFFAR等[74]成功从体外受精、孤雌生殖和NT获得的囊胚建立水牛胚胎干细胞样细胞系。孤雌生殖胚胎产生的细胞系保持了胚胎干细胞的特性,然而,衍生株显示出多能性标记的差异性表达模式,并且可能发生自发分化,在嵌合体试验中贡献有限或失败,这是其细胞潜力的局限性[76]。
2.3.3 诱导性多能干细胞 体细胞重编程技术已经被迅速且广泛地应用到家畜物种,如猪、绵羊、山羊、狗、牛和马。尽管家畜胚胎干细胞的研究先于诱导性多能干细胞开展,但许多物种已经产生了能够长期保持稳定的诱导性多能干细胞,并经历着不断的培养条件优化。大多数家畜的诱导性多能干细胞可在体内分化并形成畸胎瘤,表型出经典的多能性特征。已有报道称猪和绵羊的诱导性多能干细胞可以促进嵌合体的形成,尽管嵌合体贡献率仍有待进一步提高,但这些成果不仅展示了诱导性多能干细胞技术的进步,而且促进对家畜多能性分子机制的理解[77]。此外,牛体细胞重新编程为诱导性多能干细胞也已经进行了大量的研究,尽管建立的牛诱导性多能干细胞株系经常出现重编程遗传因子泄漏表达的问题[77-78]。
综合考察家畜诱导性多能干细胞可以发现,所获得的这些干细胞仍难以满足多能干细胞的全部标准,体外长期培养中多能性难以保持,衍生效率低下,体外和体内试验中发育潜力有限等不足,因此需要不断完善家畜诱导性多能干细胞的建系方法和培养条件。
2.3.4 扩展多能干细胞 截至目前,已经报道的关于扩展多能干细胞技术在家畜中应用的主要对象是猪和牛。GAO等[44]首先通过在野生型和转基因猪胎儿成纤维细胞中表达强力霉素(doxycycline,Dox)诱导的8个重编程转录因子来生成猪诱导性多能干细胞,然后利用这些细胞对20种小分子抑制剂进行400多种排列组合测试,从中筛选出符合Dox非依赖性的培养基条件,作为猪扩展多能干细胞培养基(pEPSCM)条件。然后利用pEPSCM条件从猪的孤雌生殖囊胚和内源性囊胚获得符合扩展多能干细胞特性的猪扩展多能干细胞。XIANG等[79]利用化学定义培养基LCDM(人类白血病抑制因子、CHIR99021、Di M和Mi H),从牛诱导性多能干细胞和牛OSKC(OCT4,SOX2,KLF4和C-MYC)转染的牛胎儿成纤维细胞(bovine fetal fibroblasts,BFF)获得了符合干细胞标准,并可在种间嵌合体产生胚胎和胚胎外组织的牛扩展多能干细胞。同年,ZHAO等[45]采用哺乳动物的扩展多能干细胞技术,从野生型和体细胞核移植的植入前胚胎成功地建立了牛扩展多能干细胞,不仅可在嵌合体中形成胚胎和胚胎外细胞系,更重要的是,精确基因编辑后的牛扩展多能干细胞可作为体细胞核移植的供体,这为生物技术和畜牧业的发展注入了强大动力。
总之,家畜多能干细胞的建立有望促进家畜胚胎早期发育的研究,加快经济性状的分子育种计划,并为基因组选择/编辑生产遗传优势家畜提供可能性。大量研究表明多能干细胞的自我更新、多能性维持和分化发育离不开合适的微环境。综合分析以上6类多能干细胞不难发现,尽管这些干细胞来源不同(见图3),然而从源细胞的获取到多能干细胞系的建立,这些多能干细胞的一个共同特征表现为细胞微环境的改变,即从原始的生存或发育微环境转换到利于干细胞多能性维持和抑制自发分化的微环境。这种微环境的转变在一定程度上促进了源细胞多能性的维持或由非多能态向多能态的转变。人们在进行多能干细胞身份鉴定过程中常用到的检测标准包括:干细胞群的克隆形态特征,碱性磷酸酶活性染色,多能性相关标记物的免疫组织化学分析,连续传代后的核型稳定性评价,三胚层的衍生物检测,即拟胚体、畸胎瘤和嵌合体实验等。哺乳动物多能干细胞具有在培养中分化为多种细胞类型的潜力,这对于胚胎发生的某些方面的研究和移植治疗将是无价的。不同来源的多能干细胞建系丰富了多能干细胞的内容,这些干细胞不仅可用于确定细胞类型特异性分化所需的培养条件和基因表达模式,还可用于分离并获得移植细胞来源的谱系限制性干细胞。此外,对这些多能干细胞进行基因修饰,还可以产生通用供体细胞或定制细胞,以满足个体需求。显然,这些目标的实现需要对多能干细胞的分离、研究和使用进行系统的调查和深入的分析。
2.4 多能干细胞研究的挑战与机遇 哺乳动物多能干细胞已经成为个体发育和再生医学等研究领域的一种变革性工具,在发育机制、疾病建模、药物筛选和细胞治疗方面具有不可估量的潜力。然而,目前仍然存在一些问题和挑战。
2.4.1 道德和监管问题 尽管多能干细胞具有潜在的应用价值,且获得了巨大进步,但多能干细胞研究仍引发了与使用人类胚胎和创造嵌合生物有关的伦理问题[80]。在科学进步和伦理考虑之间取得平衡仍然是一个复杂的问题,需要持续的对话和国际合作。此外,必须建立监管框架,以管理在研究和临床环境中负责任和安全地使用多能干细胞,确保患者安全并防止滥用这些功能强大的细胞。
2.4.2 挑战与局限 哺乳动物多能干细胞研究面临着若干挑战,需要克服这些挑战才能充分实现。例如,一个主要的障碍是产生诱导性多能干细胞的重编程技术的效率和安全性,因为目前的方法可能导致影响细胞行为的遗传异常和表观遗传变异[81]。以可控和可复制的方式将多能干细胞分化为特定的细胞类型仍然具有挑战性,这限制了它们的临床应用。此外,使用多能干细胞衍生疗法的长期安全性问题需要彻底调查,以避免对患者产生不良影响。
2.4.3 多能干细胞研究的前景 干细胞技术的终极目标是应用于疾病模型构建、再生医学、药物筛选以及人类发育生物机制研究。展望未来,除了优化多能干细胞现有的培养体系和不断推出新的培养方案之外,未来的研究还有可能集中在提高诱导性多能干细胞生成的效率和安全性、改进分化方案以及开发组织工程和器官移植的新方法上。近年来,诱导性多能干细胞技术取得了重大进展。在神经科学领域,该技术为脑损伤、脊髓损伤、帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和肌萎缩性侧索硬化症提供了可能性[82]。不仅如此,一些细胞亚型通过直接重编程,可以产生各种受疾病过程损坏的细胞的体外疾病模型,用于脊髓突发性创伤、脑卒中以及肌萎缩性侧索硬化症研究[82]。目前,人诱导性多能干细胞向活跃运动神经元的分化已经在体外和体内得到证实[83]。重要的是,这些技术存在给药途径、最佳剂量、分化状态、神经保护机制以及根据疾病发作适当的细胞注射时间等问题。鉴于SOD1,TDP-43和C9ORF72等多个基因可在肌萎缩性侧索硬化症中发生突变[82,84-85],因此,一种肌萎缩性侧索硬化症模型仅代表肌萎缩性侧索硬化症患者的一个亚群。未来的研究需要考虑到这些局限性。
动物模型研究已经证明了多能干细胞的应用价值。例如,人胚胎干细胞衍生的多巴胺神经元已被有效地移植到帕金森病动物模型中,人胚胎干细胞来源的视网膜色素上皮也被证明可以改善失明模型动物的视力[86]。截至目前,全球范围内有几个正在进行的干细胞临床试验,包括针对心脏、神经、免疫、骨/软骨、肾脏、胃肠道、肺、肝和代谢疾病的研究。人们对人胚胎干细胞和人诱导性多能干细胞衍生产物的研究特别感兴趣,这些研究集中在帕金森病、脊髓损伤、1型糖尿病、黄斑变性和严重心力衰竭方面。
将干细胞技术与CRISPR/Cas9等基因编辑工具相结合,可能在哺乳动物神经发育和脑类器官研究中建立前所未有的建模系统[87]。CRISPR/Cas9等基因编辑技术的进步有可能精确修饰多能干细胞基因组,解决遗传缺陷并增加其治疗潜力[88]。例如,亨廷顿症是一种常染色体显性遗传的神经退行性疾病,其病因是亨廷顿基因中的谷氨酰胺编码序列CAG的重复出现导致[89],其重复序列越多,疾病的严重程度越高,发病年龄越早。结合类器官和CRISPR基因编辑方法可能有助于阐明亨廷顿症的致病机制[87]。
器官移植被认为是器官衰竭的最终治疗方式,但现实中器官捐献者极度稀缺,且移植需要供体-受体匹配,因此,诱导性多能干细胞可能帮助解决这些问题。利用生物材料和生物打印技术构建的3D干细胞结构可能在未来实现器官重建[90]。虽然目前完整的功能器官尚未实现重建,但已经重建了部分的肝脏、脉管系统和骨骼[91-93]。肝脏、心脏、肺和肾脏的全器官生物工程具有很高的挑战性,因为其结构和功能非常复杂。此外,随着人工智能和机器学习的兴起,二者在生命科学领域的应用,尤其在干细胞研究中的整合有望加速多能干细胞最佳分化条件和候选药物的确定。
| [1] THOMSON JA, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282(5391): 1145-1147. [2] MARTIN GR. Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981;78(12):7634-7638. [3] EVANS MJ, KAUFMAN MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292(5819):154-156. [4] TAKAHASHI K, YAMANAKA S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676. [5] NICHOLS J, SMITH A. Naive and primed pluripotent states. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(6):487-492. [6] BRONS IG, SMITHERS LE, TROTTER MW, et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448(7150): 191-195. [7] TESAR PJ, CHENOWETH JG, BROOK FA, et al. New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2007;448(7150):196-199. [8] KINOSHITA M, BARBER M, MANSFIELD W, et al. Capture of mouse and human stem cells with features of formative pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(3):453-471.e458. [9] SPERBER H, MATHIEU J, WANG Y, et al. The metabolome regulates the epigenetic landscape during naive-to-primed human embryonic stem cell transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(12):1523-1535. [10] HARVEY AJ, RATHJEN J GARDNER DK. Metaboloepigenetic regulation of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1816525. [11] MATSUI Y, ZSEBO K, HOGAN BL. Derivation of pluripotential embryonic stem cells from murine primordial germ cells in culture. Cell. 1992;70(5):841-847. [12] TURNPENNY L, SPALLUTO CM, PERRETT RM, et al. Evaluating human embryonic germ cells: concord and conflict as pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):212-220. [13] SHAMBLOTT MJ, AXELMAN J, WANG S, et al. Derivation of pluripotent stem cells from cultured human primordial germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(23):13726-13731. [14] LIU S, LIU H, PAN Y, et al. Human embryonic germ cells isolation from early stages of post-implantation embryos. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318(3):525-531. [15] PARK JH, KIM SJ, LEE JB, et al. Establishment of a human embryonic germ cell line and comparison with mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cells. 2004;17(2):309-315. [16] TURNPENNY L, BRICKWOOD S, SPALLUTO CM, et al. Derivation of human embryonic germ cells: an alternative source of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2003;21(5):598-609. [17] SHAMBLOTT MJ, AXELMAN J, LITTLEFIELD JW, et al. Human embryonic germ cell derivatives express a broad range of developmentally distinct markers and proliferate extensively in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(1): 113-118. [18] KARAGIANNIS P, NAKAUCHI A, YAMANAKA S. Bringing induced pluripotent stem cell technology to the bedside. JMA J. 2018;1(1):6-14. [19] PARK IH, ZHAO R, WEST JA, et al. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature. 2008;451(7175):141-146. [20] YU J, VODYANIK MA, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318(5858): 1917-1920. [21] MARION RM, STRATI K, LI H, et al. Telomeres acquire embryonic stem cell characteristics in induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(2): 141-154. [22] TAKAHASHI K, ICHISAKA T, YAMANAKA S. Identification of genes involved in tumor-like properties of embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2006; 329:449-458. [23] GURDON JB. The developmental capacity of nuclei taken from intestinal epithelium cells of feeding tadpoles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1962;10: 622-640. [24] WILMUT I, SCHNIEKE AE, MCWHIR J, et al. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature. 1997;385(6619):810-813. [25] LEE OH, LEE S, PARK M, et al. Generation of a B2M homozygous knockout human somatic cell nuclear transfer-derived embryonic stem cell line using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Stem Cell Res. 2021;59:102643. [26] JU JY, PARK CY, GUPTA MK, et al. Establishment of stem cell lines from nuclear transferred and parthenogenetically activated mouse oocytes for therapeutic cloning. Fertil Steril. 2008;89(5 Suppl):1314-1323. [27] FUNDELE RH, NORRIS ML, BARTON SC, et al. Temporal and spatial selection against parthenogenetic cells during development of fetal chimeras. Development. 1990;108(1):203-211. [28] GUAN K, NAYERNIA K, MAIER LS, et al. Pluripotency of spermatogonial stem cells from adult mouse testis. Nature. 2006;440(7088):1199-1203. [29] KANATSU-SHINOHARA M, INOUE K, LEE J, et al. Generation of pluripotent stem cells from neonatal mouse testis. Cell. 2004;119(7):1001-1012. [30] WANG H, JIANG M, BI H, et al. Conversion of female germline stem cells from neonatal and prepubertal mice into pluripotent stem cells. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014;6(2):164-171. [31] GONG SP, LEE ST, LEE EJ, et al. Embryonic stem cell-like cells established by culture of adult ovarian cells in mice. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(8):2594-2601, 2601. e2591-e2599. [32] GOLESTANEH N, KOKKINAKI M, PANT D, et al. Pluripotent stem cells derived from adult human testes. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(8):1115-1126. [33] FUKUCHI Y, NAKAJIMA H, SUGIYAMA D, et al. Human placenta-derived cells have mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell potential. Stem Cells. 2004; 22(5):649-658. [34] LI Z, HU X, ZHONG JF. Mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics, function, and application. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:8106818. [35] WAGERS AJ, WEISSMAN IL. Plasticity of adult stem cells. Cell. 2004;116(5): 639-648. [36] BELTRAMI AP, CESSELLI D, BERGAMIN N, et al. Multipotent cells can be generated in vitro from several adult human organs (heart, liver, and bone marrow). Blood. 2007;110(9):3438-3446. [37] KUCIA M, RECA R, CAMPBELL FR, et al. A population of very small embryonic-like (VSEL) CXCR4(+)SSEA-1(+)Oct-4+ stem cells identified in adult bone marrow. Leukemia. 2006;20(5):857-869. [38] PARTE S, BHARTIYA D, TELANG J, et al. Detection, characterization, and spontaneous differentiation in vitro of very small embryonic-like putative stem cells in adult mammalian ovary. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(8): 1451-1464. [39] ZUBA-SURMA EK, WU W, RATAJCZAK J, et al. Very small embryonic-like stem cells in adult tissues-potential implications for aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 2009;130(1-2):58-66. [40] RATAJCZAK MZ, ZUBA-SURMA EK, SHIN DM, et al. Very small embryonic-like (VSEL) stem cells in adult organs and their potential role in rejuvenation of tissues and longevity. Exp Gerontol. 2008;43(11):1009-1017. [41] MIYANISHI M, MORI Y, SEITA J, et al. Do pluripotent stem cells exist in adult mice as very small embryonic stem cells? Stem Cell Reports. 2013;1(2):198-208. [42] CHOI YJ, LIN CP, RISSO D, et al. Deficiency of microRNA miR-34a expands cell fate potential in pluripotent stem cells. Science. 2017;355(6325):eaag1927. [43] NAKAMURA T, OKAMOTO I, SASAKI K, et al. A developmental coordinate of pluripotency among mice, monkeys and humans. Nature. 2016; 537(7618):57-62. [44] GAO X, NOWAK-IMIALEK M, CHEN X, et al. Establishment of porcine and human expanded potential stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(6):687-699. [45] ZHAO L, GAO X, ZHENG Y, et al. Establishment of bovine expanded potential stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2018505118. [46] YANG J, RYAN DJ, LAN G, et al. In vitro establishment of expanded-potential stem cells from mouse pre-implantation embryos or embryonic stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2019;14(2):350-378. [47] SHEN H, YANG M, LI S, et al. Mouse totipotent stem cells captured and maintained through spliceosomal repression. Cell. 2021;184(11):2843-2859.e2820. [48] HU Y, YANG Y, TAN P, et al. Induction of mouse totipotent stem cells by a defined chemical cocktail. Nature. 2023;617(7962):792-797. [49] XU Y, ZHAO J, REN Y, et al. Derivation of totipotent-like stem cells with blastocyst-like structure forming potential. Cell Res. 2022;32(6):513-529. [50] YANG M, YU H, YU X, et al. Chemical-induced chromatin remodeling reprograms mouse ESCs to totipotent-like stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2022; 29(3):400-418.e413. [51] BOROVIAK T, STIRPARO GG, DIETMANN S, et al. Single cell transcriptome analysis of human, marmoset and mouse embryos reveals common and divergent features of preimplantation development. Development. 2018;145(21):dev167833. [52] VASSILIEV I, NOTTLE MB. Isolation and culture of porcine embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1074:85-95. [53] HONDA A, HIROSE M, OGURA A. Basic FGF and Activin/Nodal but not LIF signaling sustain undifferentiated status of rabbit embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(12):2033-2042. [54] CIBELLI JB, STICE SL, GOLUEKE PJ, et al. Transgenic bovine chimeric offspring produced from somatic cell-derived stem-like cells. Nat Biotechnol. 1998; 16(7):642-646. [55] ZHU SX, SUN Z, ZHANG JP. Ovine (Ovis aries) blastula from an in vitro production system and isolation of primary embryonic stem cells. Zygote. 2007;15(1):35-41. [56] LI P, TONG C, MEHRIAN-SHAI R, et al. Germline competent embryonic stem cells derived from rat blastocysts. Cell. 2008;135(7):1299-1310. [57] MURRAY JT, CAMPBELL DG, MORRICE N, et al. Exploitation of KESTREL to identify NDRG family members as physiological substrates for SGK1 and GSK3. Biochem J. 2004;384(Pt 3):477-488. [58] BOGLIOTTI YS, WU J, VILARINO M, et al. Efficient derivation of stable primed pluripotent embryonic stem cells from bovine blastocysts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(9):2090-2095. [59] HAN X, XIANG J, LI C, et al. MLL1 combined with GSK3 and MAP2K inhibition improves the development of in vitro-fertilized embryos. Theriogenology. 2020; 146:58-70. [60] WU X, SONG M, YANG X, et al. Establishment of bovine embryonic stem cells after knockdown of CDX2. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28343. [61] VERMA OP, KUMAR R, NATH A, et al. In vivo differentiation potential of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryonic stem cell. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012;48(6):349-358. [62] PILICHI S, ROCCA S, DATTENA M, et al. Sheep embryonic stem-like cells engrafted into sheep femoral condyle osteochondral defects: 4-year follow-up. BMC Vet Res. 2018;14(1):213. [63] ZHAO Y, LIN J, WANG L, et al. Derivation and characterization of ovine embryonic stem-like cell lines in semi-defined medium without feeder cells. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2011;315(10):639-648. [64] KUMAR DE A, MALAKAR D, AKSHEY YS, et al. Isolation and characterization of embryonic stem cell-like cells from in vitro produced goat (Capra hircus) embryos. Anim Biotechnol. 2011;22(4):181-196. [65] BEHBOODI E, BONDAREVA A, BEGIN I, et al. Establishment of goat embryonic stem cells from in vivo produced blastocyst-stage embryos. Mol Reprod Dev. 2011;78(3):202-211. [66] CHA HJ, YUN JI, HAN NR, et al. Generation of embryonic stem-like cells from in vivo-derived porcine blastocysts at a low concentration of basic fibroblast growth factor. Reprod Domest Anim. 2018;53(1):176-185. [67] HOU DR, JIN Y, NIE XW, et al. Derivation of porcine embryonic stem-like cells from in vitro-produced blastocyst-stage embryos. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25838. [68] ZHANG M, WANG C, JIANG H, et al. Derivation of novel naive-like porcine embryonic stem cells by a reprogramming factor-assisted strategy. FASEB J. 2019; 33(8):9350-9361. [69] LI X, ZHOU SG, IMREH MP, et al. Horse embryonic stem cell lines from the proliferation of inner cell mass cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2006;15(4):523-531. [70] TOBIAS IC, BROOKS CR, TEICHROEB JH, et al. Small-molecule induction of canine embryonic stem cells toward naïve pluripotency. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(16): 1208-1222. [71] VAAGS AK, ROSIC-KABLAR S, GARTLEY CJ, et al. Derivation and characterization of canine embryonic stem cell lines with in vitro and in vivo differentiation potential. Stem Cells. 2009;27(2):329-340. [72] WANG L, DUAN E, SUNG LY, et al. Generation and characterization of pluripotent stem cells from cloned bovine embryos. Biol Reprod. 2005; 73(1):149-155. [73] GEORGE A, SHARMA R, SINGH KP, et al. Production of cloned and transgenic embryos using buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryonic stem cell-like cells isolated from in vitro fertilized and cloned blastocysts. Cell Reprogram. 2011;13(3):263-272. [74] MUZAFFAR M, SELOKAR NL, SINGH KP, et al. Equivalency of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryonic stem cells derived from fertilized, parthenogenetic, and hand-made cloned embryos. Cell Reprogram. 2012;14(3):267-279. [75] SINGH KP, KAUSHIK R, GARG V, et al. Expression pattern of pluripotent markers in different embryonic developmental stages of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos and putative embryonic stem cells generated by parthenogenetic activation. Cell Reprogram. 2012;14(6):530-538. [76] MUNOZ M, RODRIGUEZ A, DE FRUTOS C, et al. Conventional pluripotency markers are unspecific for bovine embryonic-derived cell-lines. Theriogenology. 2008;69(9):1159-1164. [77] KUMAR D, ANAND T, VIJAYALAKSHMY K, et al. Transposon mediated reprogramming of buffalo fetal fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells in feeder free culture conditions. Res Vet Sci. 2019;123:252-260. [78] PILLAI VV, KEI TG, REDDY SE, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell generation from bovine somatic cells indicates unmet needs for pluripotency sustenance. Anim Sci J. 2019;90(9):1149-1160. [79] XIANG J, WANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. LCDM medium supports the derivation of bovine extended pluripotent stem cells with embryonic and extraembryonic potency in bovine-mouse chimeras from iPSCs and bovine fetal fibroblasts. FEBS J. 2021;288(14):4394-4411. [80] SEBO J PARENT B. Human, nonhuman, and chimeric research: considering old issues with new research. Hastings Cent Rep. 2022;52 Suppl 2:S29-S33. [81] YAMANAKA S. Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(4):523-531. [82] CIERVO Y, NING K, JUN X, et al. Advances, challenges and future directions for stem cell therapy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12(1):85. [83] DIMOS JT, RODOLFA KT, NIAKAN KK, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with ALS can be differentiated into motor neurons. Science. 2008;321(5893):1218-1221. [84] GURNEY ME, PU H, CHIU AY, et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994;264(5166):1772-1775. [85] ARNOLD ES, LING SC, HUELGA SC, et al. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(8):E736-E745. [86] LUND RD, WANG S, KLIMANSKAYA I, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived cells rescue visual function in dystrophic RCS rats. Cloning Stem Cells. 2006;8(3):189-199. [87] KELAVA I, LANCASTER M A. Dishing out mini-brains: Current progress and future prospects in brain organoid research. Dev Biol. 2016;420(2):199-209. [88] DE MASI C, SPITALIERI P, MURDOCCA M, et al. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 to human-induced pluripotent stem cells: from gene editing to drug discovery. Hum Genomics. 2020;14(1):25. [89] LI LB, BONINI NM. Roles of trinucleotide-repeat RNA in neurological disease and degeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33(6):292-298. [90] ADER M, TANAKA EM. Modeling human development in 3D culture. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;31:23-28. [91] SALMASI S, KALASKAR DM, YOON WW, et al. Role of nanotopography in the development of tissue engineered 3D organs and tissues using mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(2):266-280. [92] STABLER CT, LECHT S, MONDRINOS MJ, et al. Revascularization of decellularized lung scaffolds: principles and progress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015; 309(11):L1273-L1285. [93] BAPTISTA LS, KRONEMBERGER GS, CÔRTES I, et al. Adult stem cells spheroids to optimize cell colonization in scaffolds for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1285. [94] PEPER J, KOWNATZKI-DANGER D, WENINGER G, et al. Caveolin3 stabilizes McT1-mediated lactate/proton transport in cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2021;128(6):e102-e120. [95] CHEN H, CROSS AC, THAKKAR A, et al. Selective linkage of mitochondrial enzymes to intracellular calcium stores differs between human-induced pluripotent stem cells, neural stem cells, and neurons. J Neurochem. 2021; 156(6):867-879. [96] SHARMA A, MCKEITHAN WL, SERRANO R, et al. Use of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to assess drug cardiotoxicity. Nature protocols. 2018;13(12):3018-3041. [97] SALMAN MM, KITCHEN P, YOOL AJ, et al. Recent breakthroughs and future directions in drugging aquaporins. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(1):30-42. [98] MACHIRAJU P GREENWAY SC. Current methods for the maturation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(1):33-43. [99] KHATEB S, JHA S, BHARTI K, et al. Cell-based therapies for age-related macular degeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1256:265-293. |
| [1] | 邓 丽, 刘 洋, 王 慧, 杨 秋, 董明清. 转录因子NKX2.1促进诱导多能干细胞向肺干细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7790-7796. |
| [2] | 刘 璐, 钟 畅, 余 欣, 任晨媛, 巩杨杨, 周 平, 王迎斌. 体外合成微环境促进人多能干细胞来源心肌细胞成熟的学术进展及临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7856-7862. |
| [3] | 熊挺淋, 张丽莎, 王德伟, 曹海平, 杨 燕. 体外培养时间对诱导多能干细胞源性心肌细胞成熟度的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(25): 5304-5310. |
| [4] | 赵 文, 毕玉琳, 付旭阳, 段红梅, 杨朝阳, 李晓光. 干细胞治疗肌萎缩侧索硬化症:细胞来源、数量、修饰手段及给药途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(19): 4083-4090. |
| [5] | 郑安垲, 刘瑞明, 向秋玲. 干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(1): 120-127. |
| [6] | 马阳光, 张雅永, 孟明耀, 金志豪, 李映明, 黄耀萱, 韩 燊, 李亚雄. 诱导多能干细胞在遗传性心脏疾病模型中的应用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(25): 4072-4078. |
| [7] | 崔胜男, 刘传国, 杨雯晴, 郑志娟, 张 丹. 毛蕊异黄酮对人诱导多能干细胞内皮分化的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(19): 3031-3036. |
| [8] | 胡 威, 邢 健, 陈广新, 陈泽娥, 赵 艺, 乔 丹, 欧阳昆富, 黄文华. 心肌补片:细胞来源、完善策略及最佳制作方法分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(17): 2723-2730. |
| [9] | 文廷浩, 李远迪, 何可可, 宋雯茜, 王先斌, 高 杰, 苏 敏, 胡 蓉. Wnt信号通路与自身免疫调节因子共同参与胚胎干细胞向胸腺上皮祖细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(13): 1996-2001. |
| [10] | 郑晓晗, 冯晓丽, 胡 兰, 高仕君, 魏艳召, 黄 婷, 孙圣童, 魏绪芳, 王 埮, 赵振强. 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进人胚胎干细胞分化为腹侧中脑多巴胺能神经祖细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(33): 5348-5356. |
| [11] | 黄贵才, 罗业浩, 江慧容, 李 媛, 毛德文, 官志杰. 干细胞对肝脏疾病的临床治疗前景与研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 3091-3098. |
| [12] | 郑晓晗, 魏艳召, 黄 婷, 魏绪芳, 孙圣童, 王 埮, 赵振强. 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2395-2403. |
| [13] | 黄文俊, 王 洁, 周亚飞, 李 环, 蒋丛姗, 张艳敏, 周 锐. 一种人诱导多能干细胞向内皮细胞定向分化方案的建立及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(10): 1553-1559. |
| [14] | 魏艳召, 郑晓晗, 高仕君, 黄 婷, 魏续芳, 陈薪旭, 赵振强. 人胚胎干细胞自分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子及受体表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(1): 34-41. |
| [15] | 黄文俊, 周亚飞, 王 洁, 李 环, 张艳敏, 周 锐. 建立并鉴定一种基于人诱导多能干细胞的肝脏细胞定向分化实验方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(1): 28-33. |
多能干细胞的研究可以追溯到胚胎发育的早期阶段,即早期囊胚内细胞团来源的多能干细胞,这类细胞通常被称为胚胎干细胞。虽然胚胎干细胞具有惊人的医学研究和临床应用潜力,但胚胎干细胞的研究面临着众多伦理的、法律的和科学的挑战,包括如何获得和使用这些细胞,以及如何确保它们的安全性和有效性。然而,早期的经典胚胎干细胞为后续的各类多能干细胞,提供了重要的干细胞鉴定标准和实验方法[1-3]。截至目前,已经在体外建立了多种符合干细胞鉴定标准的多能干细胞系,如来源于成体组织的诱导性多能干细胞,它们通过基因重编程的方式使分化的体细胞发生去分化而重新获得多能性,这些细胞在表型、增殖特性、基因表达、表面抗原、多能细胞特异基因的表观遗传状态和端粒酶活性等方面与胚胎干细胞相似,而且,这些细胞在拟胚体和畸胎瘤中可以衍生为3种胚层的细胞类型[4]。其他种类多能干细胞的发现引发了科学家们浓厚的兴趣,这些多能干细胞突破了胚胎干细胞所面临的的伦理和法律的瓶颈,并被用于研究许多困难疾病的治疗,如心脏病、帕金森病、糖尿病和脊髓损伤等。
该综述旨在回顾多能干细胞的研究历史,总结不同来源多能干细胞的建系方法,首次对多能干细胞的基本类别进行归纳总结,并阐述常见家畜中各类多能干细胞的建系情况。同时探讨多能干细胞研究的前景、挑战、机遇和未来可能的发展方向,为读者提供一个全面的、最新的多能干细胞研究综述,帮助读者们了解这一领域的关键概念、前沿进展和未来趋势。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一、三、四作者在2023年4月进行了文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 文献发表时限为1962-2023年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网及万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“多能干细胞,胚胎干细胞,诱导多能干细胞,扩展多能干细胞,家畜多能干细胞,患者特异性iPSCs”,英文检索词为“Pluripotent stem cells,Embryonic stem cells,Induced pluripotent stem cells,Expanded potential stem cells,Livestock pluripotent stem cells,Patient-specific iPSCs”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 未进行手工检索。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed、中国知网数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
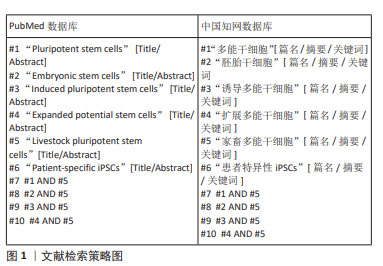
1.1.8 检索文献量 PubMed数据库共检索到英文文献49 659篇,Web of Science数据库共检索到英文文献49 167篇,中国知网检索到中文文献3 006篇,万方数据库共检索到中文文献7 482篇。
1.2 入组标准1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与哺乳动物多能干细胞体外建系和干性鉴定相关的文章;②与患者特异性诱导性多能干细胞的研究与应用相关的文章;③虽年限久远,但对文章主题有重要意义的文章;④相似文章选取时间较近者。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①研究内容重复的文章;②相同研究类型且无明显差异的文章;③年限久远且无重要意义的文章。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 初步共检索到中英文文109 314篇,包括英文数据库PubMed检索得到英文文献49 659篇,Web of Science检索到49 167篇,中文数据库中国知网检索到中文文献3 006篇,万方数据库检索到7 482篇。选择与哺乳动物多能干细胞体外培养、建系和干性鉴定相关性强、并具有重要价值的文章进行分析讨论,排除低水平文献和与哺乳动物多能干细胞建系和干性鉴定相关性差、内容陈旧、重复、数据较差的文献109 174篇,按入选标准严格筛选后最终纳入99篇高水平英文文献进行综述,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该综述系统回顾并总结了小鼠、人及家畜动物各类多能干细胞的建立方法、培养体系,对目前所取得的研究进展进行了综述。进一步讨论了干细胞研究中存在的道德和监管问题,揭示其中的挑战与局限,并展望干细胞研究的应用前景。
3.3 综述的局限性 多能干细胞研究是一个非常热门的领域,在科学界、医学界和产业界都受到了广泛的关注和支持,可以说是一个充满活力和潜力的热门领域。中英文文献检索发现截至目前,关于多能干细胞的研究论文将近6万篇,内容涉及干细胞基础研究、干细胞分化与发育机制、胚胎干细胞研究、诱导性多能干细胞研究、组织工程和再生医学、疾病建模与药物筛选、基因编辑与干细胞治疗、干细胞在神经科学中的应用和生殖医学和生育治疗等。此综述主要讨论了哺乳动物多能干细胞体外培养、建系和干性鉴定等方面的研究进展,篇幅有限,涉及内容较为基础,这是该综述的局限性。
3.4 综述的重要意义 多能干细胞研究具有广阔的应用前景,文章从多能干细胞的获取方式(来源)入手,对多能干细胞进行分类,重点总结了小鼠、人及家畜动物各类多能干细胞的建立方法和研究进展,并讨论干细胞研究中存在的问题与挑战。文章是对哺乳动物多能干细胞基础研究的全面概述,具有重要意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
多能干细胞:具有自我复制和多向分化潜能的未分化细胞,其主要特征类似于胚胎早期发育的围着床期,体外培养的多能干细胞可以长期保持自我更新,在特定的信号刺激下分化为具备所有细胞系分化潜能的3个原始胚层。多能干细胞为研究细胞命运转换、阐明发育和分化相关的重要机制,以及探索再生药物提供了宝贵的资源。
胚胎干细胞:一类经典的多能干细胞,来源于胚胎发育早期的囊胚内细胞团,可在体外无限扩增并具有分化为各种体细胞类型的潜能,在发育研究和潜在的医学应用方面具有不可估量的价值。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
多能干细胞的自我更新和多向分化的特征有可能彻底改变人们对生物学、医学,以及发育和疾病的理解。干细胞在胚胎发育的早期发挥着重要作用,研究干细胞可以深入理解生物体发育和组织器官形成的基本原理,包括细胞过程、分化机制和其中的基因调控。同时,研究干细胞对了解出生缺陷和发育异常具有重要意义。由于具备在体内发育成各种细胞类型的显著能力,干细胞被用于探索修复和再生受损组织和器官。例如治疗心脏病、脊髓损伤、糖尿病和神经退行性疾病。在实验室中干细胞可用于创建疾病模型,以针对性地研究各种疾病的潜在机制,并推动药物发现和个性化治疗。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||