中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2593-2598.doi: 10.12307/2024.277
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
miR-141-3p对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠背根神经节炎症及下肢疼痛的抑制和改善作用
许 刚,张长春,朱 坤,叶雨辰,周平辉
- 蚌埠医学院第一附属医院骨科,组织移植安徽省重点实验室,安徽省蚌埠市 233004
Effects of miR-141-3p on dorsal root ganglion inflammation and lower limb pain in rats with lumbar disc herniation
Xu Gang, Zhang Changchun, Zhu Kun, Ye Yuchen, Zhou Pinghui
- Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Tissue Transplantation, Bengbu 233004, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
miR-141-3p:是一种功能丰富的微小RNA,可通过调控其靶基因来调控许多病理、生理过程,研究表明,其在骨髓基质细胞中随着年龄的增加而增加,且与炎症信号通路的活化存在一定关系,提示其可能成为腰椎间盘突出症的治疗靶点。胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子:胰岛素样生长因子1是生长激素的介质,具有很强的促进骨组织生成作用,同时还可抑制骨中胶原降解、防止骨吸收等;而血小板源性生长因子是一种碱性蛋白质,具有促进血管再生的作用,有研究表明其可促进椎间盘中的血管内皮细胞生长,从而促进椎间盘再生以及突出椎间盘的重吸收。
背景:研究表明,胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子有抑制纤维环细胞凋亡的作用。miR-141-3p微小RNA在骨髓基质细胞中随着年龄的增加而增加,且与炎症信号通路的活化存在一定关系,提示其可能成为腰椎间盘突出症的治疗靶点。
目的:探究miR-141-3p通过调控胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠背根神经节炎症及下肢疼痛的影响。方法:选取50只SPF级SD雄性大鼠,随机分为正常组、模型组、miR-NC组、miR-141-3p inhibitor组、miR-141-3p mimics组,每组10只。除正常组外,其余大鼠采用自体髓核移植法进行腰椎间盘突出症建模。建模成功后,对miR-NC组、miR-141-3p inhibitor组和miR-141-3p mimics组大鼠鞘内分别注射10 μL 20 μmol/L miR-NC,miR-141-3p inhibitor,miR-141-3p mimics,均每天注射1次,连续注射28 d;正常组、模型组同期同位置注射同体积生理盐水。采用热缩足潜伏期阈值评价大鼠下肢疼痛,实时荧光定量 PCR 检测背根神经节组织miR-141-3p mRNA表达,ELISA法检测背根神经节组织炎症因子,免疫印迹法检测背根神经节组织胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子蛋白表达,并分析miR-141-3p与胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子的相关性。
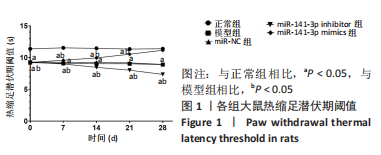
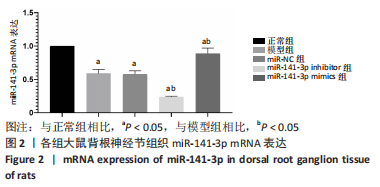
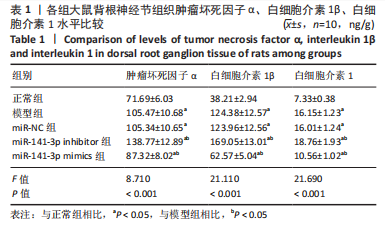
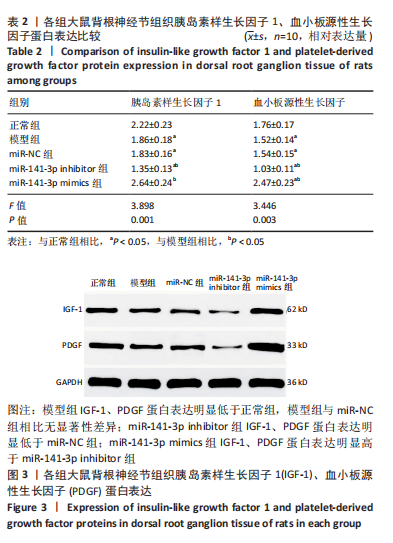
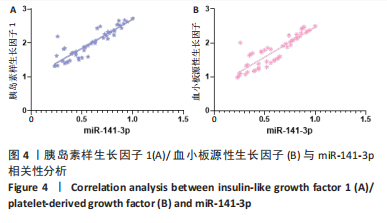
结果与结论:miR-NC组各项指标与模型组比较,差异均无显著性意义。①大鼠热缩足潜伏期阈值:模型组明显低于正常组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p inhibitor组明显低于miR-NC组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p mimics组明显高于miR-141-3p inhibitor组(P < 0.05)。②背根神经节组织miR-141-3p mRNA表达:模型组明显低于正常组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p inhibitor组明显低于miR-NC组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p mimics组明显高于miR-141-3p inhibitor组(P < 0.05)。③背根神经节组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素1含量:模型组明显高于正常组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p inhibitor组明显高于miR-NC组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p mimics组明显低于miR-141-3p inhibitor组(P < 0.05)。④背根神经节组织胰岛素样生长因子1、血小板源性生长因子蛋白表达:模型组明显低于正常组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p inhibitor组明显低于miR-NC组(P < 0.05),miR-141-3p mimics组明显高于miR-141-3p inhibitor组(P < 0.05)。⑤胰岛素样生长因子1与miR-141-3p呈正相关(r=0.904,P < 0.001),血小板源性生长因子与miR-141-3p呈正相关(r=0.879,P < 0.001)。⑥结论:miR-141-3p可显著改善腰椎间盘突出症大鼠下肢疼痛,抑制背根神经节炎症,其机制可能与促进胰岛素样生长因子1/血小板源性生长因子表达有关。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2033-3606(许刚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: