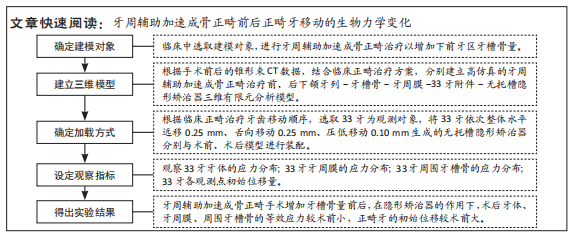
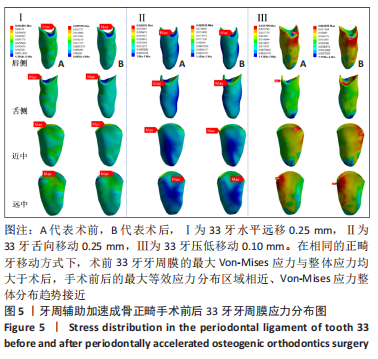
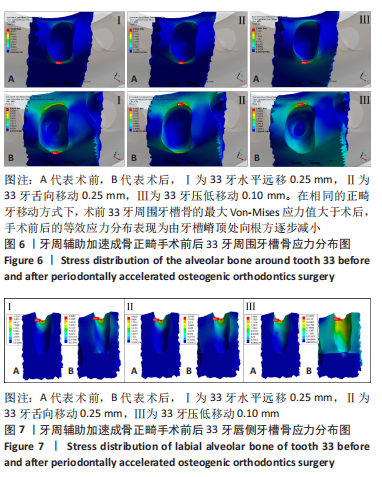
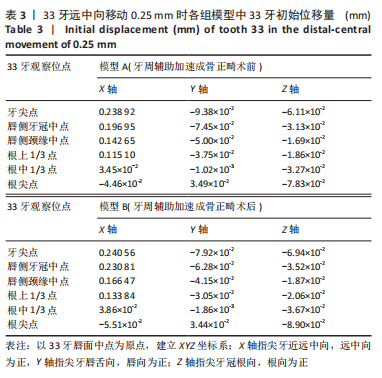
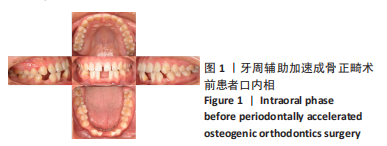
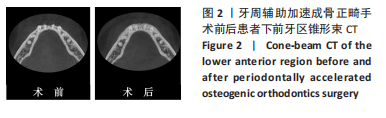
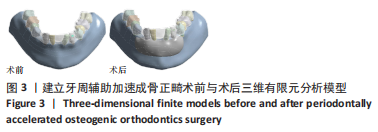
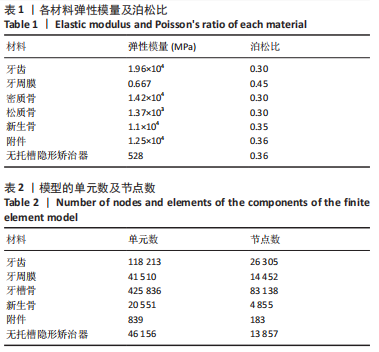
[1] ANTOUN J S, MEI L, GIBBS K, et al. Effect of orthodontic treatment on the periodontal tissues. Periodontology 2000. 2017;74(1):140-157.
[2] ALSINO HI, HAJEER MY, BURHAN AS, et al. The Effectiveness of Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics (PAOO) in Accelerating Tooth Movement and Supporting Alveolar Bone Thickness During Orthodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022; 14(5):e24985.
[3] KAMAL A T, MALIK D, FIDA M, et al. Does periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics improve orthodontic treatment outcome? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthod. 2019;17(2):193-201.
[4] DOUNIS T, PITMAN LM. Decision Making for Soft and Hard Tissue Augmentation in Surgically Facilitated Orthodontics. Clin Adv Periodontics. 2020;10(1):38-41.
[5] BRUGNAMI F, CAIAZZO A, MEHRA P. Can corticotomy (with or without bone grafting) expand the limits of safe orthodontic therapy? J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2018;8(1):1-6.
[6] XU X, WU JQ, JIANG JH, et al. Periodontal Effect of Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics in Skeletal Angle Class III: A Nonrandomized, Controlled Trial. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2020;40(4):e169-e177.
[7] KESER E, NAINI FB. Accelerated orthodontic tooth movement: surgical techniques and the regional acceleratory phenomenon. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;44(1):1.
[8] AMIT G, JPS K, PANKAJ B, et al. Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics (PAOO) - a review. J Clin Exp Dent. 2012;4(5):e292-e296.
[9] VANNALA V, KATTA A, REDDY MS, et al. Periodontal Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics Technique for Rapid Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Systematic Review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019;11(Suppl 2): S97-S106.
[10] XUAN DY. [Strategies of periodontal surgery to promote orthodontic treatment: the clinical application of periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020; 55(7):448-454.
[11] Van BILSEN MW, SCHREURS R, MEULSTEE JW, et al. Evaluation of the anterior mandibular donor site one year after secondary reconstruction of an alveolar cleft: 3-dimensional analysis using cone-beam computed tomography. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;53(8): 719-724.
[12] 雍苓,黄仕禄,刘洪,等.不同骨缺损类型牙种植体的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):148-153.
[13] GOMEZ JP, PEÑA FM, MARTÍNEZ V, et al. Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Angle Orthod. 2015;85(3):454-460.
[14] LIANG W, RONG Q, LIN J, et al. Torque control of the maxillary incisors in lingual and labial orthodontics: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(3):316-322.
[15] JIANG T, WU RY, WANG JK, et al. Clear aligners for maxillary anterior en masse retraction: a 3D finite element study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 10156.
[16] 刘倩,顾泽旭,田杰,等.材料厚度对无托槽隐形矫治器固位力影响的实验研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2013,20(1):46-48.
[17] HONG K, KIM WH, EGHAN-ACQUAH E, et al. Efficient Design of a Clear Aligner Attachment to Induce Bodily Tooth Movement in Orthodontic Treatment Using Finite Element Analysis. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(17):4926.
[18] LIU L, SONG Q, ZHOU J, et al. The effects of aligner overtreatment on torque control and intrusion of incisors for anterior retraction with clear aligners: A finite-element study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(1):33-41.
[19] WILCKO WM, WILCKO T, BOUQUOT JE, et al. Rapid orthodontics with alveolar reshaping: two case reports of decrowding. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2001;21(1):9-19.
[20] DARWICHE F, KHODARI E, ALJEHANI D, et al. Comparison of Effectiveness of Corticotomy-assisted Accelerated Orthodontic Treatment and Conventional Orthodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020;21(6):701-709.
[21] CHEN Z, ZHOU H, ZHANG K, et al. The clinical efficacy of periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics in patients with bone fenestration and dehiscence: a retrospective study. Head Face Med. 2022;18(1):40.
[22] HAN Y, MIAO L, LIU J, et al. Periodontal soft tissue increase induced by periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics surgery. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):506.
[23] MUÑOZ F, WILCKO T, ACUÑA S, et al. Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics (PAOO) technique in cleft patients: A complement to orthognathic surgery in dentoalveolar expansion. A case series report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2020;48(11):1028-1034.
[24] AGRAWAL AA, KOLTE AP, KOLTE RA, et al. Comparative CBCT analysis of the changes in buccal bone morphology after corticotomy and micro-osteoperforations assisted orthodontic treatment - Case series with a split mouth design. Saudi Dent J. 2019;31(1):58-65.
[25] BHATTACHARYA P, BHATTACHARYA H, ANJUM A, et al. Assessment of Corticotomy Facilitated Tooth Movement and Changes in Alveolar Bone Thickness - A CT Scan Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(10):C26-C30.
[26] GAO J, NGUYEN T, OBEROI S, et al. The Significance of Utilizing A Corticotomy on Periodontal and Orthodontic Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(8):803.
[27] WILCKO MT, FERGUSON DJ, MAKKI L, et al. Keratinized Gingiva Height Increases After Alveolar Corticotomy and Augmentation Bone Grafting. J Periodontol. 2015;86(10):1107-1115.
[28] WANG Y, ZHANG H, SUN W, et al. Macrophages mediate corticotomy-accelerated orthodontic tooth movement. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16788.
[29] YASHWANT VA, BALU P, KUMAR RS, et al. Effectiveness of platelet rich fibrin versus demineralized bone xenograft in periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics. Angle Orthod. 2022;92(2):180-188.
[30] ZHOU Y, HE X, ZHANG D. Study of bone remodeling in corticotomy-assisted orthodontic tooth movement in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120(9):15952-15962.
[31] XU X, WU JQ, JIANG JH, et al. Periodontal Effect of Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics in Skeletal Angle Class III: A Nonrandomized, Controlled Trial. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2020;40(4):e169-e177.
[32] MA Z, ZHU Y, ZHAN Y, et al. Periosteum coverage versus collagen-membrane coverage in periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics: a randomized controlled clinical trial in Class II and Class III malocclusions. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):439.
[33] JIANG JH. [Application, research and prospect of periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics technology]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021;56(10):971-977.
[34] WANG X, MEI M, HAN G, et al. Effectiveness of modified periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics in skeletal class II malocclusion treated by a camouflage approach. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(2):979-989.
[35] XU M, SUN XY, XU JG. Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics with platelet-rich fibrin in an adult patient with periodontal disease: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(6): 1367-1378.
[36] LIU X, CHENG Y, QIN W, et al. Effects of upper-molar distalization using clear aligners in combination with Class II elastics: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):546.
[37] 王荣,刘亦然,范勇斌,等.Bio-oss骨胶原修复牙槽骨缺损区后对牙齿移动影响的临床初探[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2012,13(4): 243-245.
[38] KESER E, NAINI FB. Accelerated orthodontic tooth movement: surgical techniques and the regional acceleratory phenomenon. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;44(1):1.
[39] QI L, GE W, CAO N, et al. Effects of autologous concentrated growth factor on gingival thickness in periodontal accelerated osteogenic orthodontics: a 6-month randomized controlled trial. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):604.
[40] YANG C, WANG C, DENG F, et al. Biomechanical effects of corticotomy approaches on dentoalveolar structures during canine retraction: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148(3):457-465. |