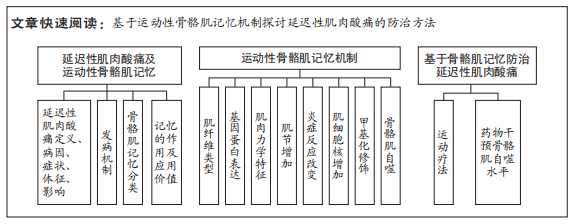
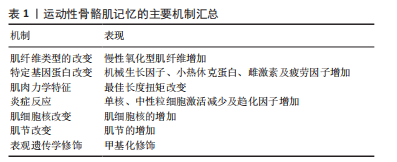
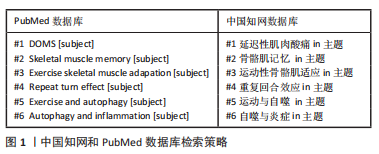
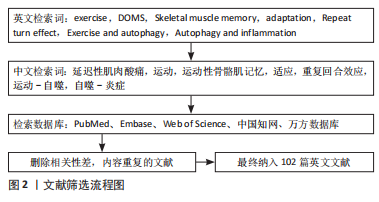
[1] ARMSTRONG RB, WARREN GL, WARREN JA. Mechanisms of exercise-induced muscle fibre injury. 1991;12(3):184-207.
[2] VEQAR Z, IMTIYAZ S. Vibration Therapy in Management of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS). J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(6):LE01-4.
[3] DEYHLE M, GIER A, EVANS K, et al. Skeletal Muscle Inflammation Following Repeated Bouts of Lengthening Contractions in Humans. 2015;6:424.
[4] ABOODARDA SJ, GEORGE J, MOKHTAR AH, et al. Muscle strength and damage following two modes of variable resistance training. J Sports Sci Med. 2011;10(4):635-642.
[5] HOTFIEL T, FREIWALD J, HOPPE MW, et al. Advances in Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS): Part I: Pathogenesis and Diagnostics. Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2018;32(4):243-250.
[6] MORGAN DL. New insights into the behavior of muscle during active lengthening. Biophys J. 1990;57(2):209-221.
[7] NOSAKA K, NEWTON M, SACCO P. Delayed-onset muscle soreness does not reflect the magnitude of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2002;12(6):337-346.
[8] ISNER-HOROBETI ME, DUFOUR SP, VAUTRAVERS P, et al. Eccentric exercise training: modalities, applications and perspectives. Sports Med. 2013;43(6):483-512.
[9] HYLDAHL RD, HUBAL MJ. Lengthening our perspective: morphological, cellular, and molecular responses to eccentric exercise. Muscle Nerve. 2014;49(2):155-170.
[10] FRIDÉN J, LIEBER RL. Structural and mechanical basis of exercise-induced muscle injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24(5):521-530.
[11] MURASE S, TERAZAWA E, HIRATE K, et al. Upregulated glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor through cyclooxygenase-2 activation in the muscle is required for mechanical hyperalgesia after exercise in rats. J Physiol. 20135;591(12):3035-3048.
[12] MIZUMURA K, TAGUCHI T. Delayed onset muscle soreness: Involvement of neurotrophic factors. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(1):43-52.
[13] LIEBER RL, FRIDÉN J. Muscle damage is not a function of muscle force but active muscle strain. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993;74(2):520-526.
[14] SCHWANE JA, ARMSTRONG RB. Effect of training on skeletal muscle injury from downhill running in rats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983;55(3):969-975.
[15] BROWN M, HOWATSON G, KEANE K, et al. Adaptation to Damaging Dance and Repeated-Sprint Activity in Women. J Strength Cond Res. 2016;30(9):2574-2581.
[16] BARSS T, MAGNUS C, CLARKE N, et al. Velocity-specific strength recovery after a second bout of eccentric exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(2):339-349.
[17] MCHUGH M. Can exercise induced muscle damage be avoided?. Br J Sports Med. 1999; 33(6):377.
[18] MCHUGH MP, TETRO DT. Changes in the relationship between joint angle and torque production associated with the repeated bout effect. J Sports Sci. 2003;21(11):927-932.
[19] CLARKSON PM, NOSAKA K, BRAUN B. Muscle function after exercise-induced muscle damage and rapid adaptation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24(5):512-520.
[20] SNIJDERS T, AUSSIEKER T, HOLWERDA A, et al. The concept of skeletal muscle memory: Evidence from animal and human studies. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020;229(3):e13465.
[21] PIERRYNOWSKI MR, TÜDUS PM, PLYLEY MJ. Effects of downhill or uphill training prior to a downhill run. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1987;56(6):668-672.
[22] BYRNES W, CLARKSON P, WHITE J, et al. Delayed onset muscle soreness following repeated bouts of downhill running. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1985;59(3):710-715.
[23] Nosaka K, Clarkson PM. Variability in serum creatine kinase response after eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Int J Sports Med. 1996;17(2):120-127.
[24] LINDSTEDT SL, LASTAYO PC, REICH TE. l. When active muscles lengthen: properties and consequences of eccentric contractions. News Physiol Sci. 2001;16:256-261.
[25] ABBOTT BC, WILKIE DR. The relation between velocity of shortening and the tension-length curve of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1952;117(3):26 P.
[26] MCHUGH M, CONNOLLY D, ESTON R, et al. Exercise-induced muscle damage and potential mechanisms for the repeated bout effect. Sports Med. 1999;27(3):157-170.
[27] HOWATSON G, VAN SOMEREN KA. Evidence of a contralateral repeated bout effect after maximal eccentric contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007;101(2):207-214.
[28] BLACK CD, MCCULLY KK. Muscle injury after repeated bouts of voluntary and electrically stimulated exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40(9):1605-1615.
[29] SHARPLES AP, STEWART CE, SEABORNE RA. Does skeletal muscle have an ‘epi’-memory? The role of epigenetics in nutritional programming, metabolic disease, aging and exercise. Aging Cell. 2016;15(4):603-616.
[30] VINCENT HK, VINCENT KR. The effect of training status on the serum creatine kinase response, soreness and muscle function following resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1997;18(6):431-437.
[31] NOSAKA K, CLARKSON PM. Muscle damage following repeated bouts of high force eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995;27(9):1263-1269.
[32] LEEDER J DC, VAN SOMEREN KA, GAZE D, et al. Recovery and adaptation from repeated intermittent-sprint exercise. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2014;9(3):489-496.
[33] NICOL C, AVELA J, KOMI PV. The stretch-shortening cycle : a model to study naturally occurring neuromuscular fatigue. Sports Med. 2006;36(11):977-999.
[34] HODY S, LEPRINCE P, SERGEANT K, et al. Human muscle proteome modifications after acute or repeated eccentric exercises. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(12):2281-2296.
[35] MURACH KA, MOBLEY CB, ZDUNEK CJ, et al. Muscle memory: myonuclear accretion, maintenance, morphology, and miRNA levels with training and detraining in adult mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(6):1705-1722.
[36] BARNETT A. Using recovery modalities between training sessions in elite athletes: does it help? .Sports Med. 2006;36(9):781-796.
[37] CHEN T, TSENG W, HUANG G, et al. Low-intensity eccentric contractions attenuate muscle damage induced by subsequent maximal eccentric exercise of the knee extensors in the elderly. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(4):1005-1015.
[38] BONTEMPS B, VERCRUYSSEN F, GRUET M, et al. Downhill Running: What Are The Effects and How Can We Adapt? A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2020;50(12):2083-2110.
[39] HYLDAHL R, CHEN T, NOSAKA K. Mechanisms and Mediators of the Skeletal Muscle Repeated Bout Effect. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2017;45(1):24-33.
[40] HODY S, LACROSSE Z, LEPRINCE P, et al. Effects of eccentrically and concentrically biased training on mouse muscle phenotype. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(8):1460-1468.
[41] DU C, ZHANG T, XIAO X, et al. Protease-activated receptor-2 promotes kidney tubular epithelial inflammation by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. Biochem J. 2017;474(16):2733-2747.
[42] NEUBAUER O, SABAPATHY S, ASHTON KJ, et al. Time course-dependent changes in the transcriptome of human skeletal muscle during recovery from endurance exercise: from inflammation to adaptive remodeling. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014;116(3):274-287.
[43] TEE JC, BOSCH AN, LAMBERT MI. Metabolic consequences of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 2007;37(10):827-836.
[44] BARASH I, MATHEW L, RYAN A, et al. Rapid muscle-specific gene expression changes after a single bout of eccentric contractions in the mouse. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286(2):C355-364.
[45] HENTZEN E, LAHEY M, PETERS D, et al. Stress-dependent and -independent expression of the myogenic regulatory factors and the MARP genes after eccentric contractions in rats. J Physiol. 2006;570(Pt 1):157-167.
[46] YU JG, MALM C, THORNELL LE. Eccentric contractions leading to DOMS do not cause loss of desmin nor fibre necrosis in human muscle. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002;118(1):29-34.
[47] OREJUELA D, JORQUERA R, BERGERON A, et al. Hepatic stress in hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT1) activates the AKT survival pathway in the fah-/- knockout mice model. J Hepatol. 2008;48(2):308-317.
[48] CLOSE G, ASHTON T, CABLE T, et al. Effects of dietary carbohydrate on delayed onset muscle soreness and reactive oxygen species after contraction induced muscle damage. Br J Sports Med. 2005;39(12):948-953.
[49] DIAS S, WEBER M, PADOIN S, et al. Circulating Concentration of Chemical Elements During Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and the Repeated Bout Effect. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200(3):1060-1070.
[50] OOSTHUYSE T, BOSCH AN. The Effect of Gender and Menstrual Phase on Serum Creatine Kinase Activity and Muscle Soreness Following Downhill Running. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017;6(1):16.
[51] CARTER A, DOBRIDGE J, HACKNEY AC. Influence of estrogen on markers of muscle tissue damage following eccentric exercise. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2001;27(5):133-137.
[52] WELSH MC, ALLEN DL, BYRNES WC. Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 response to downhill running in humans. Int J Sports Med. 2014;35(5):363-370.
[53] WESTERLIND K, BYRNES W, HARRIS C, et al. Alterations in oxygen consumption during and between bouts of level and downhill running. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994;26(9):1144-1152.
[54] HOPPELER H. Moderate Load Eccentric Exercise; A Distinct Novel Training Modality. Front Physiol. 2016;7:483..
[55] PETTITT R, SYMONS D, EISENMAN P, et al. Eccentric strain at long muscle length evokes the repeated bout effect. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(4):918-924.
[56] BROCKETT CL, MORGAN DL, PROSKE U. Human hamstring muscles adapt to eccentric exercise by changing optimum length. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(5):783-790.
[57] ARMSTRONG RB. Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1984;16(6):529-538.
[58] NEWHAM DJ, JONES DA, CLARKSON PM. Repeated high-force eccentric exercise: effects on muscle pain and damage. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1987;63(4):1381-1386.
[59] HOWELL JN, CHLEBOUN G, CONATSER R. Muscle stiffness, strength loss, swelling and soreness following exercise-induced injury in humans. J Physiol. 1993;464:183-196.
[60] FÉASSON L, STOCKHOLM D, FREYSSENET D, et al. Molecular adaptations of neuromuscular disease-associated proteins in response to eccentric exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2002;543(Pt 1):297-306.
[61] LEHTI TM, KALLIOKOSKI R, KOMULAINEN J. Repeated bout effect on the cytoskeletal proteins titin, desmin, and dystrophin in rat skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2007;28(1):39-47.
[62] MCHUGH MP. Recent advances in the understanding of the repeated bout effect: the protective effect against muscle damage from a single bout of eccentric exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2003;13(2):88-97.
[63] LYNN R, MORGAN D L. Decline running produces more sarcomeres in rat vastus intermedius muscle fibers than does incline running. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994;77(3):1439-1444.
[64] YU JG, CARLSSON L, THORNELL LE. Evidence for myofibril remodeling as opposed to myofibril damage in human muscles with DOMS: an ultrastructural and immunoelectron microscopic study. Histochem Cell Biol. 2004;121(3):219-227.
[65] YU JG, FÜRST DO, THORNELL LE. The mode of myofibril remodelling in human skeletal muscle affected by DOMS induced by eccentric contractions. Histochem Cell Biol. 2003;119(5):383-393.
[66] PEAKE J, NOSAKA K, SUZUKI K. Characterization of inflammatory responses to eccentric exercise in humans. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2005;11:64-85.
[67] PIZZA FX, DAVIS BH, HENRICKSON SD, et al. Adaptation to eccentric exercise: effect on CD64 and CD11b/CD18 expression. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1996;80(1):47-55.
[68] SEABORNE RA, STRAUSS J, COCKS M, et al. Human Skeletal Muscle Possesses an Epigenetic Memory of Hypertrophy. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1898.
[69] LEE H, KIM K, KIM B, et al. A cellular mechanism of muscle memory facilitates mitochondrial remodelling following resistance training. J Physiol. 2018;596(18):4413-4426.
[70] BRUUSGAARD JC, EGNER IM, LARSEN TK, et al. No change in myonuclear number during muscle unloading and reloading. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012;113(2):290-296.
[71] EGNER I, BRUUSGAARD J, EFTESTøL E, et al. A cellular memory mechanism aids overload hypertrophy in muscle long after an episodic exposure to anabolic steroids. J Physiol. 2013;591(24):6221-6230.
[72] GUNDERSEN K, BRUUSGAARD JC, EGNER IM, et al. Muscle memory: virtues of your youth?. J Physiol. 2018;596(18):4289-4290.
[73] MURASE S, TERAZAWA E, QUEME F, et al. Bradykinin and nerve growth factor play pivotal roles in muscular mechanical hyperalgesia after exercise (delayed-onset muscle soreness). J Neurosci. 2010;30(10):3752-3761.
[74] SHARPLES AP, HUGHES DC, DEANE CS, et al. Longevity and skeletal muscle mass: the role of IGF signalling, the sirtuins, dietary restriction and protein intake. Aging Cell. 2015;14(4):511-523.
[75] LASTAYO P, PIEROTTI D, PIFER J, et al. Eccentric ergometry: increases in locomotor muscle size and strength at low training intensities. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;278(5):R1282-1288.
[76] NITERT MD, DAYEH TD, VOLKOV P, et al. Impact of an exercise intervention on DNA methylation in skeletal muscle from first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(12):3322-3332.
[77] SAILANI MR, HALLING JF, MøLLER HD, et al. Lifelong physical activity is associated with promoter hypomethylation of genes involved in metabolism, myogenesis, contractile properties and oxidative stress resistance in aged human skeletal muscle. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3272.
[78] BARRÈS R, YAN J, EGAN B, et al. Acute exercise remodels promoter methylation in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2012;15(3):405-411.
[79] DERETIC V, LEVINE B. Autophagy balances inflammation in innate immunity. Autophagy. 2018;14(2):243-251.
[80] LAKER RC, DRAKE JC, WILSON RJ, et al. Ampk phosphorylation of Ulk1 is required for targeting of mitochondria to lysosomes in exercise-induced mitophagy. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):548.
[81] MOOREN F C, KRUGER K. Exercise, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;135:407-422.
[82] LIANG J, ZENG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Regulatory role of exercise-induced autophagy for sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol. 2020;130:110789.
[83] LIRA VA, OKUTSU M, ZHANG M, et al. Autophagy is required for exercise training-induced skeletal muscle adaptation and improvement of physical performance. FASEB J. 2013;27(10):4184-4193.
[84] YUAN JQ, YUAN Y, PAN SS, et al. Altered expression levels of autophagy-associated proteins during exercise preconditioning indicate the involvement of autophagy in cardioprotection against exercise-induced myocardial injury. J Physiol Sci. 2020;70(1):10.
[85] MOREIRA O, ESTÉBANEZ B, MARTÍNEZ-FLOREZ S, et al. Mitochondrial Function and Mitophagy in the Elderly: Effects of Exercise. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:2012798.
[86] JAMART C, BENOIT N, RAYMACKERS J, et al. Autophagy-related and autophagy-regulatory genes are induced in human muscle after ultraendurance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(8):3173-3177.
[87] JAMART C, FRANCAUX M, MILLET G, et al. Modulation of autophagy and ubiquitin- proteasome pathways during ultra-endurance running. 2012;112(9):1529-1537.
[88] HE C, BASSIK M, MORESI V, et al. Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):511-515.
[89] JAFARIYAN S, MONAZZAMI A, NIKOUSEFAT Z, et al. Inflammatory and immune responses to a 3-day period of downhill running in active females. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017;63(7):76-83.
[90] LIU X, CHEN P, ZHAO L, et al. Macrophages depletion impairs skeletal muscle regeneration by regulating inflammation and oxidative stress levels. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2018;70(1):23-32.
[91] HE Q, WANG L, ZHAO R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes exert ameliorative effects in type 2 diabetes by improving hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism via enhancing autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:223.
[92] RONG X, XU J, JIANG Y, et al. Citrus peel flavonoid nobiletinalleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by activating IL-6/STAT3/FOXO3a-mediated autophagy. Food Funct. 2021;12(3):1305-1317.
[93] PENG X, WANG Y, LI H, et al. ATG5-mediated autophagy suppresses NF-kappaB signaling to limit epithelial inflammatory response to kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(4):253.
[94] HUANG KY, QUE JQ, HU ZS, et al. Metformin suppresses inflammation and apoptosis of myocardiocytes by inhibiting autophagy in a model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2559-2579.
[95] MONKKONEN T, DEBNATH J. Inflammatory signaling cascades and autophagy in cancer. Autophagy. 2018;14(2):190-198.
[96] MA Z, WANG D, WENG J, et al. BNIP3 decreases the LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes by promoting the development of autophagy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):284.
[97] ZHANG Y, CHEN N. Autophagy Is a Promoter for Aerobic Exercise Performance during High Altitude Training. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3617508.
[98] WANG L, WANG J, CRETOIU D, et al. Exercise-mediated regulation of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(3):203-210.
[99] XING Y, YANG SD, WANG MM, et al. The beneficial roles of exercise training via autophagy in neurological diseases and possible mechanisms. Life Sci. 2019;221:130-134.
[100] LU Y, DONG Y, TUCKER D, et al. Treadmill Exercise Exerts Neuroprotection and Regulates Microglial Polarization and Oxidative Stress in a Streptozotocin-Induced Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(4):1469-1484.
[101] TANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHENG M, et al. Effects of treadmill exercise on cerebral angiogenesis and MT1-MMP expression after cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Behav. 2018;8(8):e01079.
[102] PIGNA E, BERARDI E, AULINO P, et al. Aerobic Exercisand Pharmacological Treatments Counteract Cachexia by Modulating Autophagy in Colon Cancer. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26991.
|