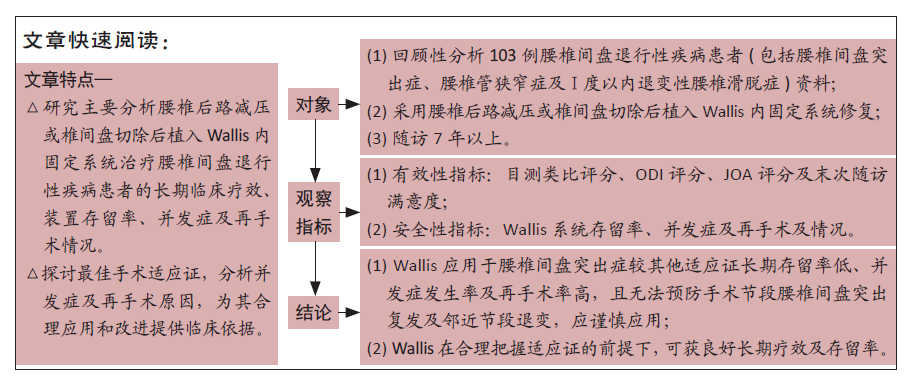
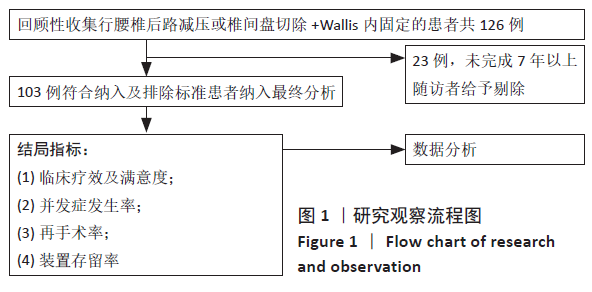
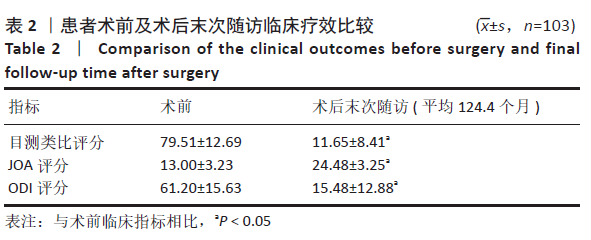
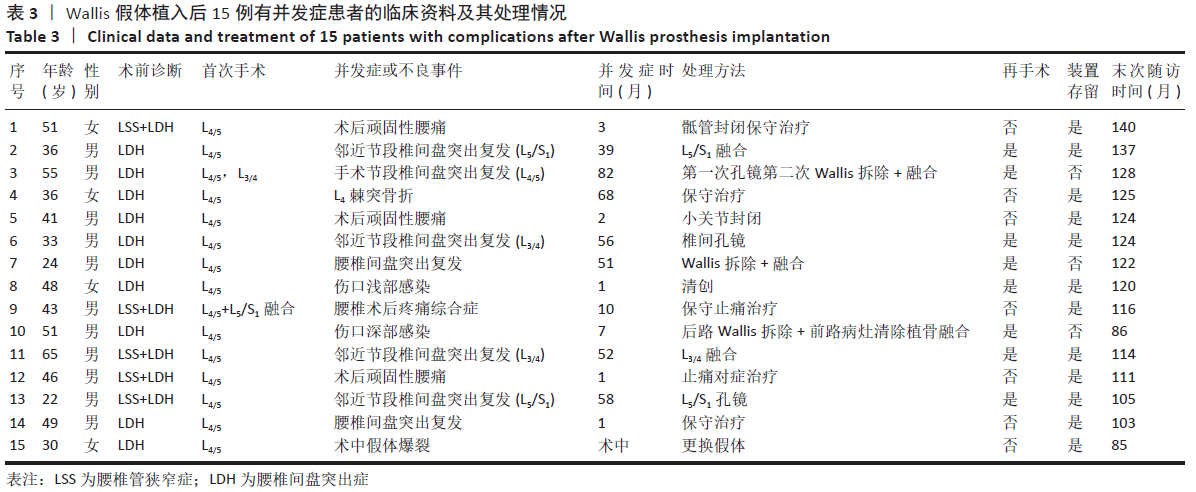
[1] MO Z, LI D, ZHANG R, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of posterior lumbar interbody fusion, Coflex, Wallis, and X-stop for lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018;172:74-81.
[2] ZINI C, BELLINI M, MASALA S, et al. Percutaneous interspinous spacer in spinal-canal-stenosis treatment: pros and cons. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019;55(7):381.
[3] 芦俊峰,王宝东,曹杨.腰椎棘突间撑开系统的分类特点及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1774-1780.
[4] BLOCK J, LAVELLE W, NUNLEY P. Toward a cure for lumbar spinal stenosis: The potential of interspinous process decompression. Med Hypotheses. 2019;132:109357.
[5] KOROVESSIS P, REPANTIS T, ZACHARATOS S, et al. Does Wallis implant reduce adjacent segment degeneration above lumbosacral instrumented fusion? Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):830-840.
[6] 赵赫,俞兴,唐向盛,等. Wallis与Coflex两种棘突间动态稳定系统修复腰椎退行性疾病的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(11):1798-1804.
[7] SENEGAS J, VITAL JM, POINTILLART V, et al. Long-term actuarial survivorship analysis of an interspinous stabilization system. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8):1279-1287.
[8] NICHOLSON JA, SCOTT C, DUCKWORTH AD, et al. Survival analysis of the Wallis interspinous spacer used as an augment to lumbar decompression. Br J Neurosurg. 2017;31(6):688-694.
[9] SVENSSON I, SJOSTROM B, HALJAMAE H. Assessment of pain experiences after elective surgery. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2000; 20(3):193-201.
[10] FUKUI M, CHIBA K, KAWAKAMI M, et al. Japanese Orthopaedic Association Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire. Part 2. Verification of its reliability: the Subcommittee on Low Back Pain and Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation of the Clinical Outcome Committee of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association. J Orthop Sci. 2007;12(6):526-532.
[11] FAIRBANK JC, PYNSENT PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(22):2940-2952 .
[12] SLOSAR PJ, REYNOLDS JB, SCHOFFERMAN J, et al. Patient satisfaction after circumferential lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(6): 722-726.
[13] KIM H, WU P, RAORANE H, et al. Generation change of practice in spinal surgery: can endoscopic spine surgery expand its indications to fill in the role of conventional open spine surgery in most of degenerative spinal diseases and disc herniations: a study of 616 spinal cases 3 years. Neurol India. 2020;68(5):1157-1165.
[14] WANG M, ALGHAMDI M. Editorial. Interspinous spacers for lumbar stenosis: time for obsolescence? J Neurosurg. Spine. 2021. doi:10.3171/ 2020.8.SPINE201205.
[15] 昌耘冰,王义生,柯雨洪,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统的初步临床应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(4):487-489.
[16] 顾宏林,詹世强,昌耘冰,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎退行性疾病的中期疗效及并发症分析[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2014,6(4):203-209.
[17] SENEGAS J, VITAL JM, POINTILLART V, et al. Clinical evaluation of a lumbar interspinous dynamic stabilization device (the Wallis system) with a 13-year mean follow-up. Neurosurg Rev. 2009;32(3): 335-342.
[18] 李宗阳,简磊,来佳辉,等.Dynesys与Wallis系统治疗单节段腰椎间盘突出症的长期疗效及安全性[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2020,34(3):268-273.
[19] 王东杰,杨彬,李宗阳,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎间盘突出症的长期疗效[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(13): 1170-1176.
[20] 孙浩林,李淳德,刘宪义,等.棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎退变性疾病的并发症分析[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(1):35-39.
[21] EPSTEIN NE. A review of interspinous fusion devices: high complication, reoperation rates, and costs with poor outcomes. Surg Neurol Int. 2012;3:7.
[22] PINTAURO M, DUFFY A, VAHEDI P, et al. Interspinous implants: are the new implants better than the last generation? A review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(2):189-198.
[23] TRAM J, SRINIVAS S, WALI A, et al. Decompression surgery versus interspinous devices for lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review of the literature. Asian Spine J. 2020;14(4):526-542.
[24] FORSTH P, OLAFSSON G, CARLSSON T, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of fusion surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374(15):1413-1423.
[25] GHOGAWALA Z, DZIURA J, BUTLER WE, et al. Laminectomy plus fusion versus laminectomy alone for lumbar spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(15):1424-1434.
[26] GOEL S, MODI H. Reoperations following lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(6):578-583.
[27] RAVINDRA VM, GHOGAWALA Z. Is There still a role for interspinous spacers in the management of neurogenic claudication? Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2017;28(3):321-330.
[28] TAMBURRELLI FC, PROIETTI L, LOGROSCINO CA. Critical analysis of lumbar interspinous devices failures: a retrospective study. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(Suppl 1):S27-S35.
[29] 朱震奇,刘海鹰,刘辰君,等.棘突间弹性固定翻修术的原因分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(7):582-588.
[30] SENEGAS J. Mechanical supplementation by non-rigid fixation in degenerative intervertebral lumbar segments: the Wallis system. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(Suppl 2):S164-S169.
[31] SANDU N, SCHALLER B, ARASHO B, et al. Wallis interspinous implantation to treat degenerative spinal disease: description of the method and case series. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011;11(6):799-807.
[32] FLOMAN Y, MILLGRAM MA, SMORGICK Y, et al. Failure of the Wallis interspinous implant to lower the incidence of recurrent lumbar disc herniations in patients undergoing primary disc excision. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(5):337-341.
[33] 金新蒙,刘杰,吕枫,等. Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗单纯腰椎间盘突出症的中长期疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(21): 1943-1948.
[34] ZHOU Z, JIN X, WANG C, et al. Wallis interspinous device versus discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a comparative study. Orthopade. 2019;48(2):165-169.
[35] ZHOU Z, XIONG W, LI L, et al. Adjacent segmental degeneration following Wallis interspinous stabilization implantation: biomechanical explanations and the value of magnetic resonance imaging. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(22):e7056.
[36] OSTER B, KIKANLOO S, LEVINE N, et al. Systematic review of outcomes following 10-year mark of spine patient outcomes research trial for intervertebral disc herniation. Spine. 2020;45(12):825-831.
[37] ATLAS SJ, KELLER RB, WU YA, et al. Long-term outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical management of sciatica secondary to a lumbar disc herniation: 10 year results from the maine lumbar spine study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(8):927-935.
[38] GU H, CHANG Y, ZENG S, et al. Wallis interspinous spacer for treatment of primary lumbar disc herniation: three-year results of a randomized controlled trial. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:e1331-e1336.
[39] SOBOTTKE R, SCHLUTER-BRUST K, KAULHAUSEN T, et al. Interspinous implants (X Stop, Wallis, Diam) for the treatment of LSS: is there a correlation between radiological parameters and clinical outcome? Eur Spine J. 2009;18(10):1494-1503.
[40] ASGARZADIE F, KHOO LT. Minimally invasive operative management for lumbar spinal stenosis: overview of early and long-term outcomes. Orthop Clin North Am. 2007;38(3):387-399.
[41] 孙英飞,张启栋,石东平,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎管狭窄患者的疗效[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2019,23(1):45-49.
[42] MARSH GD, MAHIR S, LEYTE A. A prospective randomised controlled trial to assess the efficacy of dynamic stabilisation of the lumbar spine with the Wallis ligament. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(10):2156-2160. |