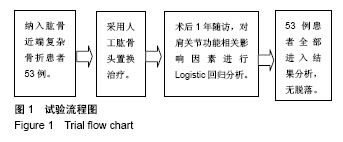
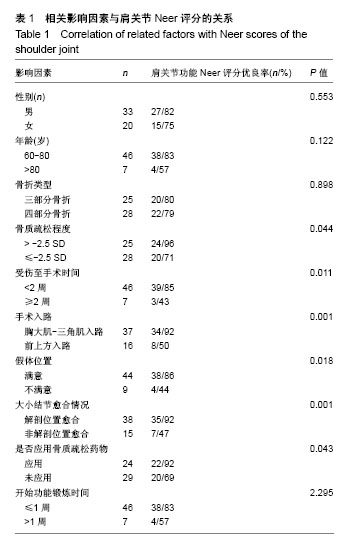
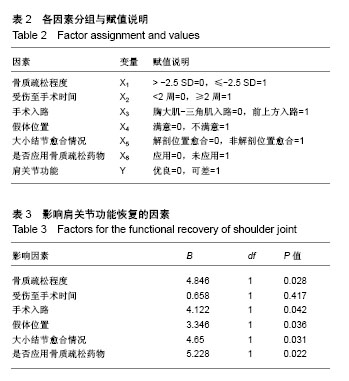
| [1] Bahrs C,Bauer M, Blumenstock G, et al.The complexity of proximal humeral fractures is age and gender specific.J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(3):465-470.[2] Neer CS 2 nd. Displaced proximal humeral fractures.Part I.Clwfifi. cation and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1970; 52:1077-1089.[3] 孟迅吾.临床诊疗指南( 骨质疏松症和骨矿盐疾病分册) [M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2007: 355-385.[4] Launonen AP,Lepola V,Flinkkilä T,et al. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Acta Orthopaedica. 2015; 86(3):280-285.[5] Richard J,David C,Brian T,et al. Proximal humerus fragility fractures: recent trends in nonoperative and operative treatment in the Medicare population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(2):256-261.[6] 季峰,谢跃,王守国,等.人工肱骨头置换治疗肱骨近端四部分骨折的疗效分析[J].山东医药,2012,52(45):87-89.[7] Yeong KP,Sae HK,Joo HO. Intermediate-term outcome of hemiarthroplasty for comminuted proximal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(1):85-91.[8] 黄宇,莫冰峰,尹东,等. 人工肱骨头置换治疗肱骨近端复杂骨折并骨质疏松老年患者的临床疗效[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014, 22(4):308-313.[9] Merwe M,Boyle MJ,Frampton CMA,et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty compared with hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of acute proximal humeral fractures.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(9):1539-1545.[10] 曾周景,叶建华,谭通, 等.肱骨近端骨折锁定钢板内固定术后影响肩关节功能的相关因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016, 24(16):1462-1465.[11] Gu J, Cai WH, Ni YJ, et al. Comparing the clinical outcomes of shoulder hemiarthroplasty versus locking plate fixation for the treatment of complex proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. Res J Biotechnol. 2016;11(12):86-92.[12] Nicole M,Mike MD,April D. Functional outcomes after shoulder resection: the patient's perspective. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(9):247-254. [13] Hoel S,Jensen TG,Falster O,et al. Hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fracture and consequences of a comminuted greater tubercle fragment. Musculoskel Surg. 2016;100(1):9-14. [14] Somerson JS,Sander P,Bohsali K,et al. What factors are associated with clinically important improvement after shoulder hemiarthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(12):2682-2682.[15] Valenti P,Aliani D,Maroun C,et al. Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: analysis of clinical and radiographic outcomes at midterm follow-up: a series of 51 patients.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(3):309-315.[16] Hashiguchi H,Iwashita S,Ohkubo A,et al. The outcome of hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures is dependent on the status of the rotator cuff. Int Orthop. 2015;39(6): 1115-1119.[17] Singh A,Padilla M,Nyberg EM,et al. Cement technique correlates with tuberosity healing in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26(3):437-442.[18] 蔡丰,刘晓东,刘亮,等. 半肩关节置换术治疗复杂性肱骨近端骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(6):499-501.[19] Mehlhorn AT, Schmal H,Sudkamp NP. Clinical evaluation of a new custom offset shoulder prosthesis for treatment of complex fractures of the proximal humerus. Acta Orthop Belg. 2006;72(4):3873-3894.[20] Thomas, W,Thomas E,Jessica B,et al. Shoulder arthroplasty and its effect on strain in the subscapularis muscle. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(4):373-376.[21] Mole D, Wein F, Dezaly C,et al. Surgical technique:the anterosuperior approach for reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 2011;469(9):2461-2468.[22] 包洪卫,王青. 肱骨近端骨折人工肱骨头置换的临床解剖研究[J]. 中华医学杂志,2010,90(45): 3217-3219. |
.jpg)
.jpg)