中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (31): 5031-5035.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.31.019
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
缺血性腰椎间盘退变模型兔的磁共振T1ρ和T2mapping成像评价
蒙仲猛1,潘希敏2,陈应明2,陈立强1,吴志强1,庄文权1,3
- 1中山大学附属第一医院放射介入科,广东省广州市 510080;2中山大学附属第一医院东院放射科,广东省广州市 510080;3中山大学附属第一医院广东省骨科学重点实验室,广东省广州市 510080
Magnetic resonance T1ρ versus T2 mapping for evaluating ischemic lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in a rabbit model
Meng Zhong-meng1, Pan Xi-min2, Chen Ying-ming2, Chen Li-qiang1, Wu Zhi-qiang1, Zhuang Wen-quan1, 3
- 1Department of Interventional Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Radiology, The Eastern Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
磁共振T2mapping成像技术:是利用固定重复时间(repetition time,TR),根据组织本身的弛豫时间设定不同的回波时间(echo time,TE),得到一系列不同参数的图像,通过后处理软件进行指数拟合重建得到T2-map图像。
磁共振T1ρ成像技术:是在旋转坐标系下,通过设定不同的自选锁定时间(time of spin lock,SPL)得到一些列MRT1ρ图像,通过后处理软件指数拟合重建得到T1ρ-map图像。
摘要
背景:磁共振T1ρ和T2mapping成像技术已用于研究人类和恒河猴腰椎间盘退变并认为可以早期评价腰椎间盘退变情况,目前尚无应用磁共振T1ρ和T2mapping成像技术研究新西兰兔腰椎间盘退变的报道。
目的:比较不同时间点新西兰兔缺血性腰椎间盘退变模型的磁共振T1ρ和T2-map弛豫时间值,评价两种成像技术对退变评估的敏感性差异。
方法:15只新西兰兔随机平均分成3组,每只兔随机干预L4-5、L5-6或L6-7椎间盘中的一个作为缺血性退变模型组,另外2个不干预椎间盘作为空白对照组。所有动物于术前行磁共振T1ρ和T2mapping扫描,3组兔分别于术后1,3或6个月再行相应磁共振扫描,分析两种成像技术在不同时间点弛豫时间值变化。
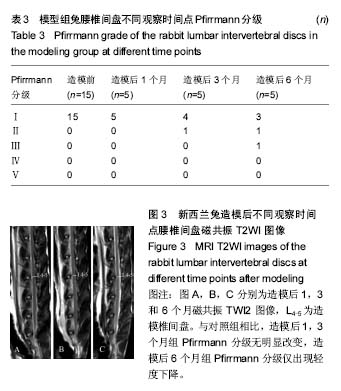
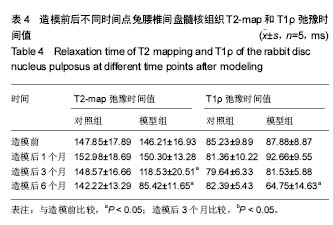
结果与结论:①模型组腰椎间盘髓核组织术前T2-map弛豫时间值(146.21±16.93) ms与造模后3个月(118.53±20.51) ms或6个月(85.42±11.65) ms比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而与造模后1个月比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②模型组椎间盘髓核组织术前T1ρ弛豫时间值(87.88±8.87) ms与造模后6个月(64.75±14.63) ms比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而与造模后1个月或3个月比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③对照组椎间盘髓核组织T1ρ和T2-map弛豫时间值各时间点差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。造模后6个月兔腰椎间盘磁共振T2WI才出现Pfirrmann Ⅱ-Ⅲ级的改变;④结果说明:磁共振T1ρ和T2mapping成像技术可用于量化评价新西兰兔缺血性腰椎间盘退变过程,T2mapping成像可能比T1ρ成像对新西兰兔缺血性退变的早期评估更敏感些。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8487-4132(蒙仲猛)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)