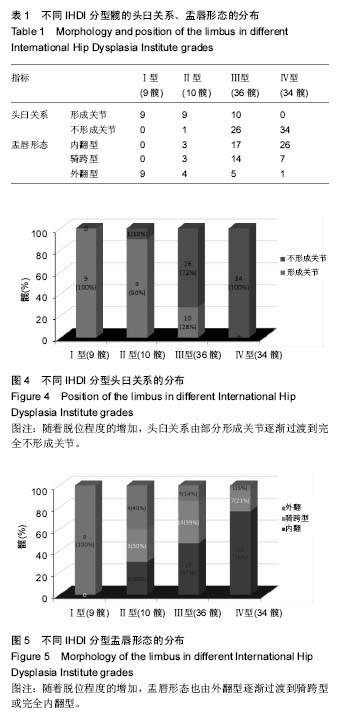
| [1] Tönnis D.Congenital dysplasia and dislocation of the hip in children and adults. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag.1987.[2] Narayanan U,Mulpuri K,Sankar WN,et al.Reliability of a new radiographic classification for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop.2015; 35(5):478-484.[3] Akgül T,Bora Göksan S, Bilgili F, et al.Radiological results of modified Dega osteotomy in Tönnis grade 3 and 4 developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2014;23(4):333-338.[4] Graf R.The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic combound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1980;97(2):117-133.[5] Sankar WN,Neubuerger CO,Moseley CF.Femoral head sphericity in untreated developmental dislocation of the hip.J Pediatr Orthop.2010;30(6):558-561.[6] Bos CF,Bloem JL.Treatment of dislocation of the hip, detected in early childhood, based on magnetic resonance imaging.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71(10):1523-1529.[7] Ponseti IV. Growth and development of the acetabulum in the normal child. Anatomical, histological, and roentgenographic studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(5):575-585.[8] Walker JM. Histological study of the fetal development of the human acetabulum and labrum: significance in congenital hip disease.Yale J Biol Med. 1981;54(4):255-263.[9] Hachiya Y, Kubo T, Horii M, et al. Characteristic features of the acetabular labrum in healthy children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2001;10(3):169-172.[10] Eberhardt O, Wirth T, Fernandez FF. Arthroscopic anatomy of the dislocated hip in infants and obstacles preventing reduction. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(6):1052-1059.[11] Scaglietti O, Calandriello B. Open reduction of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1962;44B(1): 257-283.[12] Landa J, Benke M, Feldman DS. The Limbus and the Neolimbus in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(4):776-781.[13] Cotillo JA, Molano C, Albiñana J. Correlative study between arthrograms and surgical findings in congenital dislocation of the hip.J Pediatr Orthop B. 1998;7(1):62-65.[14] Severin E. Congenital dislocation of the hip.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1950;32(3):507-518.[15] Somerville EW, Scott JC. The direct approach to congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1957;39B(4): 2504-2510.[16] Hara S, Akazawa H, Mitani S, et al.Role of the limbus in femoral-head deformation in developmental dislocation of the hip: findings of two-directional hip arthrography. Acta Med Okayama. 2002;56(2):91-97.[17] Kim YH. Acetabular dysplasia and osteoarthritis developed by an eversion of the acetabular labrum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(215):289-295.[18] Harris WH, Bourne RB, Oh I. Intra-articular acetabular labrum: a possible etiological factor in certain cases of osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg. 1979; 61(4):510-514.[19] Angliss R, Fujii G, Pickvance E, et al.Surgical treatment of late developmental displacement of the hip. Results after 33 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(3):384-394.[20] Salter RB, Dubos JP.The first fifteen year's personal experience with innominate osteotomy in the treatment of congenital dislocation and subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974;(98):72-103.[21] Hara JN. Congenital dislocation of the hip: acetabular deficiency in adolescence (absence of the lateral acetabular epiphysis) after limbectomy in infancy. J Pediat Orthop. 1989;9(6):640-648.[22] 罗殿中,张洪,张伟佳,等. 髋臼发育不良患者髋臼盂唇内翻的影像学特征及临床意义[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2013;19(7):598-601.[23] 吕学敏,冯超,董轶非, 等. 发育性髋关节发育不良闭合复位后髋臼盂唇软骨复合体对髋臼发育的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2016, 96(37):2983-2987.[24] Fukui K, Kaneuji A, Fukushima M, et al.Inversion of the acetabular labrum triggers rapidly destructive osteoarthritis of the hip: representative case report and proposed etiology. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2468-2472.[25] Byrd JW, Jones KS. Osteoarthritis caused by an inverted acetabular labrum: radiographic diagnosis and arthroscopic treatment.Arthroscopy. 2002;18(7):741-747.[26] Ramsey PL, Lasser S, Macewen GD. Congenital dislocation of the hip: use of the Pavlik harness in the child during the first six months of life. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1976;58(7): 1000-1004.[27] Li LY, Zhang LJ, Li QW, et al. Development of the osseous and the cartilaginous acetabular index in normal children and those with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94B:1625-1631.[28] Douira-Khomsi W, Smida M, Louati H, et al. Magnetic resonance evaluation of acetabular residual dysplasia in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a preliminary study of 27 patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(1):37-43.[29] Zamzam M, Khoshhal K, Bakarman KK. Acetabular cartilaginous angle: a new method for predicting acetabular development in developmental dysplasia of the hip in children between 2 and 18 months of age.J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28(5):518-523.[30] Albinana J, Dolan LA, Spratt KF, et al. Acetabular dysplasia after treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Implications for secondary procedures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86B(6):876-886. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)