| [1]Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, et al. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981;10(6):387-416.[2]Heydecke G, Kohal R, Glaser R. Optimal esthetics in single-tooth replacement with the Re-Implant system: a case report. Int J Prosthodont. 1999;12(2):184-189.[3]Weingart D, Steinemann S, Schilli W, et al. Titanium deposition in regional lymph nodes after insertion of titanium screw implants in maxillofacial region. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994;23(6 Pt 2):450-452.[4]程宁,施斌.氧化锆种植体的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究, 2011, 27(12):1115-1117.[5]Stadlinger B, Hennig M, Eckelt U, et al. Comparison of zirconia and titanium implants after a short healing period. A pilot study in minipigs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39(6): 585-592.[6]Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1--review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont. 2004;17(5):536-543.[7]Mueller C K, Solcher P, Peisker A, et al. Analysis of the influence of the macro- and microstructure of dental zirconium implants on osseointegration: a minipig study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116(1):e1-e8.[8]Gahlert M, Gudehus T, Eichhorn S, et al. Biomechanical and histomorphometric comparison between zirconia implants with varying surface textures and a titanium implant in the maxilla of miniature pigs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(5): 662-668.[9]Chintapalli RK, Marro FG, Jimenez-Pique E, et al. Phase transformation and subsurface damage in 3Y-TZP after sandblasting. Dent Mater. 2013;29(5):566-572.[10]Brull F, Van Winkelhoff AJ, Cune MS. Zirconia dental implants: a clinical, radiographic, and microbiologic evaluation up to 3 years. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(4):914-920.[11]戴文雍,印厚才,陈晨,等.热酸溶液蚀刻对氧化锆粘接强度的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013,31(6):569-573.[12]Flamant Q, Marro FG, Rovira JJR, et al. Hydrofluoric acid etching of dental zirconia. Part 1: etching mechanism and surface characterization. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2016;36(1): 121-134. [13]Gahlert M, Roehling S, Sprecher CM, et al. In vivo performance of zirconia and titanium implants: a histomorphometric study in mini pig maxillae. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(3):281-286.[14]Zhao G, Raines AL, Wieland M, et al. Requirement for both micron- and submicron scale structure for synergistic responses of osteoblasts to substrate surface energy and topography. Biomaterials. 2007;28(18):2821-2829.[15]Hirano T, Sasaki H, Honma S, et al. Proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on zirconia and titanium with different surface topography. Dent Mater J. 2015;34(6):872-880.[16]Bergemann C, Duske K, Nebe J B, et al. Microstructured zirconia surfaces modulate osteogenic marker genes in human primary osteoblasts. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015; 26(1): 5350.[17]Schliephake H, Hefti T, Schlottig F, et al. Mechanical anchorage and peri-implant bone formation of surface-modified zirconia in minipigs. J Clin Periodontol. 2010;37(9):818-828.[18]Aboushelib MN, Salem NA, Taleb AL, et al. Influence of surface nano-roughness on osseointegration of zirconia implants in rabbit femur heads using selective infiltration etching technique. J Oral Implantol. 2013;39(5):583-590.[19]Hao L, Lawrence J, Chian K S. Osteoblast cell adhesion on a laser modified zirconia based bioceramic. J Mater Science Mater Med. 2005;16(8):719-726.[20]Hauser-Gerspach I, Stubinger S, Meyer J. Bactericidal effects of different laser systems on bacteria adhered to dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study comparing zirconia with titanium. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(3):277-283.[21]Kae Kakura KY, Taniguchi Y, Yamamoto Y, et al. Zirconia Implant with Rough Surface Produced by YAG Laser Treatment Evaluation of Histomorphology and Strength of Osseointegration. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2013;23(1):77-82.[22]Kimie Yasuno KK, Taniguchi Y, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Zirconia Implants with Laser Surface Treatment Peri-Implant Bone Response and Enhancement of Osseointegration. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2014;23(1):93-100.[23]Taniguchi Y, Kakura K, Yamamoto K, et al. Accelerated osteogenic differentiation and bone formation on zirconia with surface grooves created with fiber laser irradiation. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015.[24]Calvo-Guirado JL, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Gomez-Moreno G, et al. Histological, radiological and histomorphometric evaluation of immediate vs. non-immediate loading of a zirconia implant with surface treatment in a dog model. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(7):826-830.[25]Noro A, Kaneko M, Murata I, et al. Influence of surface topography and surface physicochemistry on wettability of zirconia (tetragonal zirconia polycrystal). J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(2):355-363.[26]Vogler EA. Structure and reactivity of water at biomaterial surfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1998;74:69-117.[27]Yang Y, Zhou J, Liu X, et al. Ultraviolet light-treated zirconia with different roughness affects function of human gingival fibroblasts in vitro: the potential surface modification developed from implant to abutment. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(1):116-124.[28]Tuna T, Wein M, Altmann B, et al. Effect of ultraviolet photofunctionalisation on the cell attractiveness of zirconia implant materials. Eur Cells Mater. 2015;29:82-96.[29]Hench LL. The story of Bioglass. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(11):967-978.[30]Kirsten A, Hausmann A, Weber M, et al. Bioactive and thermally compatible glass coating on zirconia dental implants. J Dent Res. 2015;94(2):297-303.[31]Kim HW, Georgiou G, Knowles JC, et al. Calcium phosphates and glass composite coatings on zirconia for enhanced biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2004;25(18):4203-4213.[32]Oliva J, Oliva X, Oliva JD. Five-year success rate of 831 consecutively placed Zirconia dental implants in humans: a comparison of three different rough surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(2):336-344.[33]Jank S, Hochgatterer G. Success rate of two-piece zirconia implants: a retrospective statistical analysis. Implant Dent. 2016;25(2):193-198. |
.jpg)
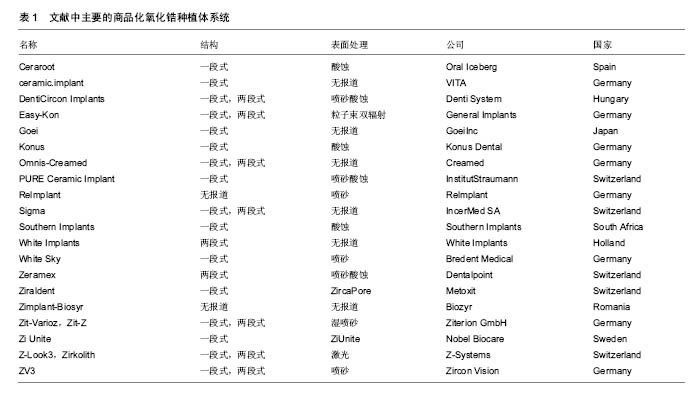
.jpg)