中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5455-5458.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.008
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
不同表面处理方式和不同粘结剂对氧化锆全瓷冠粘结强度的影响
秦敬杰1,郑翔宇1,李 睿2
- 1天津市黄河医院,天津市 300110;2天津医科大学口腔医院,天津市 300070
Effects of different surface treatments and binders on the bonding strength of zirconia crowns
Qin Jing-jie1, Zheng Xiang-yu1, Li Rui2
- 1Huanghe Hospital of Tianjin, Tianjin 300110, China; 2Stomatological Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
氧化锆全瓷的粘结:氧化锆全瓷修复体作为目前口腔临床工作中愈发常用的修复材料,其修复成功率很大程度上取决于其与牙体组织之间的粘结。由于氧化锆陶瓷表面惰性较强,常用的氢氟酸酸蚀等表面处理方法无法有效增加其与树脂水门汀的粘结强度。因此如何对氧化锆陶瓷进行表面处理成为目前较为热点的研究方向和临床工作中的关注方向。文章探讨了多种氧化锆表面处理方式以及多种粘结剂使用后对其粘结强度的影响。
树脂水门汀:目前临床工作中,口腔全瓷修复体可以选择的粘结剂种类较多,有传统的玻璃离子水门汀、聚羧酸锌水门汀等。有文献报道使用树脂水门汀对氧化锆全瓷进行粘结能够取得较好的粘结效果,实验通过检测多种类型水门汀对氧化锆全瓷的剪切粘结强度,得出了显著性差异,证实了使用树脂水门汀在氧化锆全瓷粘结时,可以获得较好的粘结强度。
背景:氧化锆全瓷修复体被广泛应用于多种复杂牙体或牙列缺损的修复。由于氧化锆的表面化学惰性原因,其粘结成为临床治疗过程中及其关键的步骤。目前临床可选择的粘结材料和修复体的表面处理方法较多。
目的:探讨不同表面处理方式和不同粘结剂对氧化锆的粘结效果。
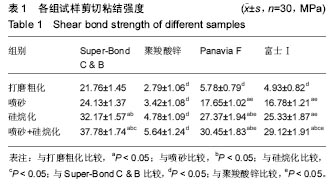
方法:将氧化锆制成不同直径的瓷片,随机分为16组,每组瓷片30个。选用Super-Bond C & B、聚羧酸锌粘结剂、Panavia F树脂水门汀和富士Ⅰ玻璃离子粘结剂4种粘结剂,分别采用打磨粗化、喷砂、硅烷化和先喷砂后硅烷化处理等4种方式对氧化锆表面进行处理。大小瓷片通过粘结剂进行粘结,静置于37 ℃蒸馏水中24 h,采用力学万能试验机检测剪切粘结强度。
结果与结论:①使用同种粘结剂进行粘结,采用打磨粗化、喷砂、硅烷化、先喷砂后硅烷化4种表面处理方式,对氧化锆粘结强度的影响有所不同,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。对氧化锆表面进行先喷砂后硅烷化处理的粘结强度最强;②用不同粘结剂进行粘结,采用同种表面处理方式,对氧化锆粘结强度的影响有所不同,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。Super-Bond C & B的粘结效果最好,其次为Panavia F树脂水门汀和富士Ⅰ玻璃离子粘结剂,聚羧酸锌粘结剂粘结效果最差;③结果表明,不同表面处理方法能够一定程度上增强粘结强度,使用Super-Bond C & B并进行先喷砂后硅烷化处理的粘结强度最高。
中图分类号:
.jpg)