| [1]Langer R, Vacanti J. Advances in tissue engineering. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(1):8-12.[2]Bossù M, Pacifici A, Carbone D, et al. Today prospects for tissue engineering therapeutic approach in dentistry. Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:151252.[3]Shokeir AA, Harraz AM, El-Din AB. Tissue engineering and stem cells: basic principles and applications in urology. Int J Urol. 2010;17(12):964-973.[4]Guo H, Sa Y, Huang J, et al. Urethral Reconstruction with Small Intestinal Submucosa Seeded with Oral Keratinocytes and TIMP-1 siRNA Transfected Fibroblasts in a Rabbit Model. Urol Int. 2016;96(2): 223-230.[5]Bulte JW, Kraitchman DL. Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004;17(7):484-499.[6]Tassa C, Shaw SY, Weissleder R. Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: a versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging, molecular diagnostics, and therapy. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44(10):842-852.[7]Azzabi F, Rottmar M, Jovaisaite V, et al. Viability, differentiation capacity, and detectability of super-paramagnetic iron oxide-labeled muscle precursor cells for magnetic-resonance imaging.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(2):182-191.[8]Ankamwar B, Lai TC, Huang JH, et al. Biocompatibility of Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles evaluated by in vitro cytotoxicity assays using normal, glia and breast cancer cells. Nanotechnology. 2010; 21(7):75102.[9]Boyer C, Whittaker MR, Bulmus V, et al. The design and utility of polymer-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications. NPG Asia Materials. 2010;2:23-30.[10]Singh N, Jenkins GJ, Asadi R, et al. Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION).Nano Rev. 2010;1. doi: 10.3402/nano.v1i0.5358. [11]Wilkinson K, Ekstrand-Hammarström B, Ahlinder L, et al. Visualization of custom-tailored iron oxide nanoparticles chemistry, uptake, and toxicity. Nanoscale. 2012;4(23):7383-7393.[12]Arami H, Khandhar A, Liggitt D, et al. In vivo delivery, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(23): 8576-8607.[13]Fu Q, Deng CL, Zhao RY, et al. The effect of mechanical extension stimulation combined with epithelial cell sorting on outcomes of implanted tissue-engineered muscular urethras. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):105-112.[14]Boennelycke M, Gras S, Lose G. Tissue engineering as a potential alternative or adjunct to surgical reconstruction in treating pelvic organ prolapse. Int Urogynecol J. 2013;24(5):741-747.[15]Amiel GE, Yoo JJ, Kim BS, et al. Tissue engineered stents created from chondrocytes. J Urol. 2001;165(6 Pt 1):2091-2095.[16]Shen Y, Shao Y, He H, et al. Gadolinium(3+)-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a potential magnetic resonance tracer for monitoring the migration of stem cells in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:119-127.[17]Brekke C, Morgan SC, Lowe AS, et al. The in vitro effects of a bimodal contrast agent on cellular functions and relaxometry. NMR Biomed. 2007;20(2): 77-89.[18]Rojas JM, Sanz-Ortega L, Mulens-Arias V, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle uptake alters M2 macrophage phenotype, iron metabolism, migration and invasion. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(4): 1127-1138.[19]Paik SY, Kim JS, Shin SJ, et al. Characterization, Quantification, and Determination of the Toxicity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles to the Bone Marrow Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):22243-22257.[20]Guzman R, Uchida N, Bliss TM, et al. Long-term monitoring of transplanted human neural stem cells in developmental and pathological contexts with MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(24):10211-10216.[21]Bulte JW, Douglas T, Witwer B, et al. Magnetodendrimers allow endosomal magnetic labeling and in vivo tracking of stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19(12):1141-1147.[22]Neri M, Maderna C, Cavazzin C, et al. Efficient in vitro labeling of human neural precursor cells with superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: relevance for in vivo cell tracking. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):505-516.[23]Shapiro EM, Sharer K, Skrtic S, et al. In vivo detection of single cells by MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2006;55(2): 242-249.[24]Farrell E, Wielopolski P, Pavljasevic P, et al. Effects of iron oxide incorporation for long term cell tracking on MSC differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;369(4):1076-1081.[25]Jing XH, Yang L, Duan XJ, et al. In vivo MR imaging tracking of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle labeled, engineered, autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells following intra-articular injection.Joint Bone Spine. 2008; 75(4):432-438. [26]Qi CM, Ma GS, Liu NF, et al. MR imaging of injected magnetically labeled stem cells in myocardial infarction: experiment with pigs. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007; 87(22):1523-1526.[27]Zhang RP, Wang LJ, He S, et al. Effects of Magnetically Guided, SPIO-Labeled, and Neurotrophin-3 Gene-Modified Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2018474.[28]Feng Y, Jin X, Dai G, et al. In vitro targeted magnetic delivery and tracking of superparamagnetic iron oxide particles labeled stem cells for articular cartilage defect repair. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011; 31(2):204-209.[29]Roeder E, Henrionnet C, Goebel JC, et al. Dose-response of superparamagnetic iron oxide labeling on mesenchymal stem cells chondrogenic differentiation: a multi-scale in vitro study.PLoS One. 2014; 9(5):e98451. [30]Huang ZY, Ge JB, Yang S, et al. In vivo cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxides-labeled mesenchymal stem cells in swines. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2007; 35(4): 344-349.[31]Zhang C, Wängler B, Morgenstern B, et al. Silica- and alkoxysilane-coated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: a promising tool to label cells for magnetic resonance imaging. Langmuir. 2007;23(3): 1427-1434.[32]Laurent S, Boutry S, Mahieu I, et al. Iron oxide based MR contrast agents: from chemistry to cell labeling. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(35):4712-4727.[33]Babic M, Horák D, Trchová M, et al. Poly(L-lysine)-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for stem cell labeling. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(3): 740-750.[34]Mishra SK, Khushu S, Gangenahalli G. Potential stem cell labeling ability of poly-L-lysine complexed to ultrasmall iron oxide contrast agent: An optimization and relaxometry study. Exp Cell Res. 2015;339(2): 427-436.[35]Jasmin, Torres AL, Nunes HM, et al. Optimized labeling of bone marrow mesenchymal cells with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and in vivo visualization by magnetic resonance imaging. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011;9:4. |
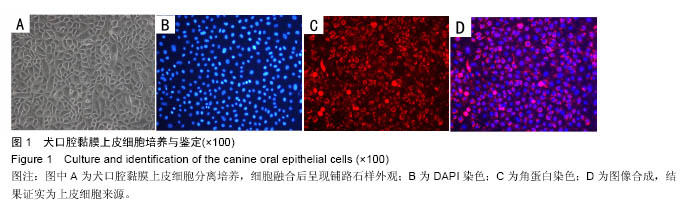
.jpg)
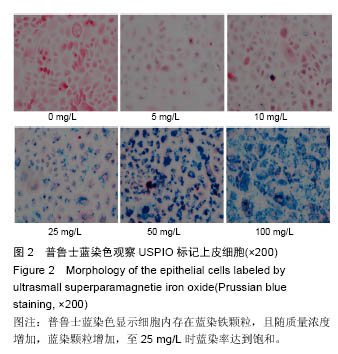
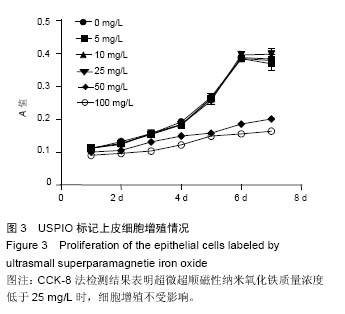
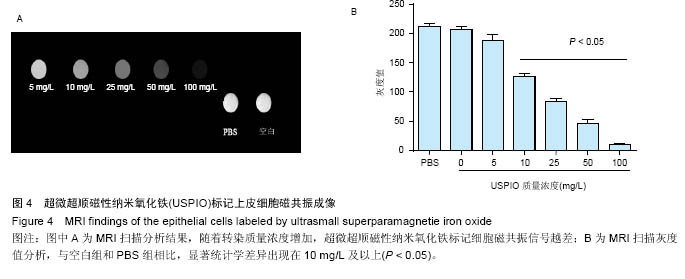
.jpg)