| [1] Tyrovola JB, Spyropoulos MN. Effects of drugs and systemic factors on orthodontic treatment. Quintessence Int. 2001; 32:365-371.[2] Brezniak N, Wasserstein A. Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption. Part I: The Basic Science Aspects. Angle Orthod. 2002;72(2):175-179.[3] 余丽霞,何姝姝,陈嵩,等.全景及根尖片对正畸相关牙根吸收诊断准确性的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2012,2(30): 169-171.[4] 沈自尹.中医肾的古今论[J].中医杂志,1997,38(1):48-50.[5] 杨收平.肾主骨生髓学说的现代理解[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2002,3(8):480-490.[6] 黄满玉,冯峰,朱太咏.从肾与骨代谢的关系探讨中医“肾主骨”现代理论内涵.[J]中国临床康复,2005,9(46): 127-129.[7] Linden A, Laan M, Anderson GP. Neutrophils, interleukin-17A and lung disease.Eur Respir J. 2005; 25(1):159-172.[8] Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, et al. IL-17 and Thl7 cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27: 485-517. [9] 苟小军,韩宝侠,王朝廷,等.肾阳虚证造模方法考察[J].吉林中医药,2009,29(9):814-815.[10] Hughes B, King GJ. Effect of orthodontic appliance reactivation during the period of peak expansion in the osteoclast population. Anat Rec. 1998;251:80-86.[11] 卢燕勤,张素银.正畸大鼠磨牙牙周膜内破骨细胞的出现与应力的关系[J].口腔医学纵横.2001,17(2):116-118.[12] 罗玲,税桦桦,徐小梅,等.大鼠正畸性牙根吸收及牙齿移动差异的研究[J].口腔医学.2008,28(12):620-622.[13] 陈英华,欧阳轶强,孙琪,等.肾阳虚动物模型规范化研究中诊断指标选择的初步探讨[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2003,9(10):26-30.[14] Brudvik P, Rygh P. The repair of orthodontic root resorption: an ultrastructural study. Eur J Orthod, 1995;17:189-198.[15] Brudvik P, Rygh P. The initial phase of orthodontic root resorption incident to local compression of the periodontal ligament. Eur J Orthod. 1993;15:249-263.[16] Lopatiene K, Dumbravaite A. Risk factors of root resorption after orthodontic treatment. Stomatologija. 2008;10(3): 89-95. [17] Lean JM, Matsuo K, Fox SW, et al. Osteoclast lineage commitment of bone marrow precursors through expression of membrane-bound trance. Bone. 2000; 27:29-40.[18] Chambers TJ. Regulation of the differentiation and function of osteoclasts. J Pathol. 2000;192:4-13.[19] Shimauchi H, Takayama S, Imai-Tanaka T, et al. Balance of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in human periapical lesions. J Endod. 1998; 24:116-119.[20] Fouad AF. Il-1 alpha and TNF-alpha expression in early periapical lesions of normal and immunodeficient mice. J Dent Res. 1997;76:1548-1554.[21] Beck BW, Harris EF. Apical root resorption in orthodontically treated subjects: analysis of edgewise and light wire mechanics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.1994;105:350-361.[22] Sameshima GT, Sinclair PM. Predicting and preventing root resorption: Part II. Treatment factors. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001;119:511-515.[23] Haruyama N, Igarashi K, Saeki S, et al. Estrous-cycle-dependent variation in orthodontic tooth movement. J Dent Res. 2002;81:406-410.[24] Wiebkin OW, Cardaci SC, Heithersay GS, et al. Therapeutic delivery of calcitonin to inhibit external inflammatory root resorption. I. Diffusion kinetics of calcitonin through the dental root. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1996;12:265-271.[25] Massler M, Perreault JG. Root resorption in the permament teeth of young adults. J Dent Child. 1954;21:158-164.[26] Reitan K. Some factors determining the evaluation of forces in orthodontics. Am J Orthod.1957;43:32-45.[27] Newman WG. Possible etiologic factors in external root resorption. Am J Orthod. 1975;67:522-539.[28] 孙理军,李翠娟,孙超越,等.肾虚质大鼠血清IL-1β、IL-4水平的实验研究[J].陕西中医学院学报,2011,34(1): 65-67.[29] 欧阳进.右归丸对自身免疫性卵巢早衰模型小鼠IL-6、IL-17、IL-21水平的影响[D].湖南中医药大学,2014.[30] Quinn JM, Saleh H. Modulation of osteoclast function in bone by the immune system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;310:40-51.[31] Li X, Yuan FL, Lu WG, et al. The role of interleukin-17 in mediating joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;397:131-135.[32] Nakanoa Y, Yamaguchi M. Interleukin-17 is involved in orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption in dental pulp cells. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148: 302-309.[33] 姚金丹,韩光红,胡敏.IL-17对破骨细胞中MMP-9表达水平的影响及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2016, 42(3): 462-466.[34] 杜江,李楠,王和鸣.肾虚模型造模方法及相关指标[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(50):9433-9436.[35] 沈自尹.中医虚证辨证参考标准[J].中国中西医结合杂志,1986,6(10):598.[36] King GJ, Keeling SD. Measuring dental drift and orthodontic tooth movement in response to various initial forces in adult rats. Am J Orthod Dent Acial Orthop. 1991;99:456-465.[37] Hellsing E, Hammarstrom L. The hyaline zone and associated root surface changes in experimental orthodontics in rats: a light and scanning electron microscope study. Eur J Orthod. 1996;18:11-18.[38] Sharpe W, Reed B, Subtelny JD, et al. Orthodontic relapse, apical root resorption, and crestal alveolar bone levels. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1987; 91:252-258.[39] 中医肾脏病学科.中医学与中药学学科发展报告[A].中华中医药学会,2006:100-148. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。
文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。.jpg) 文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。
文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。
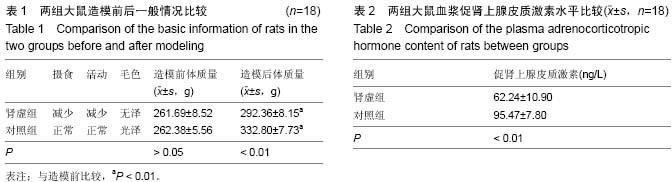
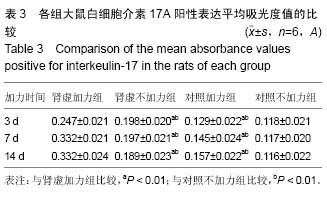
.jpg) 文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。
文题释义:
正畸致牙根吸收:在口腔正畸临床治疗过程中伴随发生的常见并发症,伴随牙移动而产生。正畸致牙根吸收多发生与根尖区域,表现为由外向内的吸收,故又被称之为根尖外牙根吸收,其发作特点为局部红、肿、热、痛,属于有炎症特点的炎性过程。
肾虚体质:现代多数学者认为中医中的“肾虚”主要与肾上腺、甲状腺、性腺三轴的紊乱及免疫力的下降有关。肾虚的主要表现为腰脊酸痛、胫酸膝软或足跟痛、耳鸣耳聋、发脱齿摇、尿有余沥或失禁、阳萎、早泄或月经不调。据中医中的虚证辩证肾虚又可分为多种,其中最常见的是肾阴虚和肾阳虚。