中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (37): 5567-5572.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.37.014
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
烧伤病房金黄色葡萄球菌分离株的分子分型及其耐药性
刘玉强1,2,王 黎2,李晓玲2,刘正祥2,袁文常2
- 1解放军第二七三医院传染结核科,新疆维吾尔自治区库尔勒市 841000;
2解放军兰州军区乌鲁木齐总医院检验科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Molecular typing and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a burn ward
Liu Yu-qiang1, 2, Wang Li2, Li Xiao-ling2, Liu Zheng-xiang2, Yuan Wen-chang2
- 1Department of Infectious Disease & Tuberculosis, the 273rd Hospital of Chinese PLA, Korla 841000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Clinical Laboratory Diagnostic Center, Urumqi General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region of Chinese PLA, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。
文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。
.jpg) 文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。
文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。摘要
背景:至20世纪80年代,耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染已经遍布全球,目前已成为院内感染的首要病原菌。
目的:了解烧伤病房金黄色葡萄球菌的分子型别及其对临床常用抗生素的耐药情况,为防控耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染提供依据。
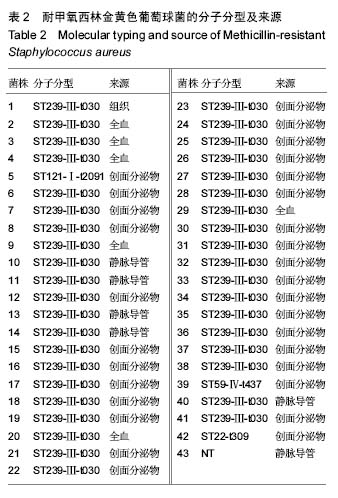
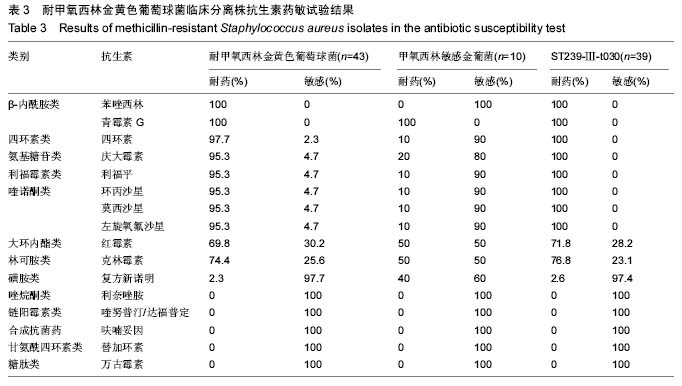
方法:收集解放军兰州军区乌鲁木齐总医院烧伤病房53株金黄色葡萄球菌,运用PCR方法以及头孢西丁实验鉴定耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌菌株,并且利用 spa分型、SCCmec分型、MLST分型方法对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌进行分子分型,同时测定所有金黄色葡萄球菌对苯唑西林等17种药物的敏感性,分析不同型别金黄色葡萄球菌特别是耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的耐药情况。
结果与结论:①53株金黄色葡萄球菌中有41株检测到meoA基因,另有2株头孢西丁实验阳性,均定义为耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌,这些耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌可分为3种SCCmec型,4种spa型,3种ST型。②优势耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌克隆为ST239-III-t030占90.7%,该克隆均对苯唑西林等10种被检抗生素高度耐药。③结果说明,该院烧伤病房耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌分离率较高,MRSA-ST239-III-t030占据绝对优势,具有高度耐药性,呈现爆发流行特征。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。
文题释义:
耐药性:根据其发生原因可分为获得耐药性和天然耐药性。自然界中的病原体,如细菌的某一株也可存在天然耐药性。当长期应用抗生素时,占多数的敏感菌株不断被杀灭,耐药菌株就大量繁殖,代替敏感菌株,而使细菌对该种药物的耐药率不断升高。目前认为后一种方式是产生耐药菌的主要原因。病原体对某种药物耐药后,对于结构近似或作用性质相同的药物也可显示耐药性,称之为交叉耐药(CrossResistance),根据程度的不同,又有完全交叉耐药和部分交叉耐药之分。随着抗生素的应用日益广泛,细菌对一些常用的药物呈现不同程度的耐药性。对于那些应用时间越长,使用范围越广泛的药物,细菌的耐药性往往越严重。
金黄色葡萄球菌:是人类的一种重要病原菌,隶属于葡萄球菌属,有“嗜肉菌”的别称,是革兰阳性菌的代表,可引起许多严重感染。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌在速冻食品中的存在量,卫生部于2011年11月24日公布食品安全国家标准《速冻面米制品》,允许金葡菌限量存在。