| [1] Komari SO,Headley PC,Klausner AP,et al.Evidence for a common mechanism for spontaneous rhythmic contraction and myogenic contraction induced by quick stretch in detrusor smooth muscle. Physiol Rep. 2013; 1(6):e00168.
[2] Ko EA,Song MY,Donthamsetty R, et al. Tension Measurement in Isolated Rat and Mouse Pulmonary Artery. Drug Discov Today Dis Models.2010;7(3-4): 123-130.
[3] Lu X, Ghassan S. Kassab GS.Assessment of endothelial function of large, medium, and small vessels: a unified myograph.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2011;300(1): H94–H100.
[4] Jespersen B, Tykocki NR, Watts SW, et al. Measurement of Smooth Muscle Function in the Isolated Tissue Bath-applications to Pharmacology Research.J Vis Exp. 2015;19(95):52324.
[5] Mulvany MJ.Procedures for investigation of small vessels using small vessel myograph. Department of Pharmacology, Aarhus University,Denmark.latest revision: August.2004.
[6] 孙亚志,朱俊铭,向求鲁,等.悬吊大鼠比目鱼肌血流量变化与肌肉力学特性的关系[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 1992, 5(2):108-121.
[7] 熊顺华,新均,赵丹,等. 张力换能器应用于机能实验教学过程中的问题探讨[J].西北医学教育,2011,19(5):1027-1029.
[8] Colhoun A, Speich J, Dolat ME, et al.MP12-15 acute length adaptation and adjust preload tension in the human detrusor: The concept of a detrucor tension sensor. J of Urol.2015;193(4):Supplement e133.
[9] 徐晓雪,徐广涛,李小鹏,等. Militarine对离体大鼠胸主动脉环的舒张作用及机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2015, 33(3):617-620.
[10] Zerpa JMP, Canelas A, SensaleB,et al. Modeling the arterial wall mechanics using a novel high-order viscoelastic fractional element. Appl Math Model. 2015;39(16):4767-4780.
[11] Ji G, Barsotti RJ, Feldman ME, et al.Stretch-induced Calcium Release in Smooth Muscle.J Gen Physiol. 2002; 119(6): 533-543.
[12] Zeidan A, Nordström I, Dreja K,et al.Stretch-Dependent Modulation of Contractility and Growth in Smooth Muscle of Rat Portal Vein.Circ Res. 2000;87(3):228-234.
[13] Gilbert G,Ducret T,Savineau JP,et al.Caveolae are involved in stretch-induced Ca2+ signaling in pulmonary hypertension.Rev Mal Respir. 2015;32(3):325–326.
[14] Weiser M, Majack RA, Tucker A,et al. Static tension is associated with increased smooth muscle cell DNA synthesis in rat pulmonary arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1995;268(3):H1133-H1138.
[15] Mantella LE, Quan A, Verma S. Variability in vascular smooth muscle cell stretch-induced responses in 2D culture.Vasc Cell.2015;21(7):7.
[16] Ghosh S, Kollar B, Nahar T, et al.Loss of the mechanotransducerzyxin promotes a synthetic phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells.J Am Heart Assoc.2015;4(6):e001712.
[17] Dangers M, Kiyan J, Grote K, et al.Mechanical stress modulates SOCS-1 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells.J Vasc Res. 2010;47(5):432-440.
[18] Sanderson MJ, Delmotte P, Bai Y, et al. Regulation of airway smooth muscle cell contractility by Ca2+ signaling and sensitivity.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008;5(1):23-31.
[19] Ford LE,Gilbert SH. The significance of variable passive compliance in smooth muscle. J ApplPhysiol, 2007;102: 1735-1736.
[20] Ratz PH,SpeichJE.Evidence that actomyosin cross bridges contribute to "passive" tension in detrusor smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.2010;298: F1424-F1435.
[21] Carre G,Ouedraogo M,Magaud C,et al.Vasorelaxation induced by dodoneine is mediated by calcium channels blockade and carbonic anhydrase inhibition on vascular smooth muscle cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;169:8-17.
[22] Fernandes VS,Xin W,Petkov GV.Novel mechanism of hydrogen sulfide-induced guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction: role of BK channels and cholinergic neurotransmission.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015;309(2):C107-116.
[23] Liu X, Yang T, Miao L, et al.Leukotriene B4 Inhibits L-Type Calcium Channels via p38 Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Cell PhysiolBiochem. 2015;37(5):1903-1913.
[24] 李光伟,苗宏志,李波,等.钙敏感受体通过G蛋白-PLC-IP3信号途径调节肺动脉张力[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015;31(1): 18-22.
[25] Wan XJ,Zhao HC,Zhang P,et al.Involvement of BK channel in differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by mechanical stretch.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;59:21-29.
[26] Dalrymple A, Mahn K,Poston L,et al.Mechanical stretch regulates TRPC expression and calcium entry in human myometrial smooth muscle cells.Mol Hum Reprod. 2007; 13(3):171-179.
[27] Dangers M, Kiyan J, Grote K,etal.Mechanical stress modulates SOCS-1 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Res.2010;47(5):432-440 |
.jpg) 文题释义:
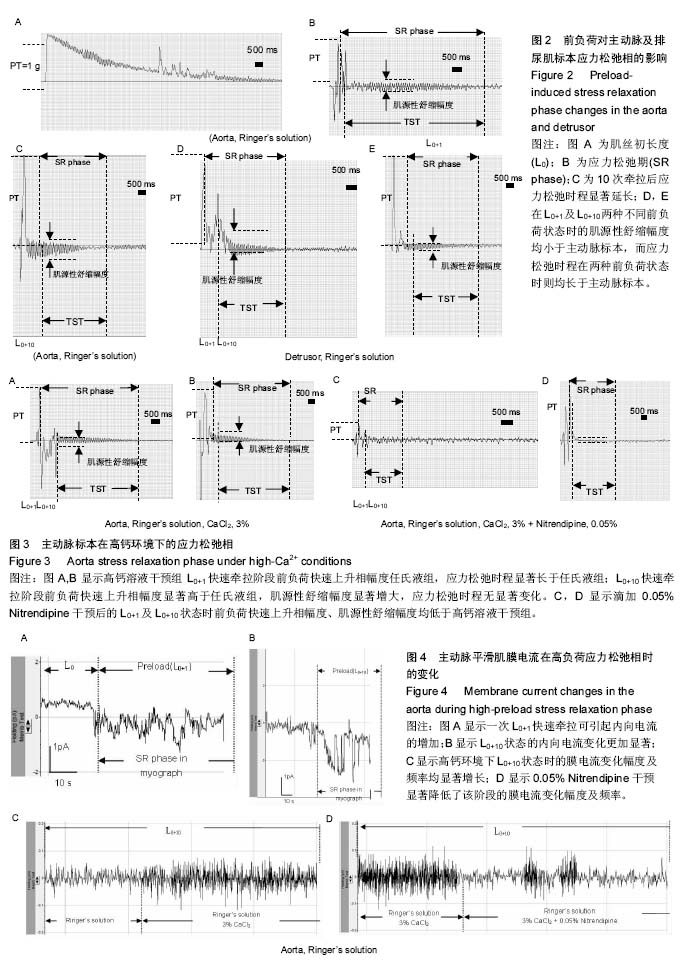
被动张力:肌丝标本受牵拉而引起的回缩现象。被动张力与肌丝标本的结构蛋白以及肌细胞外基质成分的关系更为密切;不同程度牵拉,即受负荷程度的不同会导致回缩曲线的不同;不同离子浓度环境下的回缩特性也有所不同。
细胞膜电流:肌细胞膜电位反映了肌丝标本兴奋性的变化,使用膜片钳技术可观察及记录到不同负荷状态下的肌丝膜电位变化;不同离子环境下肌丝,膜电位变化也有所不同,特别是钙离子浓度对牵拉肌丝膜电流变化影响尤为显著。
文题释义:
被动张力:肌丝标本受牵拉而引起的回缩现象。被动张力与肌丝标本的结构蛋白以及肌细胞外基质成分的关系更为密切;不同程度牵拉,即受负荷程度的不同会导致回缩曲线的不同;不同离子浓度环境下的回缩特性也有所不同。
细胞膜电流:肌细胞膜电位反映了肌丝标本兴奋性的变化,使用膜片钳技术可观察及记录到不同负荷状态下的肌丝膜电位变化;不同离子环境下肌丝,膜电位变化也有所不同,特别是钙离子浓度对牵拉肌丝膜电流变化影响尤为显著。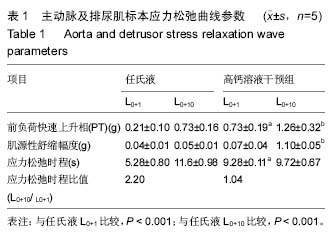
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
被动张力:肌丝标本受牵拉而引起的回缩现象。被动张力与肌丝标本的结构蛋白以及肌细胞外基质成分的关系更为密切;不同程度牵拉,即受负荷程度的不同会导致回缩曲线的不同;不同离子浓度环境下的回缩特性也有所不同。
细胞膜电流:肌细胞膜电位反映了肌丝标本兴奋性的变化,使用膜片钳技术可观察及记录到不同负荷状态下的肌丝膜电位变化;不同离子环境下肌丝,膜电位变化也有所不同,特别是钙离子浓度对牵拉肌丝膜电流变化影响尤为显著。
文题释义:
被动张力:肌丝标本受牵拉而引起的回缩现象。被动张力与肌丝标本的结构蛋白以及肌细胞外基质成分的关系更为密切;不同程度牵拉,即受负荷程度的不同会导致回缩曲线的不同;不同离子浓度环境下的回缩特性也有所不同。
细胞膜电流:肌细胞膜电位反映了肌丝标本兴奋性的变化,使用膜片钳技术可观察及记录到不同负荷状态下的肌丝膜电位变化;不同离子环境下肌丝,膜电位变化也有所不同,特别是钙离子浓度对牵拉肌丝膜电流变化影响尤为显著。