| [1] 胥少汀.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2012: 947-948.[2] Pioli G, Barone A, Giusti A, et al. Predictors of mortality after hip fracture: results from 1-year follow-up. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2006;18(5): 381-738.[3] 张魁忠,周荣平,徐聪,等.股骨近端锁定钢板治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效评估[J].南方医科大学学报, 2009, 29(12): 2561-2562.[4] 刘晓辉,张国川.锁定加压钢板生物力学原理及置入后的失败分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(4): 717-720.[5] 李亚光, 陈向军. 数字骨科临床应用研究进展[J]. 内蒙古医学杂志, 2012,44(5): 579-582.[6] 王剑,云文科.数字骨科在骨科临床的研究进展[J].中外医疗,2014,33(26): 197-198.[7] 危杰.股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(5): 79-82.[8] Evans EM. The treatment of trochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1949; 31B(2): 190-203.[9] 付淼,李莉,何叶松. Mimics与医学图像三维重建[J].中国现代医学杂志,2010,(19): 3030-3031.[10] 刘成芬.股骨粗隆手术术后护理[J]. 吉林医学, 2014, 35(29):6629.[11] Jain R, Basinski A, Kreder HJ. Nonoperative treatment of hip fractures. Int Orthop. 2003;27(1): 11-7.[12] 阮建伟,宫小康,孔劲松. 股骨近端锁定钢板内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013, 28(4):348-349.[13] 隋广维. 锁定式钢板治疗股骨粗隆间骨折20例分析[J]. 当代医学, 2010, (1): 87-88.[14] 梅雷,卞正金,陈贞庚,等. 老年股骨粗隆间骨折手术内固定的选择[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2008, 23(12): 1017-1018.[15] 刘世峰,崔文波,廖志峰,等.股骨近端锁定解剖加压钢板治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2013, (4): 4-6.[16] 张柏林.股骨粗隆间骨折采用股骨近端锁定加压钢板治疗的临床应用分析[J].中国继续医学教育, 2014, 6(6): 39-40.[17] 牛庆礼,孙辉,杨树彬,等.锁定加压钢板治疗四肢骨折术后失败原因探讨[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2009,24(9): 835-836.[18] 彭朝华,杨彬,邹秋富,等.微创锁定加压钢板固定术中失误及术后早期并发症分析[J].四川医学, 2012, 33(6): 965-967.[19] 张明辉,李国军,宋文超,等.多排CT三维重建在股骨粗隆间骨折治疗中的临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(2): 124-125.[20] 张野.多排螺旋CT后处理技术在骨关节创伤诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2015, 9(1): 33-34.[21] 曹振华, 银和平, 李树文. 股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定数字化模板的建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(31): 5017-5023.[22] 陆建华,王志刚,黄莉,等.基于健侧三维数字解剖的桡骨头假体逆向工程研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2013, 31(4): 407-410.[23] 陈刚, 廉凯,王邦军,等.计算机辅助技术联合2.4mm钢板系统在治疗桡骨远端C型骨折中的应用[J].广东医学, 2014,35(8): 1213-1216.[24] 陈刚,吴农欣,廉凯,等.利用数字骨科技术进行术前规划对儿童Ⅱ型肱骨髁上骨折复位及进针顺序的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014, 22(8): 760-762.[25] 陈刚,吴农欣,崔露,等. 数字骨科技术结合张力带钢丝在尺骨鹰嘴ⅡB型骨折中的应用[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2014, 20(2): 106-110.[26] 陆建华,倪慧玉,王志刚,等.数字化定制桡骨小头假体并术前三维虚拟置换验证研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(9): 1065-1069.[27] 杨晶,程奎,倪鹏辉,等.数字化快速成形技术在骨折畸形愈合个体化治疗的应用研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(7): 727-729.[28] 赖震,刘志祥,张兆飞,等. 三维重建技术在桡骨远端不稳定性骨折治疗中的应用[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2015, 7(2): 69-73. [29] 彭鳒侨,张占磊,钟世镇,等.基于全膝关节置换的三维术前规划实践[J].中国数字医学, 2013,(12): 45-49.[30] 凌遵龙,周友龙,沈龙山,等.计算机辅助人工髋关节置换术前规划系统及应用[J].中国现代医生,2011, 49(16): 119-120.[31] 王小平,韦展图,黄俭,等.虚拟三维重建术前规划技术在Pilon骨折的应用研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016, (1): 44-49.[32] 王光达,张祚福,齐晓军,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(52): 9702-9705.[33] Park JC, Shin HS, Cha JY, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the relationship between masticatory performance and skeletal malocclusion. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015;45(1): 8-13.[34] Yang M, Li C, Li Y, et al. Application of 3D Rapid Prototyping Technology in Posterior Corrective Surgery for Lenke 1 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients. Medicine(Baltimore). 2015; 94(8): 582.[35] 张弛. 3D打印:产品制造的新革命[J].设计, 2011, (11): 46-49.[36] 王富友,任翔,杨柳. 3-D打印技术在关节外科的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, 28(3): 272-275.[37] Deng A, Xiong R, He W, et al. [Postoperative rehabilitation strategy for acetabular fracture: application of 3D printing technique]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34(4): 591-593.[38] Wu AM, Shao ZX, Wang JS, et al. The accuracy of a method for printing three-dimensional spinal models. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0124291.[39] Zeng C, Xiao J, Wu Z, et al. Evaluation of three-dimensional printing for internal fixation of unstable pelvic fracture from minimal invasive para-rectus abdominis approach: a preliminary report. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8): 13039-13044.[40] Li XS, Wu ZH, Xia H, et al. The development and evaluation of individualized templates to assist transoral C2 articular mass or transpedicular screw placement in TARP-IV procedures: adult cadaver specimen study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014;69(11): 750-757.[41] 尤微,王大平,刘黎军,等.三维数字规划在肱骨近端骨折手术治疗中的应用研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2014,8(7): 1243-1247. |
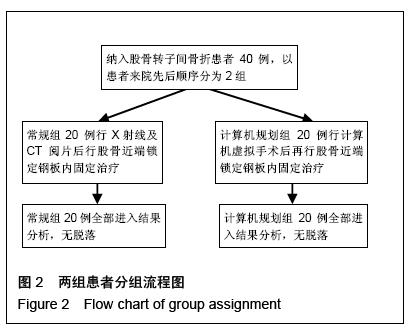
.jpg)
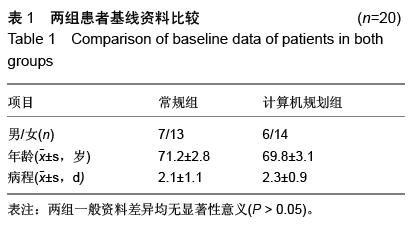

.jpg)