中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4662-4666.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2779
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
三维数字化测量肾结石的解剖学病因及临床意义
武利兵1,2,许阳阳3,和雨洁2,王海燕2,高 尚2,恩和吉日嘎拉2,李筱贺2,李志军2
- 1北京市房山区良乡医院泌尿外科,北京市 102446;内蒙古医科大学,2基础医学院人体解剖教研室,3研究生院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010110
Anatomical etiology and clinical significance of three-dimensional digital measurement of kidney stones
Wu Libing1, 2, Xu Yangyang3, He Yujie2, Wang Haiyan2, Gao Shang2, Enhejirigala2, Li Xiaohe2, Li Zhijun2
1Department of Urinary Surgery, Liangxiang Hospital in Fangshan District, Beijing 102446, China; 2Department of Anatomy, Basic Medical College, 3Graduate School, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
肾结石:是泌尿系统最常见的疾病,与饮食中的钙含量和酸性物质增高有关,严重者常需要进行手术治疗,肾结石手术几乎占了泌尿外科手术数量的一半。
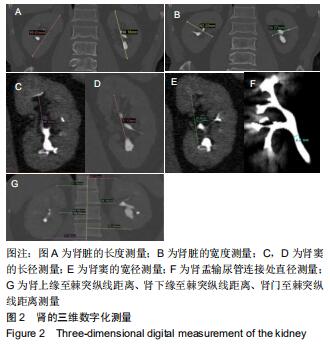
三维数字化:利用医学工程软件把人体脏器的实体模型进行虚拟创建,之后进行修改、模拟、设计等一些操作。
背景:肾结石发生病因有很多,但对于肾脏解剖形态学研究是否影响结石的产生还未有明确答案。
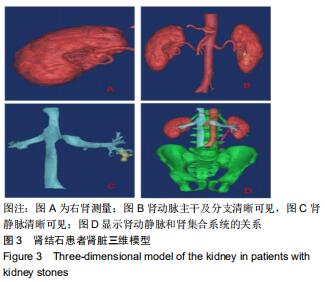
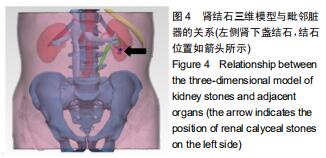
目的:重建肾脏的三维立体模型;测量与肾结石病因的相关解剖结构数据进行分析。
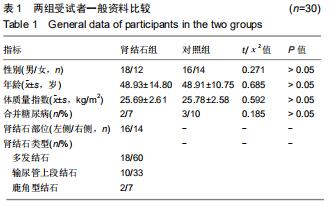
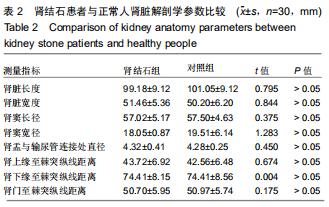
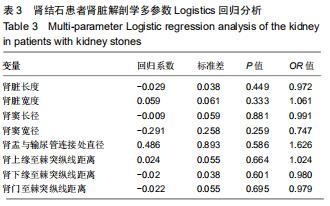
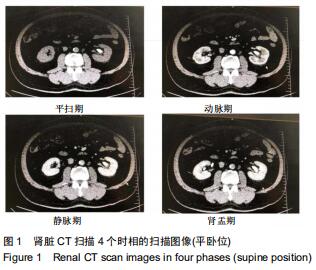
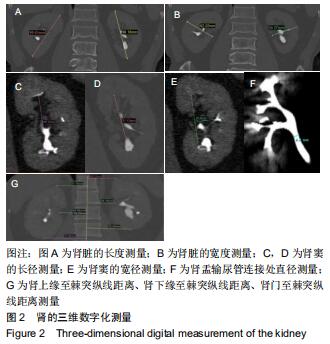
方法:随机选取2017年12月至2019年2月在北京房山区良乡医院就诊的30例肾结石患者作为肾结石组,对照组是同期进行体检的正常人30例。两组受试者采集肾脏CT的扫描数据后,利用Mimics 16.0.软件通过图像分割和融合来重建肾脏的三维立体模型;测量肾脏长度、肾脏宽度、肾窦长径、肾窦宽径、肾盂与输尿管连接处直径、肾上缘至棘突纵线距离、肾下缘至棘突纵线距离、肾门至棘突纵线距离;并对肾结石患者肾脏解剖学指标进行多参数Logistics回归分析。
结果与结论:①肾结石患者与正常人的肾在肾脏长度、肾脏宽度、肾窦长径、肾窦宽径、肾盂与输尿管连接处直径、肾上缘至棘突纵线距离、肾下缘至棘突纵线距离、肾门至棘突纵线距离方面的三维数字化测量结果差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。②肾结石患者肾脏解剖学多参数Logistics回归分析结果表明,肾结石患者的肾脏长度、肾脏宽度、肾窦长径、肾窦宽径、肾盂与输尿管连接处直径、肾上缘至棘突纵线距离、肾下缘至棘突纵线距离、肾门至棘突纵线距离等与肾结石的形成无明显相关性(P > 0.05)。提示肾脏形态学的不同与结石形成无关。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6850-7615(武利兵);0000-0001-5877-8358(许阳阳)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: