中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (11): 1558-1583.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.11.006
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
瘢痕疙瘩组织中Livin、Smac、Caspase-3的表达及其相关性
张远贵1,段 冬1,李攀登1,陈润芳2,李之华1,高新宇1,吴 炜1
- 徐州医学院附属医院,1烧伤整形外科,2检验科,江苏省徐州市 221002
Expression of Livin, Smac and Caspase-3 in keloids and their correlation
Zhang Yuan-gui1, Duan Dong1, Li Pan-deng1, Chen Run-fang2, Li Zhi-hua1, Gao Xin-yu1, Wu Wei1
- 1Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery, 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
瘢痕疙瘩:皮肤组织愈合后所形成的过度生长的异常瘢痕组织,常具有病变超过原皮损范围、呈持续性生长、凸出皮面、质硬、呈条索状或蟹足样生长特点。
相关性研究:对2个或多个具备相关性的变量元素进行分析,从而衡量2个或多个变量因素相关的密切程度。
背景:目前临床治疗瘢痕疙瘩效果较差、常易复发。瘢痕疙瘩的发病机制仍不完全清楚,而关于成纤维细胞增殖及凋亡的研究为研究的热点。
目的:分析瘢痕疙瘩组织中Livin、Smac、Caspase-3的表达的相关性,初步探讨3种因子在瘢痕疙瘩组织发病机制中的作用。
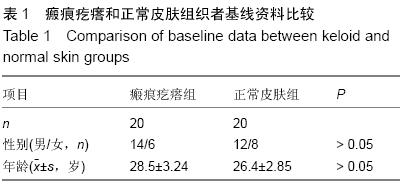
方法:采用RT-PCR和免疫组织化学分别检测Livin、Smac、Caspase-3的mRNA和蛋白在20例瘢痕疙瘩组织和20例正常皮肤组织中的表达,并进行相关性分析
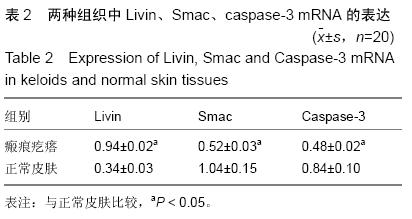
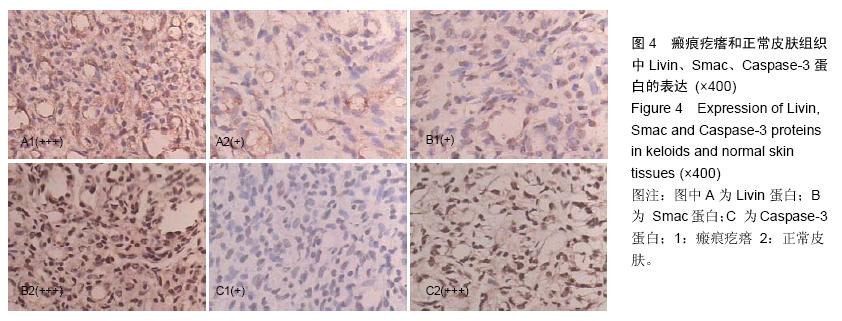
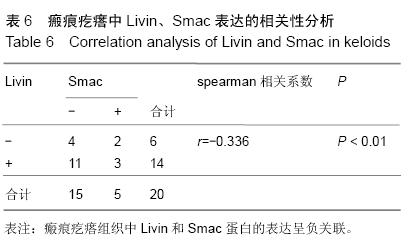
结果与结论:瘢痕疙瘩组织中Livin 的mRNA表达水平和蛋白的阳性表达率显著高于正常皮肤组织(P < 0.05),瘢痕疙瘩组织中Smac和Caspase-3 的mRNA表达水平和蛋白的阳性表达率低于正常皮肤组织(P < 0.05)。瘢痕疙瘩组织中Livin和Smac、Caspase-3蛋白的表达呈负关联。结果提示Livin基因高表达可能抑制了Smac、Caspase-3基因表达从而导致了瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞增殖和凋亡的失衡,最终导致了瘢痕疙瘩的形成。
ORCID:0000-0002-9531-0196(张远贵)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 2.2 PCR结果 见图1-3及表2。
图1为2种组织Livin mRNA(245 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;图2为两种组织Smac mRNA(303 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;图3为两种组织Caspase-3 mRNA(326 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;表2为3种组织mRNA的表达强度灰度值及统计学分析结果,说明了3种因子的mRNA水平在2种组织中的表达均有差异性。
2.2 PCR结果 见图1-3及表2。
图1为2种组织Livin mRNA(245 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;图2为两种组织Smac mRNA(303 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;图3为两种组织Caspase-3 mRNA(326 bp)的表达条带灰度图像;表2为3种组织mRNA的表达强度灰度值及统计学分析结果,说明了3种因子的mRNA水平在2种组织中的表达均有差异性。
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)