中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 292-296.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.02.024
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
心肺运动试验与6 min上下楼梯试验评价心肺功能的比较
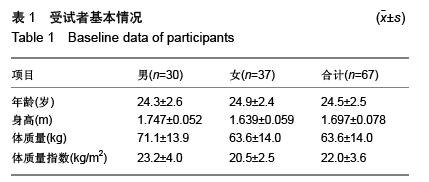
郭 辉1,2,孙景权1,张一民1
- 1School of Human Movement Sciences, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; 2School of Mechanical Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110870, Liaoning Province, China
Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary function: cardiopulmonary exercise test versus 6-minute stair climbing and descending test
Guo Hui1, 2, Sun Jing-quan1, Zhang Yi-min1
- 1北京体育大学运动人体科学学院,北京市 100084;2沈阳工业大学机械工程学院,辽宁省沈阳市 110870
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
6 min上下楼梯试验:是一种运动试验。试验场地为符合国家标准的一层楼梯间(每个台阶高度为16 cm)。以一步一阶的方式在一层楼梯上尽可能快的上下楼梯6 min。监测人员每2 min报时1次,并密切观察受试者是否发生气促、面部表情变化等情况。6 min试验结束时,检测人员说“停止”并记录受试者最后一个往返所在的台阶数。检测人员统计受试者上下楼梯的往返数。
心肺运动试验:是评估患者心肺功能的一种无创方法。心肺运动试验在心血管疾病的诊断、治疗评价、危险分层、愈后预测、康复指导等各方面已经得到了广泛应用,并被证实在许多方面优于传统检测方法。
背景:心肺运动试验在评价人的心肺功能方面起着重要的作用,但需要昂贵的仪器和专业测试人员才能完成,且需要受试者达到极量强度,所以寻找一种亚极量水平,且操作简便,费用低廉,容易推广使用的运动试验方法迫在眉睫。
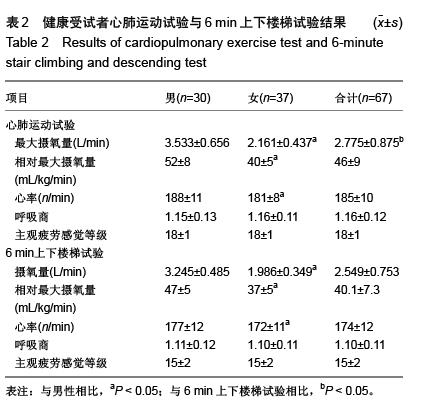
目的:通过比较心肺运动试验与6 min上下楼梯试验的最大摄氧量,探讨2种不同试验方法评价心肺功能的一致性。
方法:随机招募67名志愿者,按Bruce方案进行心肺运动试验,检测每位受试者的最大摄氧量,再进行6 min上下楼梯试验,测量每位受试者在上下楼梯过程中的最大摄氧量,将心肺运动试验所测得的最大摄氧量与6 min上下楼梯试验所测得的最大摄氧量进行比较。
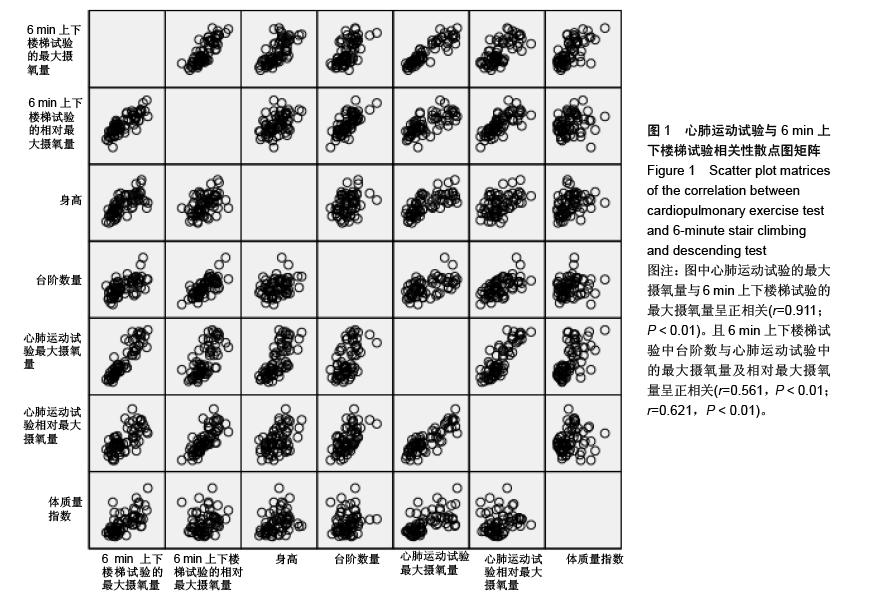
结果与结论:6 min上下楼梯试验所测得的最大摄氧量小于心肺运动试验所测得的最大摄氧量(P < 0.01);6 min上下楼梯试验的最大摄氧量与心肺运动试验的最大摄氧量呈正相关(r=0.911,P < 0.01);2种测试方案下获得的最大摄氧量具有高度相关关系且一致性较好。因此可以用6 min上下楼梯试验来推测最大摄氧量,并且这可能成为一种评价心肺功能的有效方法。
ORCID: 0000-0002-1656-4412(张一民)