中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 202-207.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.02.009
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
Auto-CAD计算机辅助设计软件定点测量儿童上颌窦前壁及上颌结节位置变化
韩 蕊1,马 雷1,米丛波2,王 丽3,王永亮1,张 倩1
- 1青岛大学附属医院黄岛院区口腔科,山东省青岛市 266555;2新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔正畸科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;3新疆乌鲁木齐市口腔医院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002
Localizing the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus and maxillary tuberosity using Auto-CAD software
Han Rui1, Ma Lei1, Mi Cong-bo2, Wang Li3, Wang Yong-liang1, Zhang Qian1
- 1Department of Stomatology, Huangdao Branch, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qiangdao 266555, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Stomatological Hospital of Urumqi, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
上颌窦:为上颌骨体内的锥形空腔,窦壁为骨质,大部份为薄的密质骨板,内稍有松质骨,最薄的地方只有密质骨。窦壁直接被覆黏膜,支配牙齿及牙周组织的血管、神经,通行于骨内牙槽管之中或黏膜下。上颌窦的形状基本上与上颌骨体一致,可以分为一底、一尖及前、后、上、下四个壁。其底即上颌体的鼻面,尖深入上颌骨的颧突,前壁为上颌体的前面,后壁即上颌体的颞下面,上壁为上颌体眶面,下壁为牙槽突。
上颌结节:上颌骨后面下部有比较粗糙的圆形隆起,称为上颌结节,为翼内肌浅头附着点。上颌结节下方有牙槽孔,有上牙槽后神经、血管通过,行上牙槽后神经麻醉时,应注射于牙槽孔周围。
背景:研究上颌窦前壁及上颌结节的位置变化,分析上颌骨的发育情况,并可掌握上颌骨骨量的多少以及发育的时机,来为正畸做更好的准备和分析,但用计算机Auto-CAD软件定点,并研究上颌窦前壁及上颌结节的位置变化尚未见报道。
目的:调查分析新疆乌鲁木齐市300名4-14岁汉族儿童生长发育过程中上颌窦前壁及上颌结节的位置变化及其发育的情况。
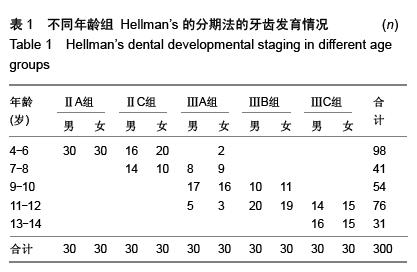
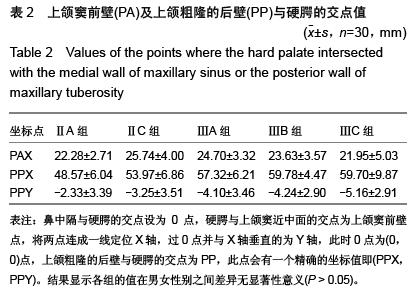
方法:对乌鲁木齐市口腔医院就诊的300例4-14岁儿童,将收录的人群按Hellman’s牙齿发育阶段分为5组(ⅡA组、ⅡC组、ⅢA组、ⅢB组、ⅢC组)。通过Auto-CAD计算机辅助设计软件对全颌曲面断层片进行画图分析,将鼻中隔与硬腭的交点设为O点,硬腭与上颌窦近中面的交点为上颌窦前壁点(PA),将两点连成一线定位X轴,过O点并与X轴垂直的为Y轴,此时O点为(0,0)点,上颌粗隆的后壁与硬腭的交点为上颌粗隆的后壁点(PP),此点会有一个精确的坐标值即(PPX,PPY),将数据进行统计分析,了解牙齿发育的不同时期,上颌窦前壁点与上颌粗隆的后壁点的位置变化。
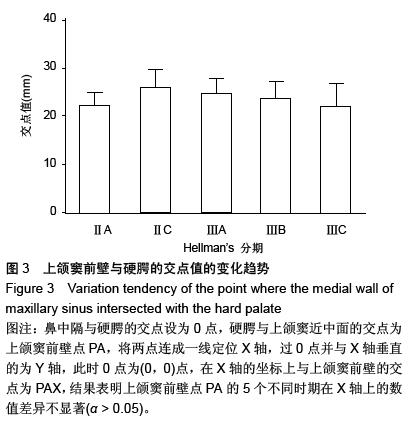
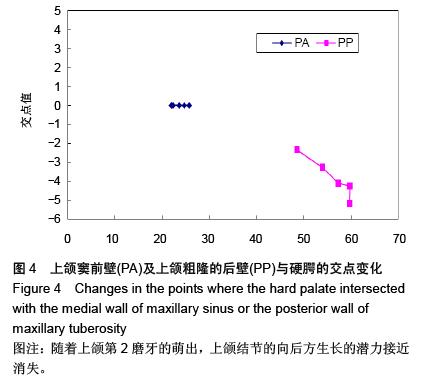
结果与结论:方差分析表明上颌窦前壁点在5个不同时期在X轴上的数值差异不显著(α > 0.05)。从IIA期到ⅢA期上颌粗隆后壁的值是明显的水平向后方和垂直向下方的生长。从ⅢA期到ⅢB期,上颌粗隆的后壁点是仅发生了水平向后方的生长,垂直方向的生长不明显。从ⅢB到ⅢC期,上颌粗隆的后壁点出现明显的垂直向下的生长,而水平向后方的生长不明显。即此期是第2磨牙萌出的时间,说明第2磨牙的萌出对上颌骨垂直向的生长有一定作用。
ORCID: 0000-0003-0258-9325(马雷)
.jpg)
.jpg)