[2] 黄彩华.格斗对抗性项目代谢调节与适应的核磁共振代谢组学研究[D].福建师范大学, 2012.
[3] 李江华,王智慧,朱小娟,等.代谢组学运动选材与传统生化选材方法的比较[J].体育学刊,2013,(1):123-128.
[4] Nicholson JK, Lindon JC, Holmes E. 'Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica; the fate of foreign compounds in biological systems.1999;29(11): 1181-1189.
[5] Enea C, Seguin F, Petitpas-Mulliez J, et al. H-1 NMR-based metabolomics approach for exploring urinary metabolome modifications after acute and chronic physical exercise. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. 2010;396(3): 1167-1176.
[6] Huang CC, Lin WT, Hsu FL, et al. Metabolomics investigation of exercise-modulated changes in metabolism in rat liver after exhaustive and endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010; 108(3):557-566.
[7] 王磊,武露凌,盛蕾.优秀游泳运动员冬训周期中的代谢组学研究[J].体育与科学, 2008, (6): 43-46.
[8] Yan B, AJ, Wang G, et al. Metabolomic investigation into variation of endogenous metabolites in professional athletes subject to strength-endurance training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;106(2):531-538.
[9] Lehmann R, Zhao XJ, Weigert C, et al. Medium Chain Acylcarnitines Dominate the Metabolite Pattern in Humans under Moderate Intensity Exercise and Support Lipid Oxidation. PloS one. 2010;5(7):e11519
[10] Lee R, West D, Phillips SM, et al. Differential Metabolomics for Quantitative Assessment of Oxidative Stress with Strenuous Exercise and Nutritional Intervention: Thiol-Specific Regulation of Cellular Metabolism with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine Pretreatment. Analytical chemistry.2010;82(7): 2959-2968.
[11] Pohjanen E, Thysell E, Jonsson P, et al.A multivariate screening strategy for investigating metabolic effects of strenuous physical exercise in human serum. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(6):2113-2120.
[12] Chorell E, Moritz T, Branth S, et al. Predictive metabolomics evaluation of nutrition-modulated metabolic stress responses in human blood serum during the early recovery phase of strenuous physical exercise. J Proteome Res. 2009;8(6): 2966-2977.
[13] Miccheli A, Marini F, Capuani G, et al. The influence of a sports drink on the postexercise metabolism of elite athletes as investigated by NMR-based metabolomics.J Am Coll Nutr.2009;28(5):553-564.
[14] Dai W, Zhang F, Jia Z, et al.Evaluation of the effect of the traditional Chinese medicine tongxinluo or ginseng on excess fatigue rats studied by metabonomics approach based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Se pu = Chinese journal of chromatography / Zhongguo hua xue hui.2011; 29(11): 1049-1054.
[15] Zhang F, Jia Z, Gao P, et al. Metabonomics study of urine and plasma in depression and excess fatigue rats by ultra fast liquid chromatography coupled with ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometry. Molecular bioSystems.2010;6(5): 852-861.
[16] Nieman DC, Gillitt ND, Henson DA, et al.Bananas as an Energy Source during Exercise: A Metabolomics Approach.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37479.
[17] Kiss A, Jacquet A L, Paisse O, et al. Urinary signature of anabolic steroids and glucocorticoids in humans by LC-MS. Talanta.2011;83(5): 1769-1773.
[18] 蒋启飞. 800米跑日益趋向短距离跑项目特征[J].田径,2015,(2): 24.
[19] 郭层城,舒有谟,韩佐生,等.对800米跑重新认识的探讨-兼议800米跑的翼项特点[J].中国体育科技,1990, (3): 23-28.
[20] 贾昌志.提高800 m跑成绩的途径探讨[J]. 唐山师范学院学报, 2002, (5): 81-83.
[21] 郑陆,潘力平,隋波,等. 800米跑比赛前后血氨的变化特点及其与血乳酸水平变化的关系[J].山东体育学院学报, 2005,(1): 43-45.
[22] 石茗茗,王永象.浅谈800米制胜的核心因素的机制和训练[J].中国科教创新导刊, 2007,(17): 120.
[23] 毛海峰,刘显东. 800米跑的供能特点及其体能训练初探[J].宜春学院学报, 2007,(4):149-151.
[24] 查锡良,药立波.生物化学与分子生物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013: 202.
[25] 张爱芳.实用运动生物化学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2005: 104.
[26] 王镜岩,朱圣庚,徐长法.生物化学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2002: 320.
[27] Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2011;472(7341): 57-63.
[28] Cho SS, Reddy G, Straub JE, et al. Entropic stabilization of proteins by TMAO . J Phys Chem B. 2011;115(45): 13401-1340.
[29] Huo T, Cai S, Lu X, et al. Metabonomic study of biochemical changes in the serum of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients after the treatment of metformin hydrochloride. J Pharm Biomed Anal.2009;49(4):976-982.
[30] Munroe KL, Magers DH, Hammer NI. Raman spectroscopic signatures of noncovalent interactions between trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) and water.J Phys Chem B. 2011;115(23):7699-707.
[31] 卜立平.对我国青少年中长跑项目训练特征的研究[D].北京体育大学, 2009.
[32] 练艺影,曹建民,邓艳香,等.肌酸代谢动力学研究进展[J].北京体育大学学报, 2006,(12):1672-4.
[33] 苏茂义,赵河清,田桂仁,等.尿碘尿肌酐与运动[J].地方病通报, 1992,(1): 69-71.
[34] 胡慧.运动诱导氧化应激相关适应机制及其对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响[D].湖南师范大学, 2012.
[35] Vollaard NB, Shearman JP, Cooper CE. Exercise-induced oxidative stress:myths, realities and physiological relevance. Sports medicine.2005;35(12):1045-1062.
[36] Pechlivanis A, Chatziioannou AC, Veskoukis AS, et al. GC-MS analysis of blood for the metabonomic investigation of the effects of physical exercise and allopurinol administration on rats.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2014; 966:127-131.
[37] Lewis GD, Farrell L, Wood MJ, et al.Metabolic Signatures of Exercise in Human Plasma. Sci Transl Med.2010, 2(33): 33ra37.
[38] 李江华,刘承宜,徐晓阳,等.2006年多哈亚运会短距离游泳男运动员代谢组学研究 [J].体育科学, 2008,(2): 42-46,53.
[39] 李江华,刘承宜,沙海燕,等. 高水平男子中短距离游泳成绩预测的代谢组学模型[J]. 体育学刊, 2010, (4): 103-106.
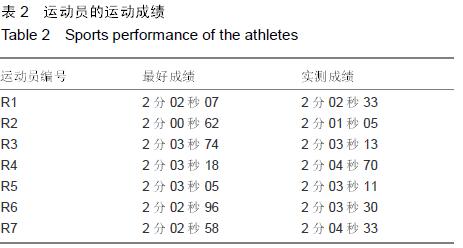
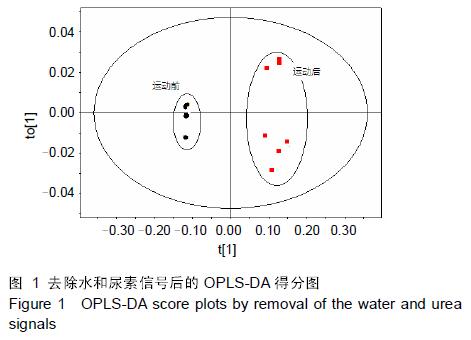

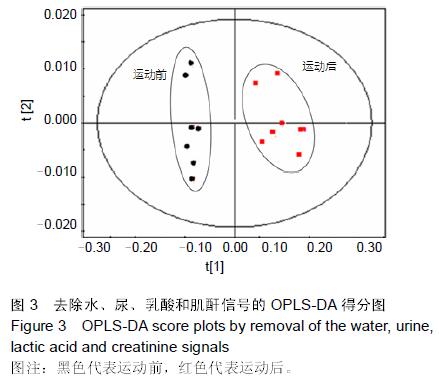
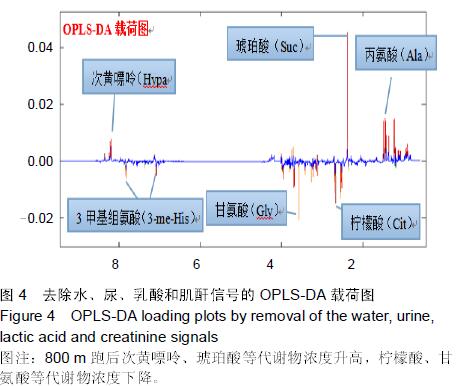

.jpg)