中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (46): 7478-7483.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.46.019
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
正常及挫伤脊髓血管的三维直视化:同步辐射相衬成像
吴天定1,吕红斌2,曹 勇1,倪双飞1,李 平1,胡建中1
- 1中南大学湘雅医院脊柱外科,湖南省长沙市 410008;2中南大学湘雅医院运动医学科,运动医学研究中心,湖南省长沙市 410008
Three-dimensional visualization of angioarchitecture in spinal cord contusion using propagation phase contrast tomography
Wu Tian-ding1, Lv Hong-bin2, Cao Yong1, Ni Shuang-fei1, Li Ping1, Hu Jian-zhong1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China; 2Department of Sports Medicine, Research Center of Sports Medicine, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
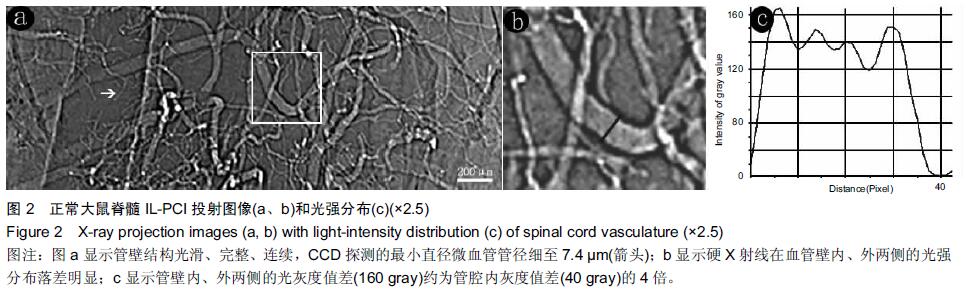
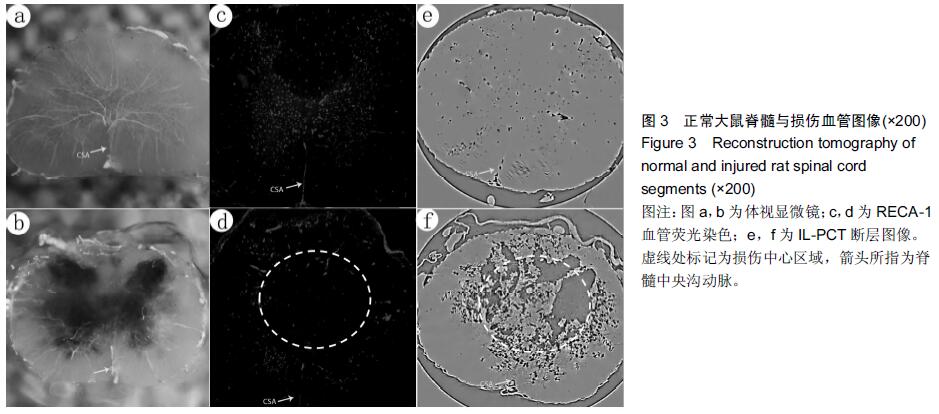
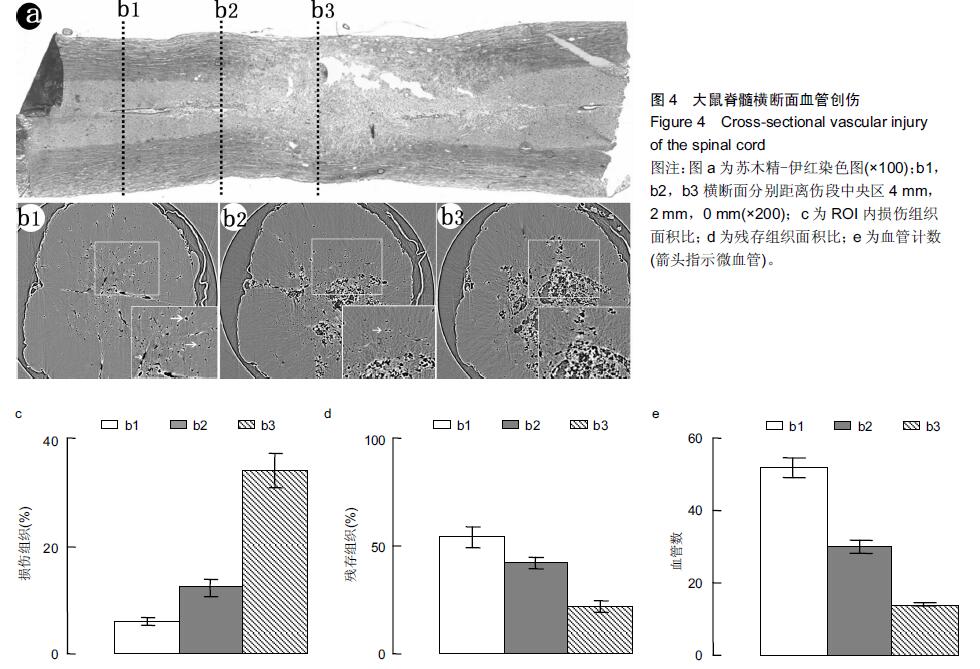
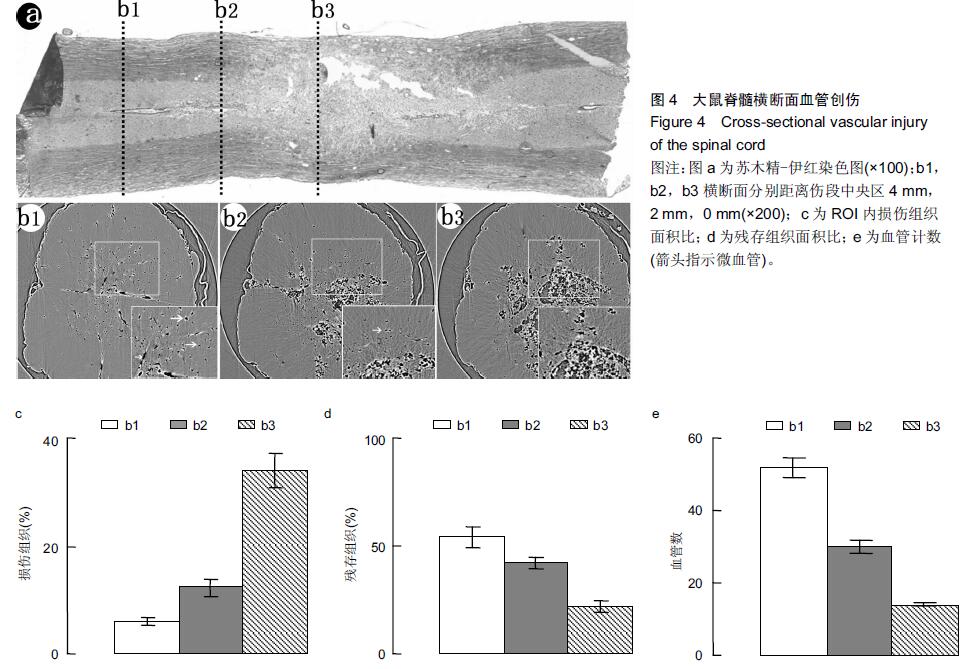
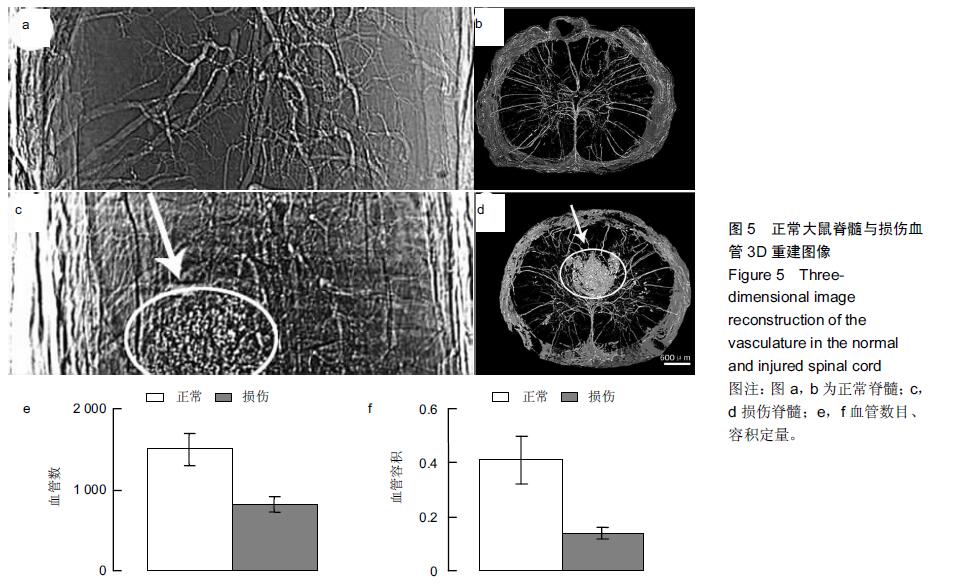
背景:同步辐射相位衬度成像凭借硬X射线光源的高准直、高相干等特性,其能大幅度提高对软骨细胞及微血管的空间分辨能力。 目的:利用高空间分辨率同步辐射相衬成像技术观察大鼠正常及急性损伤脊髓的微血管的形态变化。 方法:雄性SD大鼠分为2组:实验组以改良ALLEN’s打击法制作大鼠急性脊髓挫伤模型;伪手术组大鼠只行椎板减压术,不打击脊髓作为正常对照。术后第1天取正常及伤段脊髓标本经甲醛-水杨酸甲酯序贯处理48 h,标本于上海光源BL13W1硬X射线站进行扫描和成像。采集数据以利用VG Studio Max 2.1软件包进行3D图形重建及血管量化分析。 结果与结论:相位衬度成像以特有的血管边缘增强效应直观呈现脊髓微血管形态,其结合CT技术(相衬断层成像)从三维视角对脊髓微血管进行直观成像,急性脊髓挫伤后神经组织的破坏伴随着严重的血管结构的损毁,组织损伤及血供的缺失在髓内由中央区向头、尾两侧呈梭性蔓延。三维血管量化数据显示脊髓挫伤后微血管数目及血管灌注容积急剧减少(P < 0.01)。结果表明无需血管造影的条件下,相衬断层成像可作为一种新的有潜力的超高分辨率可视化技术用于脊髓微血管3D结构成像及量化分析。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
.jpg)