2.1 历时性的研究动态分析
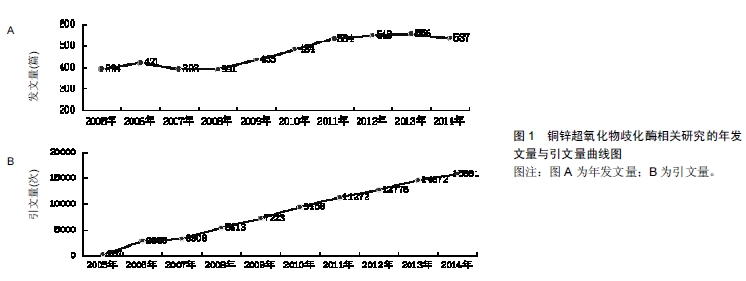
2.1.1 年发文量与引文量 年发文量呈现的是一个研究领域的历时性变化趋势,在一定程度上反映了该学科领域学术研究的理论水平和发展速度。同时,引文量是科技工作者对已有科技成果和最新文献信息吸收量的主要标志, 同时也是考查其信息利用能力的主要手段。由
图1可以看出,近10年有关铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究的发文量整体上处于上升的趋势,2014年的发文量达到了2005年2倍多,同时引文量也逐年增加,表明近年来该领域研究的关注度正在不断提高。
2.2 共时性的研究动态分析
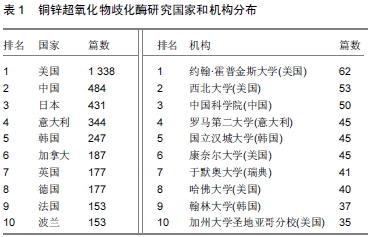
2.2.1 研究国家和机构分布 科研成果和著者分析是了解某一学科领域研究力量分布状况的有效方法。利用CiteSpace软件对研究铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的国家、机构进行可视化分析,可以明确研究国家与机构分布,并显示其研究现状。表1显示4 693篇文献作者分布在77个国家,其中频次(频次代表发表文献的数量)超过150的共有10个国家(
表1),其发文频次占世界发文数的 78.6% 以上,其中美国占有绝对优势,占到总成果的28.5%;中国与日本发文频次较为接近,分别为484与431。目前世界上有关铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的研究成果涉及219个机构,发文频次排名前10的机构中,美国占半数,韩国有2所,中国、意大利与瑞典各占1所。
 主要来源期刊计量分析
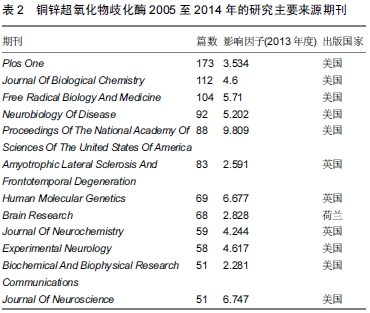
主要来源期刊计量分析:对一个学术领域做期刊分析能够确定该学科的核心。因此依据期刊载文量检索出的2005至2014年间的4 693篇文献分布于674种来源出版物,其中载文80篇的以上有6种来源出版物,这6种期刊占总刊物数的13.89%以上,载文30-79篇的有13种来源出版物,占总刊物数的13.27%以上。铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的研究共涉及91个学科方向,如神经科学与神经学、生物化学与分子生物学、临床神经病、细胞生物学、内分泌学和代谢、化学、药理学、毒理学、基因与遗传学等。可以看出,铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的研究已延展到各个领域,成为众多学者关注的焦点。
表2列出了铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究文献的高载文量期刊。从刊物出版国别来看,美国占据8种,英国3种,荷兰1种,这也是美国发文总量占据世界第一的原因之一。从刊物影响因子来看,这12种期刊平均影响因子在4.9左右,其中前3名分别是Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America(PNAS)、Journal Of Neuroscience与Human Molecular Genetics,其影响因子均在6.5以上,在一定程度反映了近年来铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究受到学者的广泛关注,其研究的重要性与创新性不断在高级别期刊上体现出来。
主要来源期刊关注点分析:对期刊的关注点进行分析,可以帮助该领域研究人员更便捷的查阅发现这一领域的主要进展,制定具有针对性的收藏及期刊投稿方案,及时了解捕捉该领域的前沿动态。其中,载文量最大的
Plos One是2006年创办的开源性期刊,重点关注生物医学、分子生物学等方向,年发文量较大。
Journal Of Biological Chemistry长期关注信号转导、生物化学、细胞生物学等领域,是生物化学领域的老牌杂志。
Free Radical Biology And Medicine是1987年创刊的半月刊杂志,影响因子在这12种期刊中排名第4,它主要关注自由基、氧化应激、生物医学等。
Neurobiology Of Disease主要探讨神经系统疾病、神经生物学、神经科学等相关主题,也是中科院神经科学分类下的2区期刊。
PNAS是美国国家科学院出版的综合性期刊,在中科院的分区为1区,它关注的是科学研究领域的最新进展,是一本颇具影响力的杂志。
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis And Frontotemporal Degeneration、Human Molecular Genetics与Journal Of Neurochemistry是英国创办的有关退行性疾病、分子遗传与神经化学的杂志,其中
Human Molecular Genetics是牛津大学在1992年创办的遗传学杂志,接受文章方向较广,近年来影响因子分别为6.677(2013)、7.692(2012)、7.363(2011)与8.058(2010),在遗传疾病相关研究方面享有较高的
声誉。Brain Research是荷兰研究神经科学方面的重要期刊,1966年创刊,年发文量较大,对神经科学、电生理学、神经病学等相关领域很感兴趣。
Journal Of Neuroscience同样是在中科院神经科学分类下的 2 区期刊,鼓励神经学各领域的研究人员和专业人员发表主题涉及神经病学、神经科学等较为广泛领域的研究文章。
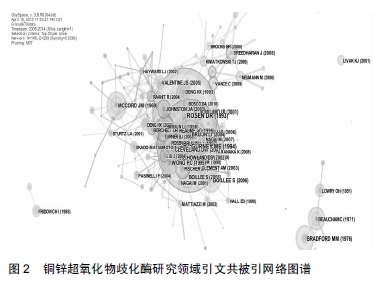
2.3 知识基础—高被引文献研究方向分析 通过对知识基础进行分析可使研究者更好地了解铜锌超氧化物歧化酶领域的发展脉络和研究基础。从文献计量学来看,共被引关系的实质在于为施引文献所要反应的研究前沿提供知识基础,从而有利于进一步指明研究前沿本质,而知识基础则是由引文文献中被引文献组成的
[3]。
图2呈现了本研究所收录文献的共被引网络图谱,其中图谱中节点的大小代表了该文献被引的频率,厚度越大,说明关注度也越高。在分析知识图谱基础上,对高被引文献进行二次检索,重点分析、探测高被引文献的主要研究方向,从而得出10年来铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究的知识基础。
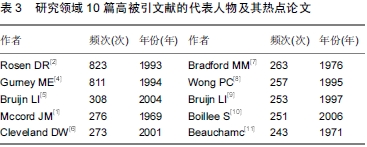
这10篇高被引论文不仅是本聚类中的核心文献,也是整个共被引网络中的核心文献(
表3)。其中被引频率最高的一篇文章是Rosen等
[2]于1993年发表在
Nature上的,充分反映了这篇文章在铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究中的重要性,在这篇文章中Rosen等首次提出家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症的发病与编码铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的基因突变有关,并从13个不同的家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症家族中确定了11个不同铜锌超氧化物歧化酶错义突变,开启了研究肌萎缩侧索硬化症疾病中铜锌超氧化物歧化酶突变的新时期。Gurney
[4]发现表达人肌萎缩侧索硬化症突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的转基因老鼠在同时也表达它们正常的野生型(WT)铜锌超氧化物歧化酶基因时, 发生的运动神经元疾病(MND)与人肌萎缩侧索硬化症相似,然而,表达人的野生型铜锌超氧化物歧化酶转基因老鼠在同时也表达它们正常的野生型(WT)铜锌超氧化物歧化酶基因时, 却不发生MND。2004年,Bruijn
[5]发现在肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者和转基因鼠的运动神经元中存在细胞质内含物,且在肌萎缩侧索硬化症小鼠模型中这些内含物包含铜锌超氧化物歧化酶和泛素化蛋白。超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)是1938年Marn等首次从牛红血球中分离出来的,Mccord 等
[1]在1969年重新发现这种具有生物活性的蛋白,弄清了它催化过氧阴离子发生歧化反应的性质,并将其正式命名为超氧化物歧化酶。Cleveland等
[6]则从铜锌超氧化物歧化酶突变致毒性、铜锌超氧化物歧化酶细胞内聚集毒性、肌萎缩侧索硬化症兴奋性毒性、肌萎缩侧索硬化症治疗方法等方面进行了详细地综述。根据蛋白质可与考马斯亮蓝G-250定量结合的原理,Bradford
[7]在1976年建立了用于测定蛋白质浓度的考马斯亮蓝法,这种蛋白质测定法具有超过其他几种测定方法的突出优点,长期以来得到了人们的广泛应用,也是目前灵敏度最高的蛋白质测定法。通过对表达G37R突变的老鼠模型进行研究,Wong等
[8]证实了铜锌超氧化物歧化酶上G37R突变能够引起进行性神经元疾病。Bruijn等
[9]通过对表达不同水平的G85R突变的老鼠进行实验发现,老鼠在铜锌超氧化物歧化酶活性不变或增强时均表现出进行性运动神经元缺失,表达低水平的突变已经足够引起严重的运动神经元疾病,而且在实验老鼠身上,G85R的毒性要比G93A和G37R强。Boillee等
[10]则通过选择性敲除小胶质细胞中的突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶使得突变小鼠存活增加,强调了表达突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的胶质细胞在肌萎缩侧索硬化症中的病理作用,认为在肌萎缩侧索硬化症疾病的后期小胶质细胞释放的毒性造成了运动神经元的进一步丢失。Beaucham
[11]利用核黄素在光照下产生超氧自由基,用硝基蓝四氮唑(nitro blue
tetrazolium,NBT)光照还原反应法间接测定超氧化物歧化酶活性,他用产生超氧自由基的系统检测产生的自由基,再以超氧化物歧化酶对此反应的抑制程度来间接测定超氧化物歧化酶的活性。硝基蓝四氮唑光照还原反应法是测定超氧化物歧化酶活性常用的方法之一,被广泛应用于生物、医学、植物学等领域。

2.4 研究热点—高频次关键词分析 通过了解铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的研究热点,有助于把握整个研究动向,使研究人员更加明确有关铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究的发展态势。关键词是文献的核心,是对研究内容的高度概括与集中描述,所以作者运用CiteSpace信息可视化分析软件,以关键词共现知识图谱展现近10年内相关文献集中反映的关键词汇(
图3),并对高频关键词进行分析以把握铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究的热点领域。
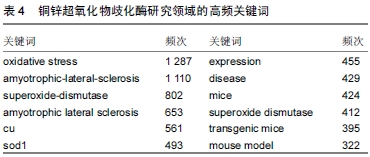
作者选择频次在300以上的关键词为高频关键词,如
表4所示,其中氧化应激、肌萎缩侧索硬化症是出现频次最高的两个关键词,均达到了1 000以上。铜锌超氧化物歧化酶所扮演的角色正是氧化应激的“保护伞”,氧化应激是一个复杂的动态的过程,是由于过多的活性氧和自由基不能被细胞清除引起
[12]。在生理状态下,机体内多种抗氧化酶不断地清除细胞内产生的活性氧和自由基,以保持氧化-还原系统的稳定。平衡被破坏则会导致活性氧过剩,从而产生氧化应激,影响细胞正常生理功能,最后导致细胞变性坏死。自从1993年Rosen
[2]提出家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症的发病与编码铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的基因突变有关,这30年中对于铜锌超氧化物歧化酶与肌萎缩侧索硬化症的研究一直备受关注。肌萎缩侧索硬化症是一种影响运动神经元的进行性神经变性疾病,主要通过侵犯脊髓前角、脑干和额叶皮质运动神经元,使其发生进行性改变从而引起相应的上、下运动神经元损害,所以与肌萎缩侧索硬化症相关的关键词均有较高频次。同时,氧化应激损伤页是肌萎缩侧索硬化症致病机制中重要学说之一。Shibata等
[13]学者发现在肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者脑脊液和大脑皮质中,DNA 氧化损伤的标记物:8-羟基2-脱氧鸟苷酸浓度升高, 脂质过氧化产物丙二醛含量增多, 肯定了氧化应激在肌萎缩侧索硬化症发病过程中的作用。铜锌超氧化物歧化酶是超氧化物歧化酶的一种,真核细胞的铜锌超氧化物歧化酶是32 ku的同源二聚体,每个亚基上结合1个铜和1个锌,铜对其歧化超氧阴离子的活性起着至关重要的作用,它不能被其他的金属离子代替,所以超氧化物歧化酶、Cu均有较高的频次。迄今为止,人突变超氧化物歧化酶基因老鼠是肌萎缩侧索硬化最为相似的实验动物模型,各种表达不同位点突变的转基因老鼠成为了研究肌萎缩侧索硬化的重要模型,如表达人正常铜锌超氧化物歧化酶基因的Hwt铜锌超氧化物歧化酶模型
[14]、表达A4V突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的铜锌超氧化物歧化酶A4V
[15-16]、表达G93A突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的铜锌超氧化物歧化酶G93A
[14]、表达正常铜锌超氧化物歧化酶和N端126aa的hwt铜锌超氧化物歧化酶/铜锌超氧化物歧化酶
L126Z
[17]以及表达H46R突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶的铜锌超氧化物歧化酶H46R
[18]。目前已经建立多种转基因动物模型,一些著名的转基因老鼠模型甚至已经实现商品化,如铜锌超氧化物歧化酶G
93A转基因动物模型,就可以从 Jackson Laboratory获得,这明显加速了研究进程。
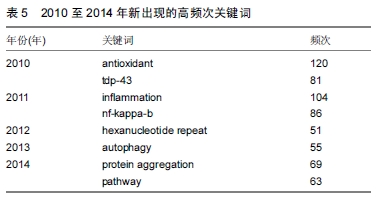
2.5 研究前沿—近5年新出现高频次关键词分析 为了对关键词有更清晰的认识,作者对不同年份出现的关键词进行了分类,排除了意思相同或相近的关键词,重点关注了近5年新出现的高频次关键词(频次高于50),它们可以一定程度上代表最近铜锌超氧化物歧化酶研究领域的研究前沿,如
表5所示。2010年新出现的关键词是antioxidant与tdp-43。Antioxidant(抗氧化剂)是指能减缓或防止氧化作用的分子,氧化是一种使电子自物质转移至氧化剂的化学反应,过程中可生成自由基,进而启动链反应。当链反应发生在细胞中,细胞受到破坏或凋亡。抗氧化剂则能去除自由基,终止连锁反应并且抑制其它氧化反应,同时其本身被氧化
[19]。有多种抗氧化酶相互作用所构成的网络能保护细胞免受氧化应激的损害,超氧化物歧化酶便是其中之一,它可以催化超氧化物阴离子分解产生氧气和过氧化氢,接着由多个不同的过氧化物酶来负责清除过氧化氢
[20]。Neumann等
[21]在肌萎缩侧索硬化症和伴有泛素阳性包涵体的额颞叶痴呆患者的神经细胞和神经胶质细胞的胞浆中发现了主要成分是tdp-43的泛素化包涵体,指出tdp-43聚集与神经元发生自主性退行性改变密切相关。而在2010年,Higashi等
[22]首次提出突变铜锌超氧化物歧化酶蛋白和TDP-43的相互作用可能与肌萎缩侧索硬化症的发病有关,但该相互作用还需大量实验验证。inflammation、nf-kappa-b是2011年新出现的3个关键词。随着近年来对多种神经系统神经退行性病变(如阿尔茨海默症、帕金森症、多发性硬化)发病机制的研究表明,胶质细胞介导的脑内慢性炎症反应可能是其重要病理特征之一,由此提出了此类疾病的炎症机制,非运动神经元细胞特别是小胶质细胞星形胶质细胞与运动神经元的相互作用在肌萎缩侧索硬化症发病中的作用日益受到关注
[23]。利用细胞转染技术,Maruyama等
[24]对视神经蛋白的突变基因Q398X与E478G进行分析发现这两种突变破坏了nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB)活性抑制作用,指出视神经蛋白基因与肌萎缩侧索硬化症的发病机制有关,而且NF-kB抑制剂能够用来治疗肌萎缩侧索硬化症。2012年新的关键词只有hexanucleotide repeat,DeJesus- Hernandez等
[25]应用高通量测序技术发现在肌萎缩侧索硬化症和FTD患者中,C9ORF72基因的第1个内含子非编码区GGGGCC六核苷酸发生了大量重复突变,通过临床系列分析发现C9ORF72上六核苷酸重复扩增是家族性FTD(11.7%)和家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症(23.5%)最常见的基因异常,是肌萎缩侧索硬化症和FTD(额颞叶痴呆)的一个主要原因。Renton等
[26]指出在C9ORF72第1个基因内区有一个六核苷酸(GGGGCC)重复扩增在影响单体型,而且这个重复扩增存在于1/3远系繁殖的欧洲血统家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症里,成为目前为止这些致命神经退行性疾病最常见的遗传原因。2013年新的关键词为autophagy。自噬(autophagy)是继凋亡(apoptosis)后,当前生命科学最热的研究领域,Pubmed记录的文献数量在最近几年呈爆炸式增长。自噬在机体的
免疫、感染、炎症、肿瘤、心血管病、神经退行性病的发病中具有十分重要的作用,可防止一些疾病的发生[27]。目前有关自噬作用研究最热的3类疾病是肿瘤、神经退行性疾病和免疫性疾病,而在神经退行性疾病中,细胞内的自噬作用可以降解异常的TDP-43,自噬作用的调控可以作为由TDP-43引起的神经退行性疾病的治疗手段之一。2014年出现了两个新关键词protein aggregation、pathway,SOD1的错误折叠与蛋白聚集与肌萎缩侧索硬化症息息相关,有实验表明在家族型和散发型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者身上发现的不可溶的蛋白聚集是免疫反应性的铜锌超氧化物歧化酶
[28]。同时,家族型与散发型肌萎缩侧索硬化症共同的分子机制一直是科研人员关注的焦点,Ivanova等
[29]发现铜锌超氧化物歧化酶C末端的两个片段
101DSVISLS
107与
147GVIGIAQ
153很有可能参与铜锌超氧化物歧化酶纤维具核化和生长的过程,它们的暴露与相互作用为家族型和散发型肌萎缩侧索硬化症提供了一个共同的分子路径。







