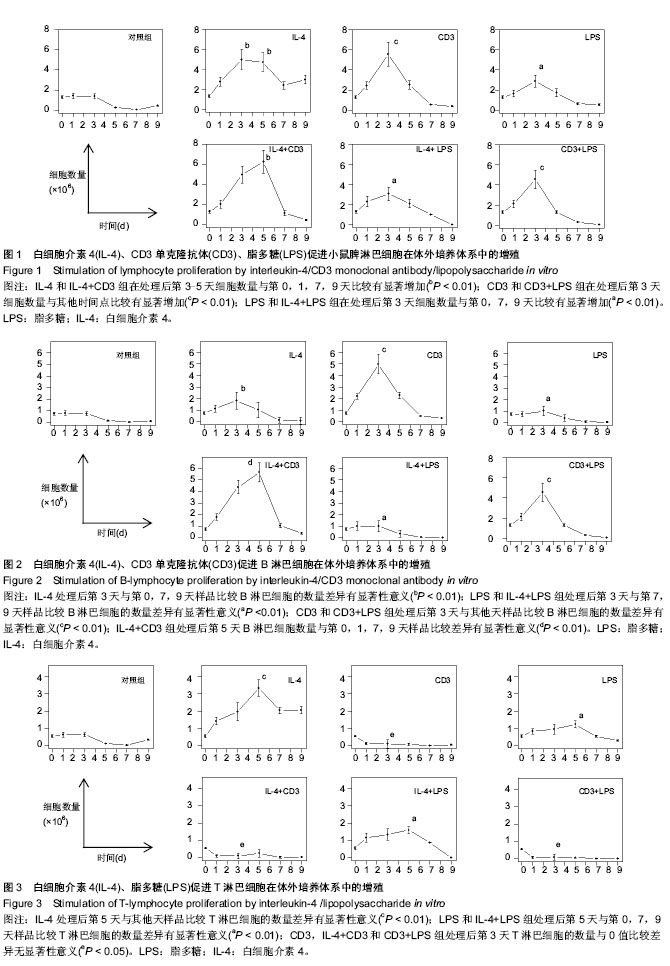
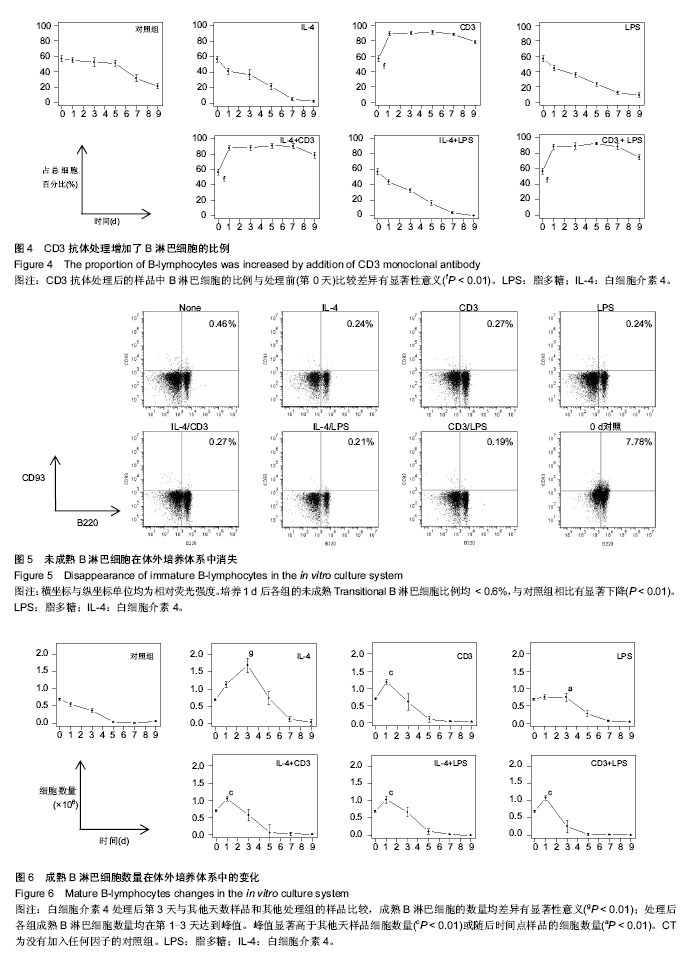
| [1] Pieper K, Grimbacher B, Eibel H. B-cell biology and development. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(4):959-971.
[2] Tobon GJ, Izquierdo JH, Canas, CA. B lymphocytes: development, tolerance, and their role in autoimmunity-focus on systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmune Dis. 2013; 2013: 827254 .
[3] Vossenkamper A, Spencer J. Transitional B cells: how well are the checkpoints for specificity understood? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2011;59(5):379-384.
[4] Khan WN, Wright JA, Kleiman E, et al. B-lymphocyte tolerance and effector function in immunity and autoimmunity. Immunol Res. 2013;57(1-3):335-353.
[5] Roth K, Oehme L, Zehentmeier S, et al. Tracking plasma cell differentiation and survival. Cytometry A. 2014;85(1):15-24.
[6] Good-Jacobson KL, Tarlinton DM. Multiple routes to B-cell memory. Int Immunol. 2012;24(7):403-408.
[7] Pone EJ, Xu Z, White CA, et al. B cell TLRs and induction of immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination, Front Biosci (Landmark. Ed). 2012;17:2594-2615.
[8] Heine G, Sims GP, Worm M, et al. Isolation of human B cell populations. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2011;Chapter 7:Unit7.
[9] Ibrahim SF, van den Engh G. High-speed cell sorting: fundamentals and recent advances. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2003;14(1):5-12.
[10] Zuccolo J, Unruh TL, Deans JP. Efficient isolation of highly purified tonsil B lymphocytes using RosetteSep with allogeneic human red blood cells. BMC Immunol. 2009;10:30.
[11] Grutzkau A, Radbruch A. Small but mighty: how the MACS-technology based on nanosized superparamagnetic particles has helped to analyze the immune system within the last 20 years. Cytometry A. 2010;77(7):643-647.
[12] Scholz Jean L, William JQ, Michael PC. B-Cell Repertoire Changes in Mouse Models of Aging. In Handbook on Immunosenescence. Springer Netherlands. 2009.
[13] Bao Y, Cao X. The immune potential and immunopathology of cytokine-producing B cell subsets: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2014;55C:10-23.
[14] Chokeshai-u-saha K, Lepoivre C, Grieco L, et al. Comparison of immunological characteristics of peripheral, splenic and tonsilar naive B cells by differential gene expression meta-analyses. Asian Pac. J Allergy Immunol. 2012;30(4): 326-330.
[15] Pi CC, Chu CL, Lu CY, et al. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma formosanum function as a Th1 adjuvant and stimulate cytotoxic T cell response in vivo. Vaccine. 2014; 32(3):401-408.
[16] Pritchard AJ, Mir AK, Dev KK. Fingolimod attenuates splenocyte-induced demyelination in cerebellar slice cultures. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99444.
[17] Rowland SL, Tuttle K, Torres RM, et al. Antigen and cytokine receptor signals guide the development of the naive mature B cell repertoire. Immunol Res. 2013;55(1-3):231-240.
[18] Giltiay NV, Chappell CP, Clark EA. B-cell selection and the development of autoantibodies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012;14 Suppl 4:S1.
[19] Zhong Y, Byrd JC, Dubovsky JA. The B-cell receptor pathway: a critical component of healthy and malignant immune biology. Semin. Hematol. 2014;51(3):206-218.
[20] Browne EP. Regulation of B-cell responses by Toll-like receptors. Immunology. 2012;136(4):370-379.
[21] Rawlings DJ, Schwartz MA, Jackson SW, et al. Integration of B cell responses through Toll-like receptors and antigen receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(4):282-294.
[22] Yu X, Lin J, Yu Q, et al. Activation of Toll-like receptor 9 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand expression in rat B lymphocytes. Microbiol Immunol. 2014;58(1):51-60.
[23] Snow AL, Pandiyan P, Zheng L, et al. The power and the promise of restimulation-induced cell death in human immune diseases. Immunol Rev. 2010;236:68-82.
[24] Wong DW, Mittal KK. HLA-DR typing: a comparison between nylon wool adherence and T cell rosetting in the isolation of B cells. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):177-186.
[25] Wohler JE, Barnum SR. Nylon wool purification alters the activation of T cells. Mol. Immunol. 2009;46(5):1007-1010.
[26] Goodnow CC, Vinuesa CG, Randall KL, et al. Control systems and decision making for antibody production. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(8):681-688.
[27] Ranasinghe C, Trivedi S, Wijesundara DK, et al. IL-4 and IL-13 receptors: Roles in immunity and powerful vaccine adjuvants. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25(4): 437-442.
[28] Granato A, Hayashi EA, Baptista BJ, et al. IL-4 regulates Bim expression and promotes B cell maturation in synergy with BAFF conferring resistance to cell death at negative selection checkpoints. J Immunol. 2014;192(12):5761-5775.
[29] Schweighoffer E, Vanes L, Nys J, et al. The BAFF receptor transduces survival signals by co-opting the B cell receptor signaling pathway. Immunity. 2013;38(3):475-488.
[30] Tan C, Wei L, Vistica BP, et al. Phenotypes of Th lineages generated by thecommonly used activation with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies differ from those generated by the physiological activation with the specific antigen. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014;11(3):305-313.
[31] Vossenkamper A, Spencer J. Transitional B cells: how well are the checkpoints for specificity understood? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz ). 2011;59(5):379-384.
[32] Chung JB, Silverman M, Monroe JG. Transitional B cells: step by step towards immune competence. Trends Immunol. 2003;24(6):342-348. |