| [1]Diaz-Corrales FJ, Asanuma M, Miyazaki I,et al. Rotenone induces aggregation of gamma-tubulin protein and subsequent disorganization of the centrosome: relevance to formation of inclusion bodies and neurodegeneration. Neuroscience. 2005;133(1):117-135.
[2]Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY,et al. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975;72:1858-1862.
[3]Geodert M,Jakes R.Expression of esparate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J.1990;9: 4225-4230.
[4]Fellous A, Francon J, Lennon AM, et al. Microtubule assembly in vitro. J. Biochem.1997;78:167-174.
[5]Mandelkow EM, Stamer K, Vogel R, et al. Clogging of axons by tau, inhibition of axonal traffic and starvation of synapses. Neurobiol Aging.2003;24(8):1079-1085.
[6]Alim MA, Hossain MS, Arima K, et al. Tubulin seeds synuclein fibril formation.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(3):2112-2117.
[7]Alim MA, Ma QL, Takeda K, et al.Demonstration of a role for synuclein as a functional microtubule-associated protein. J Alzheimers Dis. 2004;6(4):435-442.
[8]Jensen PH, Hager H, Nielsen MS,et al.synuclein binds to tau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356, J Biol Chem. 1999;(274):25481-25489.
[9]Guangwei L, Wang P, Xin L, et al. Alpha-synuclein promotes early neurite outgrowth in cultured primary neurons. Neural Transm.2013;120(9):1331-1343.
[10]Cappelletti G, Surrey T, Maci R. The parkinsonism producing neurotoxin MPP+ affects microtubule dynamics by acting as a destabilising factor. FEBS Lett. 2005; 579(21): 4781-4786.
[11]Clement MJ, Jourdain I, Lachkar S, et al, N-Terminal Stathmin-like Peptides Bind Tubulin and Impede Microtubule Assembly.Biochemistry.2005; 44(44):14616-14625.
[12]Hamel E, Sackett DL, Vourloumis D, et al. The coral-derived natural products eleutherobin and sarcodictyins A and B: effects on the assembly of purified tubulin with and without microtubule-associated proteins and binding at the polymer taxoid site. Bio-chemistry.1999;38(17): 5490.
[13]Plosker GL, Hurst M. Paclitaxel: a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in non2small cell lung cancer. Pharmacoeconomics. 2001;19(11):1111.
[14]Gunasekera SP, Gunasekera M, Longley RE, et al. Dicodermolide: a new bioactive polydroxylated lactone from the marine sponge, Discodermia dissolute. J Org Chem. 1991;56 (3):1346.
[15]Gunasekera SP,Longley RE,Isbrucker RA.Semisynthetic analogues of the microtubule2stabilizing agent discodermolide: preparation and biological activity. J Nat Prod.2002;65 (12):1830.
[16]Pryor DE, O’ Brate A, Bilcer G, et al.The microtubule stabilizing agent laulimalide does not bind in the taxoid site , kills cells resistant to paclitaxel and epothilones , and may not require its epoxide moiety for activity. Biochemistry.2002;41(29): 9109.
[17]Iqbal K, Alonso Adel C, El-Akkad E,et al. Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: therapeutic targets and high-throughput assays. J Mol Neurosci. 2003; 20(3):425-429.
[18]Delacourte A, Sergeant N, Champain D, et al. Nonoverlapping but synergetic tau and APP pathologies in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology.2002;59(3):398-407.
[19]王建枝,刘世杰.神经退行性疾病神经细胞死亡机理[J].国外医学:分子生物学分册, 2003, 25(1):41-44.
[20]Amadoro G, Serafino AL, Barbato C, et al. Role of N-terminal tau domain integrity on the survival of cerebellar granule neurons. Cell Death Differ.2004; 11(2):217-230.
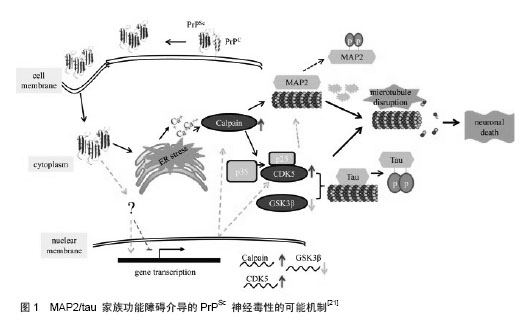
[21]Zhang J, Dong XP. Dysfunction of microtubule-associated proteins of MAP2/tau family in Prion disease.Prion. 2012;6(4): 334-338.
[22]Wolfe MS.Tau mutations in neurodegenerative diseases.J Biol Chem.2009;284(10):6021-6025.
[23]Souter S, Lee G.Tubulin-independent tau in Alzheimer's disease and cancer: implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment.Curr Alzheimer Res.2010;7(8):697-707.
[24]Baird FJ, Bennett CL.Microtubule defects & Neurodegeneration.J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2013;4:203.
[25]Yu D, LaPointe NE, Guzman E,et al.Tau proteins harboring neurodegeneration-linked mutations impair kinesin translocation in vitro.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;39(2):301-314.
[26]Brunden KR, Yao Y, Potuzak JS,et al.The characterization of microtubule-stabilizing drugs as possible therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies.Pharmacol Res. 2011;63(4):341-351. |