Design
A randomized controlled animal experiment.
Time and setting
This study was performed in the Institute of Basic Medical, Chengde Medical College in China from September 2012 to November 2013.
A total of 72 adult, clean, male, Sprague-Dawley rats, weighting 250-300 g and aged 12-14 weeks, were provided by Beijing Tonglihua Experimental Animal Technical Co., Ltd. (case number: SCXK (Jing) 2012- 0001). All rats lived in the same room, were allowed free access to water and ventilated. All experimental procedures were in accordance with the Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, formulated by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Drugs
Total Flavone of Hawthorn Leaf was gathered from Chengde local hawthorn leaves from July to August. Total Flavone of Hawthorn Leaf was extracted by water frying alcohol sinking method, with a purity of 65.2%.
Ginkgo leaf was provided by China Yantai Rongchang as long as the Cable Co., Ltd.
.jpg)
Methods
Experimental groups
All 72 rats were randomly divided into sham surgery group, model group, Total Flavone of Hawthorn Leaf group and ginkgo leaf group.
Establishment of rat models of chronic cerebral ischemia by ligating bilateral common carotid artery
Using the method called permanent bilateral carotid artery ligation[6], chronic cerebral ischemia model was prepared. The animals were anesthetized with 30 mg/kg sodium pentobarbital by enterocoelia injection. A median sagittal incision was made on the neck, followed by blunt dissection of the subcutaneous tissue and fascia, freed bilateral carotid artery at the carotid triangle, double ligation both sides of carotid arteries, and cut from the middle by electric knife, and then the incision was sutured. Bilateral carotid artery was only separated, without ligating in the sham surgery group. After natural awakening, in accordance with Longa’s standard[7], there was 5 levels 4 scores, 1 to 3 scores in the experimental groups.
Drug intervention
At 36 days postoperation, rats in the Total Flavone of Hawthorn Leaf and ginkgo leaf groups were respectively given Total Flavone of Hawthorn Leaf 140 mg/kg per day (equivalent to twice the clinical dose) and gingko leaf 12.3 mg/kg per day (equivalent to one time the clinical dose) by gavage for 36 days. Sham surgery group and model group were given the saline 3.5 mL/kg per day .
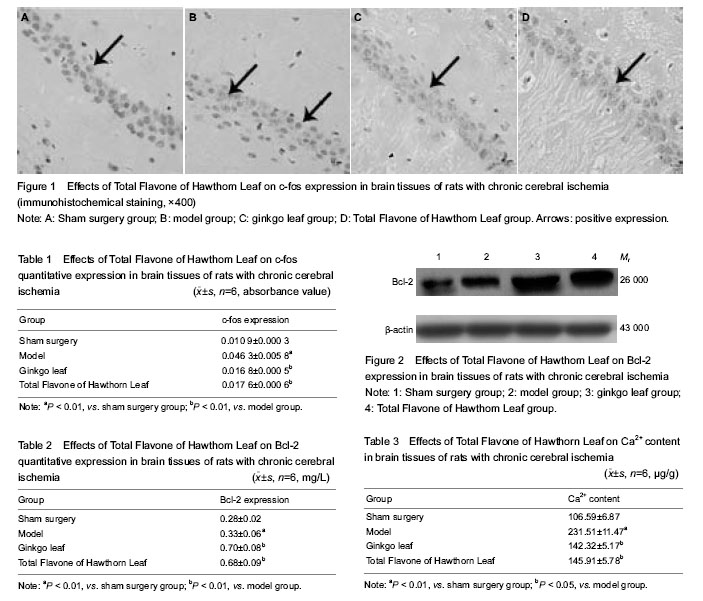
Immunohistochemical detection of c-fos expression in the rat brain
At 1 hour after the last drug given, aniamls were anesthetized with 4% chloral hydrate, followed by heart perfusion and fixation with 10% formaldehyde. Brain tissue was taken out which was 2 mm to 8 mm behind optic chiasma, conventionally paraffin embed, and sliced into 5 µm coronal slices. Slices were dewaxed with the dimethy lbenzene, dehydrated by graded alcohol, incubated with 0.3% H2O2 for 30 minutes, and blocked by goat serum for 30 minutes. Subsequently, c-fos antibody (1:100) 40 µL was added in 4 ℃ refrigerator for a night. Then sections were incubated with biotin-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG 50 μL for 30 minutes, visualized for 5 minutes with 3,3'-diaminobenzidine, counterstained by hematoxylin, dewatered in gradient alcohol, permeabilized, and mounted with neutral gum, and then observed under the optical microscope (400 ×; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Absorbance of the product was analyzed which was positive expression by MINT image analysis system (Xingwan Electronics Factory, Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China).
Western blot assay of Bcl-2 expression in the rat brain
At 1 hour after the last drug given, animals were decapitated, leptomeninges was peeled. Brain tissue was taken out which was 2 to 8 mm behind optic chiasma. The tissue was washed with 0.01 mol/L PBS. Lysate and 10 µL phenylmethyl sulfonylfluoride (10 mg/mL) were added, followed by 4 ℃ homogenate, centrifugation at 10 000 r/min for 30 minutes. The supernatant was taken for protein quantization by BCA protein assay kit. After sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electropheresis, samples were transferred to membrane, which were blocked with 10% skim milk powder, and then treated with Bcl-2 primary antibody (1:150), overnight at 4 ℃, followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody (1:1 000) at room temperature for 2.5 hours. Super ECL Plus ultra-sensitive luminescent liquid was used. Samples were exposed in X-ray film cassette and developed by D72 developer. The Quantity One software (Discovery Series, USA) was utilized to analyze the grey value of X-ray film.
Spectrophotometry of the content of Ca2+ in the rat brain
At 1 hour after the last drug given, the rats were decollated. Brain tissue was gotten out and leptomeninges was peeled. The tissue was rinsed with ultrapure water to remove residual blood, baked in oven at 60 ℃ for 48 hours, and then weighed by analytical balance. Concentrated nitric acid was added to digest the tissue into solution gradually. Samples were diluted with 1% CaCl2. In the end, spectrophotometry was used to detect the content of Ca2+ in the sample.
Main outcome measures
There were expressions of c-fos and Bcl-2, as well as the content of Ca2+ in the rat brain.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean±SD, and analyzed using SPSS16.0 statistical software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). One-way analysis of variance was utilized to analyze the comparison between groups. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
.jpg)