中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (38): 6146-6152.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.38.014
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
模拟4 000 m高住及抗炎活血解痉中药干预力竭运动大鼠肾细胞超微结构变化
林喜秀1,2,赵用强1,谢亚萍1,邱继旺1,罗自强2,瞿树林3
- 1湖南工业大学体育学院,湖南省株洲市 412000;2中南大学基础医学院博士后流动站,湖南省长沙市 410000;3湖南师范大学医学院,湖南省长沙市 410012
A Chinese herb for anti-inflammation, blood circulation promotion and spasmolysis improves renal ultrastructure of rats undergoing 4-week exhaustive exercise at simulated altitude of 4 000 meters
Lin Xi-xiu1, 2, Zhao Yong-qiang1, Xie Ya-ping1, Qiu Ji-wang1, Luo Zi-qiang2, Qu Shu-lin3
- 1Physical Education College of Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412000, Hunan Province, China; 2Postdoctoral Station, College of Basic Medicine, Central South University, Changsha 410000, Hunan Province, China; 3Medical College of Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
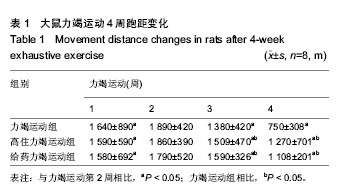
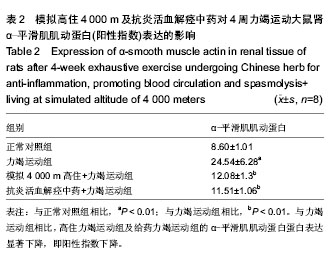
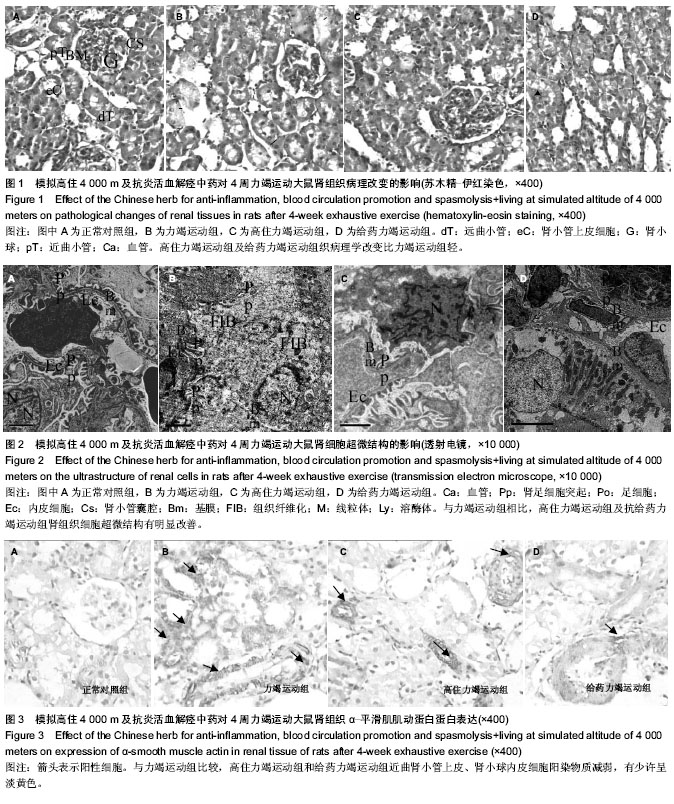
背景:抗炎活血解痉中药具有修复肾脏组织,改善肾脏血液供应,降低肾小球毛细血管的通透性,增强肾小管的滤过功能的作用。 目的:探讨模拟4 000 m高住及抗炎活血解痉中药对4周力竭运动大鼠肾细胞超微结构及α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达的影响。 方法:将大鼠在速度为10 m/min坡度为0的跑台上进行适应性跑15 min,筛选出32只能完成跑的大鼠,随机分为正常对照组、力竭运动组、高住力竭运动组和给药力竭运动组,每组8只。正常对照组不进行运动,其他3组均进行力竭运动。高住力竭运动组模拟4 000 m高住后再进行力竭运动;给药力竭运动组先给予抗炎活血解痉中药灌胃,再进行4周力竭运动。采用苏木精-伊红染色、透射电子显微镜观察各组大鼠肾细胞的超微结构,免疫组织化学法检测肾组织α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达。 结果与结论:力竭运动组可出现慢性肾损伤,肾小球滤过膜3层超微结构破坏,肾小管间质大量纤维化改变。与力竭运动组相比,高住力竭运动组和给药力竭运动组大鼠的运动量(跑距)增强(P < 0.05),肾超微结构的损伤有明显的改善,α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达显著下降(P < 0.01)。结果证实,抗炎活血解痉中药灌胃与模拟 4 000 m高住干预对4周力竭运动诱导的肾超微结构损伤起保护作用。
中图分类号: