| [1] 史跃,黄玉杰,蔡廷江,等.Willis环周围窄颈动脉瘤与栓塞材料选择的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(3):547-550. [2] Huang YM, Chou IC, Jiang CP, et al. Finite element analysis of dental implant neck effects on primary stability and osseointegration in a type IV bone mandible. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1):1407-1415. [3] Lu S, Li T, Zhang Y, et al. Biomechanical optimization of the diameter of distraction screw in distraction implant by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2013;43(11):1949-1954.[4] Cift H, Deniz S, Ek?io?lu F. Determination of the effect on the proximal femoral load distribution of diaphyseal cement support in femoral intertrochanteric fractures with calcar defect by finite element analysis. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2013;24(3):163-168. [5] von Sachsen S, Senf B, Burgert O, et al. Stent graft visualization and planning tool for endovascular surgery using finite element analysis. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2013, in press.[6] Weichert F, Walczak L, Fisseler D, et al. Simulation of intra-aneurysmal blood flow by different numerical methods. Comput Math Methods Med. 2013;2013:527654. [7] Gambaruto AM, Janela J, Moura A, et al. Sensitivity of hemodynamics in a patient specific cerebral aneurysm to vascular geometry and blood rheology. Math Biosci Eng. 2011;8(2):409-423.[8] Chang HS. Simulation of the natural history of cerebral aneurysms based on data from the International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2006; 104(2):188-194.[9] Ohshima T, Miyachi S, Hattori K, et al. Risk of aneurysmal rupture: the importance of neck orifice positioning-assessment using computational flow simulation. Neurosurgery. 2008;62(4):767-775. [10] Ma B, Lu J, Harbaugh RE, et al. Nonlinear anisotropic stress analysis of anatomically realistic cerebral aneurysms. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1):88-96.[11] Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, et al. Fluid-structure interaction modeling of aneurysmal conditions with high and normal blood pressures. Comput Mech. 2006;38(4): 482-490. [12] 曾堃.不同截面支架治疗囊状和梭形动脉瘤的流固耦合数值模拟研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2012. [13] 王芙昱,许百男,孙正辉,等.基于CTA影像数据的个体化颅内动脉瘤的流固耦合力学模型[J].南方医科大学学报, 2012,32(10): 1407-1414.[14] Sende J, Jabre P, Leroux B, et al. Invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring in an out-of-hospital setting: an observational study. Emerg Med J. 2009;26(3):210-212. [15] Hager H, Mandadi G, Pulley D, et al. A comparison of noninvasive blood pressure measurement on the wrist with invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring in patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2009;19(6): 717-724. [16] Cao H, Norris P, Ozdas A, et al. A simple non-physiological artifact filter for invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring: a study of 1852 trauma ICU patients. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;1:1417-1420.[17] Cebral JR, Löhner R. From medical images to anatomically accurate finite element grids. Inter J Numer Method Eng. 2001;51(8):985-1008. [18] Pedley TJ. The Fluid Mechanics of Large Blood Vessels. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. 1980.[19] Qiao A, Liu Y. Influence of graft-host diameter ratio on the hemodynamics of CABG. Biomed Mater Eng. 2006;16(3): 189-201.[20] Aenis M, Stancampiano AP, Wakhloo AK, et al. Modeling of flow in a straight stented and nonstented side wall aneurysm model. J Biomech Eng. 1997;119(2):206-212.[21] 付文宇,乔爱科.基于个性化颈内动脉瘤模型的流固耦合分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(4):421-426. [22] 闫亭亭,刘芳芳,陈雪,等.三角形截面丝裸支架治疗梭形颅内动脉瘤的流固耦合数值模拟研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012, 29(5):867-871. [23] Di Martino ES, Guadagni G, Fumero A, et al. Fluid-structure interaction within realistic three-dimensional models of the aneurysmatic aorta as a guidance to assess the risk of rupture of the aneurysm. Med Eng Phys. 2001;23(9):647-655.[24] Wani A, Behari S, Lyndoh B, et al. Multiple aneurysms associated with agenesis of internal carotid artery. Turk Neurosurg. 2011;21(1):83-85.[25] Kaminogo M, Yonekura M, Shibata S. Incidence and outcome of multiple intracranial aneurysms in a defined population. Stroke. 2003;34(1):16-21. [26] Matouk CC, Mandell DM, Günel M, et al. Vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging identifies the site of rupture in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms: proof of principle. Neurosurgery. 2013;72(3):492-496.[27] Li M, Lin N, Wu J, et al. Multiple intracranial aneurysms associated with multiple dural arteriovenous fistulas and cerebral arteriovenous malformation. World Neurosurg. 2012;77(2):398.E11-15. [28] Auricchio F, Conti M, Ferrara A, et al. Patient-specific finite element analysis of carotid artery stenting: a focus on vessel modeling. Int j numer method biomed eng. 2013;29(6):645- 664.[29] Bahraseman HG, Hassani K, Khosravi A, et al. Estimation of maximum intraventricular pressure: a three-dimensional fluid-structure interaction model. Biomed Eng Online. 2013; 12:122. [30] Le TB, Sotiropoulos F. Fluid-structure interaction of an aortic heart valve prosthesis driven by an animated anatomic left ventricle. J Comput Phys. 2013;244:41-62.[31] Morris PP, Choi IS. Cerebral vascular anatomy. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1996;6(3):541-560.[32] Liu B, Wang X, Zhu H, et al. ANSYS simulation of subcutaneous pustule electrical characteristics. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011;28(6):1110-1113.[33] Hu Z, Lu P, Xie H, et al. The study of noninvasive ventilator impeller based on ANSYS. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011;28(3):456-459.[34] Peng D, Yu F, Hu J, et al. Boundary conditions for simulating large SAW devices using ANSYS. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2010;57(8):1712-1714. [35] Qi R, Ng D, Cormier BR, et al. Numerical simulations of LNG vapor dispersion in Brayton Fire Training Field tests with ANSYS CFX. J Hazard Mater. 2010;183(1-3):51-61.[36] Salvi D, Boldor D, Ortego J, et al. Numerical modeling of continuous flow microwave heating: a critical comparison of COMSOL and ANSYS. J Microw Power Electromagn Energy. 2010;44(4):187-197.[37] 郭星辉,崔海坡,徐秀林.平衡功能障碍康复训练装置的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26):4863-4866. [38] 陈纪宝,奚春阳,焦力刚,等.有限元分析在腰椎生物力学应用中的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26):4908-4912. [39] 黄宇文.有限元分析在口腔生物力学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2423-2426. [40] 吴克启,舒朝晖.高等流体力学[M].北京:中国电力出版社,2009.[41] 伍悦滨.高等流体力学[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2013.[42] 王松岭.高等工程流体力学[M].北京:中国电力出版社,2011.[43] Hynecek RL, Sadek M, Derubertis BG, et al. Evaluation of pressure transmission and intra-aneurysmal contents after endovascular repair using the Trivascular Enovus expanded polytetrafluoroethylene stent graft in a canine model of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2007;46(5):1005- 1013. [44] Timaran CH, Ohki T, Veith FJ, et al. Influence of type II endoleak volume on aneurysm wall pressure and distribution in an experimental model. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41(4):657-663.[45] Takeuchi S, Karino T. Flow patterns and distributions of fluid velocity and wall shear stress in the human internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries. World Neurosurg. 2010 Mar; 73(3):174-85; discussion e27. [46] Yosibash Z, Tal D, Trabelsi N. Predicting the yield of the proximal femur using high-order finite-element analysis with inhomogeneous orthotropic material properties. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2010;368(1920):2707-2723. [47] Schwiedrzik JJ, Wolfram U, Zysset PK. A generalized anisotropic quadric yield criterion and its application to bone tissue at multiple length scales. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2013;12(6):1155-1168. [48] Wang F, Xu B, Sun Z, et al. [Individualized fluid-solid coupled model of intracranial aneurysms based on computed tomography angiography data]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012;32(10):1407-1414. [49] Bai-Nan X, Fu-Yu W, Lei L, et al. Hemodynamics model of fluid-solid interaction in internal carotid artery aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev. 2011;34(1):39-47. [50] Mieth A, Revermann M, Babelova A, et al. L-type calcium channel inhibitor diltiazem prevents aneurysm formation by blood pressure-independent anti-inflammatory effects. Hypertension. 2013;62(6):1098-1104. [51] Gaál EI, Salo P, Kristiansson K, et al. Intracranial aneurysm risk locus 5q23.2 is associated with elevated systolic blood pressure. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3):e1002563. |
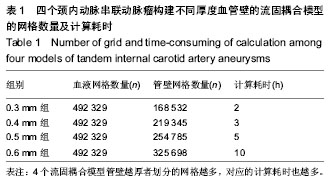
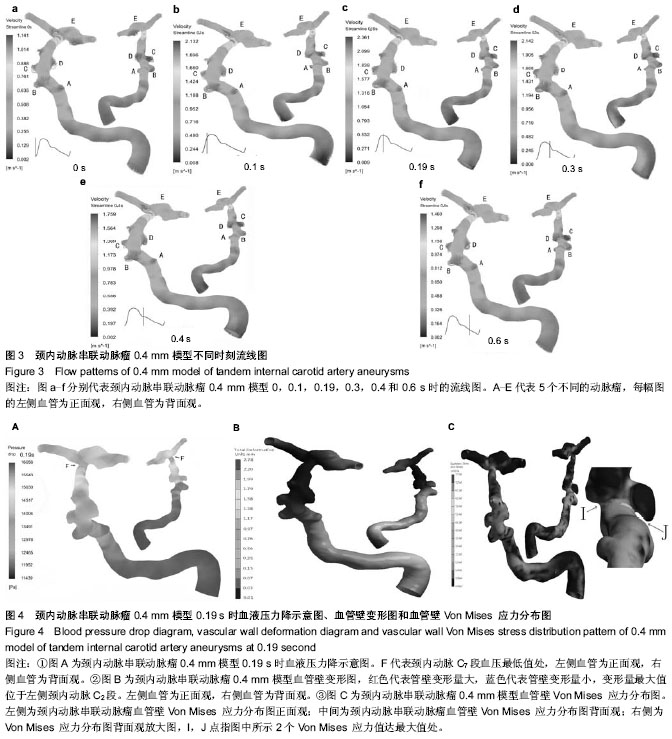

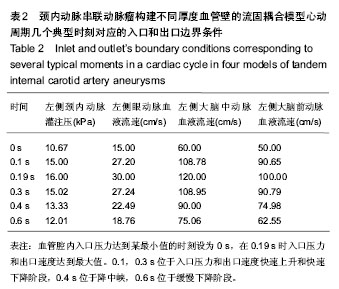
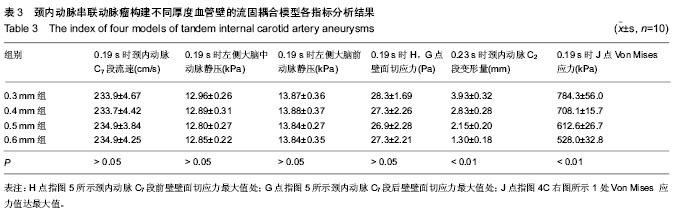
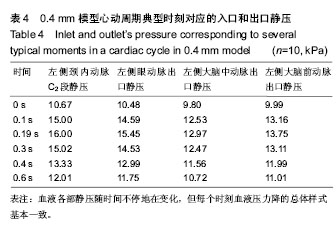
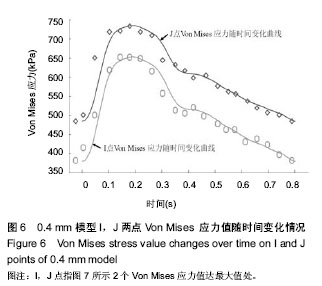
.jpg)
.jpg)