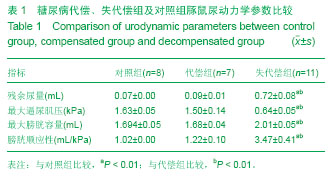
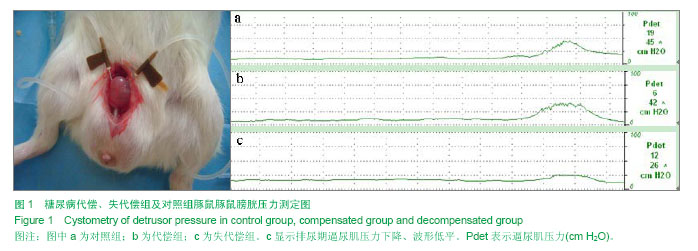
| [1] Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12): 1090-1101.[2] Daneshgari F and Moore C. Diabetic uropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2006;26(2):182-185.[3] Golbidi S, Laher I. Bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol. 2010;1:136.[4] Lin TL, Chen GD, Chen YC, et al. Aging and recurrent urinary tract infections are associated with bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51(3): 381- 386.[5] Gomez CS, Kanagarajah P, Gousse AE. Bladder dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Curr Urol Rep. 2011;12(6):419-426. [6] Lee WC, Wu HP, Tai TY, et al. Investigation of urodynamic characteristics and bladder sensory function in the early stages of diabetic bladder dysfunction in women with type 2 diabetes. J Urol. 2009;181(1):198-203.[7] Alimohammadi S, Hobbenaghi R, Javanbakht J, et al. Protective and antidiabetic effects of extract from Nigella sativa on blood glucose concentrations against streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic in rats: an experimental study with histopathological evaluation. Diagn Pathol.2013;15(8):137- 144.[8] Chaudhry ZZ, Morris DL, Moss DR, et al. Streptozotocin is equally diabetogenic whether administered to fed or fasted mice. Lab Anim. 2013;47(4):257-265. [9] 孙丽华,崔海峰,孙明杰,等.链脲佐菌素制备糖尿病大鼠模型探讨[J].中国实验动物学报,2012,12(6):15-19.[10] Li Y, Sun Y, Zhang Z, et al. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 are associated with bladder dysfunction in an experimental diabetic rat model. BJU Int. 2013;112(2):E143-150.[11] Jiang YJ, Gong DX, Liu HB, et al. Ability of alpha-lipoic acid to reverse the diabetic cystopathy in a rat model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008n;29(6):713-719. [12] Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, Goins WF, et al. Gene therapy using replication-defective herpes simplex virus vectors expressing nerve growth factor in a rat model of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes. 2004;53(10):2723-2730.[13] Mustafa S. Effect of diabetes on the ion pumps of the bladder. Urology. 2013;81(1):211.e17-21. [14] Wang Z, Cheng Z, Cristofaro V, et al. Inhibition of TNF-α improves the bladder dysfunction that is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(8):2134-2145. [15] Bansal R, Agarwal MM, Modi M, et al. Urodynamic profile of diabetic patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: association of diabetic cystopathy with autonomic and peripheral neuropathy. Urology. 2011;77(3):699-705. [16] Li WJ, Oh SJ. Diabetic cystopathy is associated with PARP/JNK/mitochondrial apoptotic pathway-mediated bladder apoptosis. Neurourol Urodyn.2010;29(7):1332-1337. [17] Saito M,Wada Y,Ireda K,et al.Gene expression,localization, and pharmacololgical characterization of endothelin receptors in diabetic rat bladder dome.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;387(3): 253-263.[18] 李世芬,王心如,王玉翠,等.SD大鼠糖尿病肾病模型构建的比较[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2010,30(8):1123-1128.[19] Joseph DiMattio. Alterations in ascorbic acid transport into the lens of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and guinea pig. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33(10):2926-2935.[20] Hagstroem S, Kamperis K, Rittig S, et al. Monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis is associated with abnormal nocturnal bladder emptying.J Urol.2004;171(6 Pt. 2):2562-2566.[21] Daneshgari F, Huang X, Liu G, et al. Temporal differences in bladder dysfunction caused by diabetes, diuresis, and treated diabetes in mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006; 290(6):R1728-1735.[22] Kebapci N, Yenilmez A, Efe B, et al. Bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients. Neurourol Urodyn. 2007;26(6):814-819.[23] Daneshgari F, Leiter EH, Liu G, et al. Animal Models of Diabetic Uropathy. J Urol. 2009;182(6 Suppl):S8-13.[24] 曹石金,何朝辉,李逊,等.糖尿病大鼠膀胱结构与功能的改变[J]. 广东医学,2012,33(16):2372-2375.[25] 冯建华,邓丽萍,曾祥建,等. 糖尿病大鼠膀胱逼尿肌超微结构的改变[J]. 中国热带医学,2012,12(1):15-17.[26] Daneshgari F, Liu G, Imrey PB. Time dependent changes in diabetic Cystopathy in rats include compensated and decompensated bladder function. J Urol. 2006;176(1): 380-386.[27] 李维仁,王勤章,丁国富,等.豚鼠糖尿病膀胱模型的建立[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2008,13(5):368-370.[28] Lee MS,Song KD,Yang HJ, et al. Development of a type II diabetic mellitus animal model using micropig. Lab Anim Res. 2012;28(3):205-208.[29] Turner WH,Brading AF. Smooth muscle of the bladder in the normal and the diseased state: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 1997;75(2):77-110.[30] 毕铮铮,郭剑超,郑少雄,等.早期糖尿病性膀胱病的无创尿动力学变化[J].中国医师进修杂志,2010,32(7):19-21.[31] 高宏飞,王东文.2型糖尿病膀胱重构的受体机制研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2013,11(6):716-718.[32] Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, GoinsS WF, et al. Gene therapy using replication-defective herpes simplex virus vectors expressing nerve growth factor in a rat model of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes. 2004;53(10):2723-2730.[33] Kikuno N, Kawamoto K, Hirata H, et al. Nerve growth factor combined with vascular endothelial growth factor enhances regeneration of bladder acellular matrix graft in spinal cord injury-induced neurogenic rat bladder. BJU Int. 2009;103(10): 1424-1428.[34] Ichiyanagi N, Tsujii T, Masuda H, et al. Changed responsiveness of the detrusor in rabbits with alloxan induced hyperglycemia: possible role of 5-hydroxytryptamine for diabetic bladder dysfunction. J Urol. 2002;168(1):303-307.[35] Bezuijen MW,Levendusky MC,Longhurst PA.Functional response of bladder strips from streplozotocon diabetic rats depends on bladder mass. J Uro. 2003;169(6):2397-2401.[36] Oberbach A, Jehmlich N, Schlichting N, et al. Molecular fingerprint of high fat diet induced urinary bladder metabolic dysfunction in a rat model. PLoS One. 2013;8(6): e66636. [37] Kanika ND, Chang J, Tong Y, et al. Oxidative stress status accompanying diabetic bladder cystopathy results in the activation of protein degradation pathways. BJU Int. 2011; 107(10):1676-1684. [38] Li Y, Sun Y, Zhang Z, et al. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 are associated with bladder dysfunction in an expenrimental diabetic rat model. BJU Int. 2013;112(2):E140-150.[39] Leiria LO, Mónica FZ, Carvalho FD, et al. Functional, morphological and molecular characterization of bladder dysfunction in streptozotocin-induceddiabetic mice: evidence of a role for L-type voltage-operated Ca2+ channels. Br J Pharmacol.2011;163(6):1276-1288.[40] Fedele D. Therapy insight: sexual and bladder dysfunction associated with diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005; 2(6):282-290. [41] Van Poppel H, Stessens R, Van Damme B, et al. Diabetic cystopathy: neuropathological examination of urinary bladder biopsies. Eur Urol.1998;15(1-2):128-131.[42] Brown JS, Wessells H, Chancellor MB, et al. Urologic complications of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(1):177-185.[43] 郭学敬,白艳,王秀丽,等. 神经生长因子对糖尿病大鼠膀胱病变的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(9):1909-1911.[44] Apodaca G. The uroepithelium: not just a passive barrier. Traffic. 2004;5(3):117-128.[45] Apodaca G, Kiss S, Ruiz W, et al. Disruption of bladder epithelium barrier function after spinal cord injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.2003;284(5):F966-976.[46] 李云飞,丁国富,蔡志强,等. 豚鼠糖尿病性膀胱病逼尿肌中c-kitmRNA和蛋白的表达变化及意义[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2010,25(2):345-348.[47] Kanika ND, Chang J, Tong Y, et al. Oxidative stress status accompanying diabetic bladder cystopathy results in the activation of protein degradation pathways. BJU Int. 2011; 107(10):1676-1684. [48] Johnston L, Carson C, Lyons AD, et al. Cholinergie induced Ca^2+ signaling in interstitial cells of Cajal from the guinea pig bladder. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294(3):R645- R655.[49] Lee WC, Wu CC, Wu HP, et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and uroflowmetry in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without bladder dysfunction. Urology. 2007;69(4): 685-690.[50] Li WJ, Shin MK, Oh SJ. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is involved in the development of diabetic cystopathy via regulation of nuclear factor kappa B. Urology. 2011;77(5): 1265.e1-8.[51] Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A, et al. Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;335(3):517-527. |