血液是在循环系统中,心脏和血管腔内循环流动的一种组织,由血浆和血细胞组成。血细胞包括红细胞、白细胞和血小板。因为血液在心血管内循环流动,遍及全身,它保持着整个身体与外界环境间的联系,也维持着各器官组织间的相互联系,一旦血液的总量过分减少,或其组成成分发生异常变化,都可引起严重的后果。
一般健康人血液占全身体质量的7%-8%,如果一次失血不超过总血量的10%,对身体影响不太大。当一次失血超过总血量的20%时,则对健康有严重影响;超过总血量的30%时就会危及生命。输血是临床上抢救危重患者和治疗某些疾病的一项重要措施。
近百年来,人口数量剧增,环境污染加重等因素导致外伤、疾病增加,随着科学的发展,历史的进步,心血管外科、矫形外科、移植外科、神经外科及急诊手术广泛开展,手术期间失血和输血问题日益突出。
中国每年用血量800-1 000吨,并以每年10%的速度增长,临床用血日益增多,血源日趋紧张,且异体输血有传播肝炎、爱滋病,输错血型导致溶血等危险,使血红蛋白氧离曲线左移,组织供氧减少,诱发多器官功能衰竭,酸中毒,凝血功能异常,DIC,还可引起免疫抑制,使术后感染发生率升高。
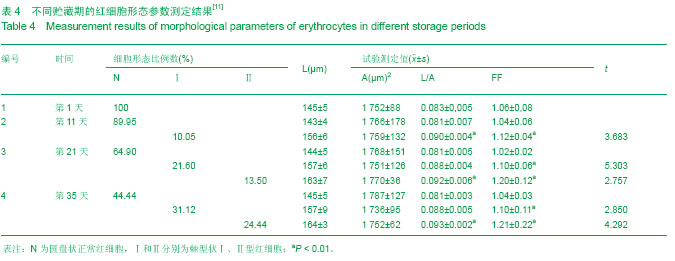
库血制备包括血液采集和血液贮藏。在一定血液贮藏期内、一定的贮藏条件下,贮藏对库血的质量不产生实质影响。但随着保存时间的延长,或环境因素及其血液生理生化特性等受到影响,会引起红细胞物理化学特性以及结构形态的变化[11]。
红细胞形态变化可反映红细胞黏滞度的变化,目前已证实贮藏期血液红细胞黏滞度发生改变,可对输血后红细胞存活率和心血管系统的血液黏滞度产生影响。随着库血贮藏时间延长,所使用的保存液会引起血液悬浮液中乳酸和丙酮酸水平上升,以至于出现红细胞形态学的变化
(表4)
[11]。
.jpg)
自体血回输避免了上述缺点,是避免或减少异体输血的有效方法,有其优越性,具体表现在:及时提供完全相容的同型血液,缓解血源紧张;自体血回输通常不需配型及疾病检验,避免了这些操作过程中出现的失误;避免输血所致感染HBV、HCV、HIV等病毒所致疾病的危险;几乎避免异体输血所致的发热、过敏、溶血及移植物抗宿主反应和机体免疫抑制;自体血储存的红细胞的ATP及
2,3-DPG含量均高于库血,有较好的携氧功能;避免了异体输血所致的高钾、低钙血症及代谢性酸中毒。
中国很多城市的医院都在提倡和实践自体输血技术,以外科整形手术、创伤手术和心脏手术运用较多。相比一线城市,基层医院由于缺乏细化的法规及对自体输血全程进行管理,也导致一些患者对于该技术是否安全提出了怀疑。
在中国,献血全过程统一由地方血站完成,而自体输血则完全由医院来操作。卫生部要求,三级综合医院自体输血比例要达到15%。然而,国内目前自体输血比例很低,仅占1%左右。一台血细胞回输仪价值几十万元,每次使用的基本耗材费用在1 100-1 900元之间。相比从血液中心取的每袋230块钱的血,回收所用的价格确实高了不少。术前自体储备血(PAD)由于比较费时费力,患者取血时痛苦,其效价比受到质疑。而急性等容血液稀释不仅可以节省用血而且可以有效避免异体输血带来的风险[12]。
随机对照研究的Meta分析报告表明,急性等容血液稀释可减少31%术中异体输血,平均每个患者减少1.9单位输血量。急性等容血液稀释提供新鲜的自体血液成分,仅在手术当天实施,价格和费用更低,可避免血型检测和储存,也没有废弃的问题,且在一定程度上更为方便、效价比更高。尽管急性等容血液稀释在收集血液时需要一些时间和良好的静脉通路,但费用可能是几种自体输血中成本最低的。
急性等容血液稀释自体输血简便又经济,但由于液状保存期、储血量有一定的限度,且保存中的血液成分的变化不能避免[13-14],安全使用尤为重要。研究证明红细胞储存早期就有S-亚硝基硫醇降低,然而S-亚硝基硫醇含量将有利于红细胞输血患者,温度和时间是影响红细胞功能的最重要因素[15-16],急性等容血液稀释采血后放入4 ℃低温贮存,既增加了开展急性等容血液稀释成本,又带来繁琐的工作(标记患者姓名、住院号、存取、复温、反复核对),还可能增加输错血的风险;若没有条件保存在4 ℃条件下,室温保存(手术室23 ℃),如果估计6 h内可以回输的患者,采集的自体血液常温贮存,红细胞变形率及发生细菌繁殖的危险究竟有多大?
众所周知,红细胞的完整性、变形能力、体积和形态等同红细胞的功能密切相关,通过显微镜下观察红细胞的体积形态可用来研究红细胞的功能[17],红细胞是血液中最主要的成分,其生理功能主要是运输氧和二氧化碳。
哺乳动物正常红细胞静态时其形状为双凹圆盘形,人的红细胞直径6-9 µm,中央厚度1 µm,边缘厚度214 µm,表面积103-163 µm2,容积86-90 µm3,红细胞的这种形态特点有利于红细胞变形,这取决于红细胞具有较大的表面积(S)与体积(V)之比[18]。在正常情况下,其表面积S/V>1.5,这有利于红细胞经历多种变形而无需增加其表面积。当S/V等于1.0,红细胞呈星球形;当S/V等于0.7,红细胞则呈椭圆球形。后二者均会使得红细胞变形性下降[19],导致红细胞通过毛细血管为组织供氧能力下降。
通过对比23 ℃常温贮存和4 ℃贮存不同时间点的红细胞畸形率,来观察自体血后贮存在23 ℃常温下6 h以内,与贮存在4 ℃下的自体血的红细胞形态差异,确保常温贮存自体血的安全性和可行性。经过专业人员取样、涂片,并选取红细胞稀疏程度适中,计数红细胞总数及异常细胞数,取均数作比较,发现两组在所有观察时间的红细胞变形率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)(表3),确保自体血贮存在23 ℃常温下6 h以内红细胞形态功能正常。常温下贮存自体血简单易行,费用较低,安全可靠,基本不受医疗条件限制,有很大的临床推广价值。
有关研究证明,由于血液在低温保存期间仍进行缓慢的代谢,释放的乳酸和CO2等可使血液的PH值降低,伴随细胞膜电压发生改变,Ca2+-ATPase 活性降低,增加了细胞内Ca2+浓度,钙超载使红细胞膜丧失其柔韧应变的性质,变得僵硬[20],进一步导致细胞膜破裂,细胞内K+大量释放、游离血红蛋白增加。所以pH、K+、游离血红蛋白是反应血液储存状态较理想指标,库血红细胞保存期间平均以每天1%的速度死亡,红细胞形态在保存第2周即出现显著性变化,并随时间延长出现进行性改变。随着血液23 ℃常温贮存时间延长,血液内环境会发生不同程度的变化,所以对 6 h段的23 ℃常温血样随机选择了6份与有效期内的ACD库存血样进行血气生化对比(表2),发现23 ℃常温血样pH、K+、游离血红蛋白等与当天库存血参数十分接近,远远优于7,14,21 d库存血参数,非常接近生理值,pH直接反应红细胞糖酵解中乳酸水平,pH越低说明糖酵解越多,K+和游离血红蛋白值的升高说明红细胞破坏越多,通过血气生化对比,发现6 h内储存在23℃常温下的自体血优于有效期内的ACD库存血。
无菌是血液保存安全性基本而极其重要的指标,细菌培养阴性是血液保存研究的基本要求,有关报道已经证实红细胞贮存有常温下72 h血培养阴性结果[21],本文也对6 h段的两组血样随机选择了6份进行血培养,结果同报道一致。
从图表可以看出无论在常温和低温下红细胞畸形率变化趋势6 h内变化不大,虽然第4 h和第5 h红细胞畸形率有所下降,但差异无显著性意义。对于自体血常温下贮存大于6 h的红细胞畸形率及变化趋势和自体血内的血浆成分变化有待进一步研究。


.jpg)