| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2011:792.
[2] 赵俊奇,邱莉.踝关节骨折伴下胫腓关节分离的治疗[J].中国实用医学, 2009,4(10):70-71.
[3] 徐菲.踝足数值模型的建立及踝关节外侧失稳的距骨有限元分析[D].天津:天津医科大学,2009.
[4] Greenwald AS, Matejczyk MB, Keppler L, et al. Preliminary observations on the weight-bearing surfaces of the human ankle joint. Surg Forum. 1976;27(62):505-506.
[5] Matricali GA, Bartels W, Labey L, et al. High inter-specimen variability of baseline data for the tibio-talar contact area. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(1):117-120.
[6] Suckel A, Muller O, Wachter N, et al. In vitro measurement of intraarticular pressure in the ankle joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(5):664-668.
[7] 吴水培,俞立新,等.外踝缺损修复与重建前后力学变化的对比研究[J].2009,11(6):481-484.
[8] 邹宇炜,杨新明,苏峰,等.外踝短缩对踝关节应力分布的影响[J].河北北方学院学报,2006,23(6):1-3.
[9] 裴国献.数字骨科学的概念于临床初步应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):101-102.
[10] Bono CM, Khandha A. Residual sagittal motion after lumbar fusion:a finite element analysis with implications on radiographic flexion-extension criteria. J Spine. 2007;32(2): 417-422.
[11] Ozan F, Yildiz H, Bora OA,et al.The effect of head trauma on fracture healing: biomechanical testing and finite element analysis. J Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2010;44(4):313-321.
[12] Arabmotlagh M, Pilz M, Warzecha J,et al. Changes of femoral periprosthetic bone mineral density 6 years after treatment with alendronate following total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res,2009,27(2):183-188.
[13] Dudda M, Gueleryuez A, Gautier E,et al. Risk factors for early dislocation after total hip arthroplasty:a matched case-control study.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2010;18(2):179-183.
[14] Wheeldon JA, Pintar FA, Knowles S, et al. Experimental flexion/extension data corridors for validation of finite element models of the young, normal cervical spine. J Biomech.2006; 39(2):375-380.
[15] 马信龙,付鑫,马剑雄,等.人股骨近端空间结构重建新方法及有限元模型的建立[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(1):71-75.
[16] 牛文鑫,杨云峰,俞光荣,等.人体足部三维有限元模型的有效构建方法及其合理性的实验分析研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2009,26(1):80-84.
[17] Cheung J T ,Zhang M , An KN. Effects of plantar fascia stiffness on the biomechanical responses of the ankle-foot complex. J Clin Biomech.2004;19(8):839.
[18] Chen WP, Ju CW, Tang FT. Effects of total contact insoles on the plantar stress redistribution: a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(6):S17-24.
[19] 王旭,马昕,陶凯,等.足踝有限元模型的建立与初步临床应用[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2008,27(2):287-292.
[20] 中国解剖学会体质调查委员会.中国人解剖学数值[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:27.
[21] Burkwalter JA.骨科基础科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001: 231.
[22] Turner CH, Cowin SC, Rho JY, et al. The fabric dependence of the orthotropic elastic constants of cancellous bone. J Biomech. 1990;23(6):549-561.
[23] Duchemin L, Bousson V, Raossanaly C, et al. Prediction of mechanical properties of cortical bone by quantitative computed tomography. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(3):321-328.
[24] Anderson DD, Goldsworthy JK, Shivanna K, et al. Intra-articular contact stress distributions at the ankle throughout stance phase-patient-specific finite element analysis as a metric of degeneration propensity. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2006;5(2-3):82-89.
[25] Corazza F,O’connor JJ,Leardini A,et al.Ligament fibre recruitment and forces for the anterior drawer test at the human ankle joint. J Biomech. 2003;36(3):363-372.
[26] 唐芳根,袁芬连,钟敬亮.通络生骨胶囊促进兔膝关节全层软骨缺损修复的研究[J].中国实用方剂学,2010,16(12):153-156.
[27] 王亦聪.骨与关节损伤.人民卫生出版社[M].第3版.北京:2001: 296.
[28] Seireg A, Arvikar. The prediction of muscular lad sharing and joint forces in the lower extremities during walking. J Biomech. 1975;8(2):89-102.
[29] Stauffer RN, Chao EY, Brewster RC. Force and motion analysis of the normal, diseased, and prosthetic ankle joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;127:189-196.
[30] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.
[31] 李孝林.基于CT精细扫描构建人体胸腰段脊柱三维有限元模型的方法及意义[J].山东医药,2009,14(49):8-10.
[32] 张功恒.寰枢椎三维有限元模型的建立及其应用[D].广西:广西医科大学,2009.
[33] 林冬.一个退变颈椎三维有限元模型的建立和应用[D].四川:四川大学,2007.
[34] 刘士明,周恩昌,张铮,等.肘关节三维有限元模型的建立及意义[J].山东医药,2009,27(49):22-23.
[35] Amit G.Stress analysis of the standing foot following surgical plantar fascia release.J Biomech.2002;35(5):629-637.
[36] 曹志林.肱二头肌长头腱有限元力学分析[D].吉林:吉林大学, 2009.
[37] 史振满,史疆,王鑫,等.骨折髋支撑关节治疗股骨颈骨折的有限元力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(13): 2462-2466.
[38] Beaupre GS. Effect of fracture gap on stability of compression plate fixation: a finite element study.J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(1): 152.
[39] Amin S, Kopperdhal DL, Melton LJ 3rd, et al. Association of hip strength estimates by finite-element analysis with fractures in women and men. J Bone Miner Res. 2011; 26(7):1593-1600.
[40] Huang CH, Liau JJ, Huang CH, et al.Stress analysis of the anterior tibial post in posterior stabilized knee prostheses. J Orthop Res.2007;25(4):442-449.
[41] 刘文芳,王菲,宋哲,等.以螺旋CT数据建立的颅底三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(52):9726-9729.
[42] 陈伯华,孙鹏.颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(2):105-107.
[43] 郭国新,郭继涛,李伟,等.基于有限元模型的踝关节生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(17):3056-3060.
[44] 刘峻滔,刘云鹏.跟骨 Bohler’s角的改变对踝关节接触面积及压影响的实验研究[J].滨州医学院学报,2011,34(3):198-200.
[45] 郑文奎,刘勇,焦建宝,等. 胫骨骨折侧方成角畸形对胫股关节生物力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,14(28): 8988-8992.
[46] 刘勇,彭阿钦,等.腓骨短缩对胫距关节生物力学接触特性的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(2):134-136.
[47] 适存,郭霞.肌肉骨骼系统基础生物力学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:150-170.
[48] Ramse PL,Hamlton W.Changes in tibiotalar area of contact caused by lateral talar shift. J Bone Joint surg AM.1976; 58(3):356-357.
[49] Greenwald AS, Matejczyk MB, Keppler L, et al. Preliminary observations on the weight-bearing surfaces of the human ankle joint. Surg Forum. 1976;27(62):505-506.
[50] Egol KA ,Wolinsky P, Koval KJ.Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial pilon fractures.J Foot Ankle Clin.2000;5(4): 873-885.
[51] McCann PA ,Jackson M ,Mitchell ST,et al .Complications of definitive open reduction and internal fixation of pilon fractures of the distal tibia. J Int Orthop. 2011;35 (3):413-418.
[52] 陈志龙,蔡林.Pilon骨折骨折的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26((4):383-384.
[53] 朱玮,窦帮,秦涛,等.关节镜辅助下微创经皮钢板内固定治疗Pilon骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(3):266-269.
[54] 王景超,朱勇,欧兆强. 闭合性Ⅲ型Pilon骨折不同时机手术的疗效分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(2):28-32.
[55] 姜丹生,汪志明,施铁军.锁定加压钢板治疗 Pilon骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(3):357. |

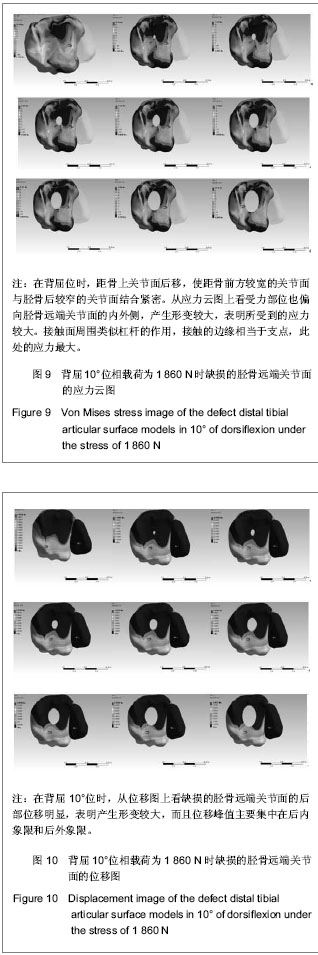
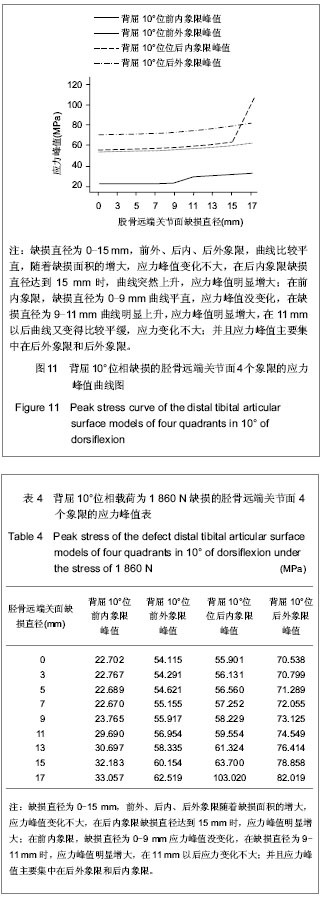

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)