| [1] Halland M, Talley NJ. Fecal incontinence: mechanisms and management. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28(1):57-62.[2] Zhang R, Wu QK. Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban. 2012;32(4):67-69. 张睿,吴氢凯.女性肛门失禁的病因学研究进展——基于“整体理论”的认识[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2012,32(4):67-69.[3] Peden-McAlpine C, Bliss D, Becker B, et al. The experience of community-living men managing fecal incontinence. Rehabil Nurs. 2012;37(6):298-306. [4] Macarthur C, Wilson D, Herbison P, et al. Faecal incontinence persisting after childbirth: a 12 year longitudinal study. BJOG. 2013;120(2):169-179.[5] Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, et al. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(2):512-517, 517.e1-2. [6] Rasmussen OO, Sørensen M, Tetzschner T, et al. Dynamic anal manometry in the assessment of patients with obstructed defecation. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993;36(10):901-907.[7] Williams NS, Patel J, George BD, et al. Development of an electrically stimulated neoanal sphincter. Lancet. 1991; 338(8776): 1166-1169.[8] Xiao YH, Liu GL, Liu ZL, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(30):44-47. 肖元宏,刘贵麟,刘洲禄,等.外括约肌主动收缩放松训练改善肛门失禁患者的肛门节制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(30):44-47.[9] XU JP, Wang Z, Chen JX. Waike Lilun yu Shijian. 2009; 14(4): 87-90. 徐嘉鹏,王争,陈锦先.外伤性肛门失禁的外科治疗[J].外科理论与实践,2009,14(4):87-90.[10] Goos M, Ruf G, Jargon D, et al. CT-Guided Electrode Placement for Sacral Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Faecal Incontinence (cSNS). Zentralbl Chir. 2012. in press. [11] Norton C, Dibley LB, Bassett P. Faecal incontinence in inflammatory bowel disease: Associations and effect on quality of life. J Crohns Colitis. 2012.in press. [12] Danielson J, Karlbom U, Wester T, et al. Efficacy and quality of life 2 years after treatment for faecal incontinence with injectable bulking agents. Tech Coloproctol. 2012.in press. [13] Thomas GP, Dudding TC, Rahbour G, et al. A Review of Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence. Colorectal Dis. 2012.in press. [14] Findlay JM, Maxwell-Armstrong C. Posterior tibial nerve stimulation and faecal incontinence: a review. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26(3):265-273.[15] Liu LB. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(29):119-122. 刘利兵.人工肛门括约肌的材料学特征及其临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(29):119-122.[16] Rasmussen OØ. Fecal incontinence. Studies on physiology, pathophysiology and surgical treatment. Dan Med Bull. 2003;50(3):262-282. [17] Brown SR, Nelson RL. Surgery for faecal incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(2):CD001757. [18] Rotholtz NA, Wexner SD. Surgical treatment of constipation and fecal incontinence. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2001; 30(1):131-166. [19] Ruthmann O, Fischer A, Hopt UT, et al. Dynamic graciloplasty vs artificial bowel sphincter in the management of severe fecal incontinence. Chirurg. 2006;77(10):926-938.[20] He YX. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University. 2009. 何远翔.人成肌细胞移植治疗肛门失禁的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009.[21] Huo XK, Zhang RY. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2006;29(30): 73-75. 霍新凯,张汝一.原位肛门再造在直肠癌根治中的研究进展[J].中国医师进修杂志,2006,29(30):73-75.[22] Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Treatment of urinary incontinence by an implantable prosthetic urinary sphincter. 1974. J Urol. 2002;167(2 Pt 2):1125-1130. [23] Pan WH, Shi CR, Jin LY. Linchuang Erke Zazhi. 2001;19(4): 27-30. 潘伟华,施诚仁,金凌宇.人工泵式肛门括约肌节制排便的最适肠管约束压选择[J].临床儿科杂志,2001,19(4):27-30.[24] Xia D, Shen BH, Zhu XW, et al. Zhonghua Miniao Waike Zazhi. 2004;25(7):41-43. 夏丹,沈柏华,朱选文,等.人工尿道括约肌治疗尿失禁(附四例报告)[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2004,25(7):41-43.[25] Michot F, Costaglioli B, Leroi AM, et al. Artificial anal sphincter in severe fecal incontinence: outcome of prospective experience with 37 patients in one institution. Ann Surg. 2003; 237(1):52-56.[26] Schrag HJ, Ruthmann O, Doll A, et al. Development of a novel, remote-controlled artificial bowel sphincter through microsystems technology. Artif Organs. 2006;30(11):855-862.[27] Finlay IG, Richardson W, Hajivassiliou CA. Outcome after implantation of a novel prosthetic anal sphincter in humans. Br J Surg. 2004;91(11):1485-1492.[28] Luo Y, Higa M, Amae S, et al. Preclinical development of SMA artificial anal sphincters. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2006;15(4):241-245.[29] Luo Y. Zhongguo Putong Waike Zazhi. 2008;17(3):86-88. 罗永.人工肛门括约肌临床应用进展[J].中国普通外科杂志,2008, 17(3):86-88.[30] Lumi CM, Miravalle OR, La Rosa L, et al. Anorectal manometry and ultrasound in the study of patients with fecal incontinence. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam. 2012;42(3):193-198. [31] Huang ZH, Chen F, Yang LC, et al. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2009;29(4):177-178. 黄宗海,陈飞,杨六成,等.人工肛门括约肌对兔结肠血流影响的研究[J].南方医科大学学报,2009,29(4):177-178.[32] Lin HC, Su D, Kang L, et al. Jiezhichang Gangmen Waike. 2009;15(4):82-84. 林宏城,苏丹,康亮,等.人工肛门括约肌的研究进展[J].结直肠肛门外科,2009,15(4):82-84.[33] Guo XB. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University. 2010. 郭雄波.人工肛门括约肌植入材料的改进[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.[34] Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng yu Linchang. 2003;7(2):70. 人工肛门括约肌治疗严重大便失禁[J].生物医学工程与临床,2003,7(2):70.[35] Shi CR, Wu YM, Jin LY. Zhonghua Xiaoer Waike Zazhi. 2001;22(5):45-46. 施诚仁,吴晔明,金凌宇.新型人工泵式肛门括约肌研制与其排便作用观察[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2001,22(5):45-46.[36] Yun QL. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 2003. 贠青琳.基于嵌入式系统的人工括约肌研究[J].上海:上海交通大学,2003.[37] Shu J, Yan DT, Yan GZ. Guangxue Jingmi Gongcheng. 2004; 12(1):43-46. 舒晶,颜德田,颜国正.生物反馈式括约肌的研制[J].光学精密工程,2004,12(1):43-46.[38] Devesa JM, Rey A, Hervas PL, et al. Artificial anal sphincter: complications and functional results of a large personal series. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(9):1154-1163.[39] Whitehead WE, Burgio KL, Engel BT. Biofeedback treatment of fecal incontinence in geriatric patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1985;33(5):320-324.[40] Mahony RT, Malone PA, Nalty J, et al. Randomized clinical trial of intra-anal electromyographic biofeedback physiotherapy with intra-anal electromyographic biofeedback augmented with electrical stimulation of the anal sphincter in the early treatment of postpartum fecal incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191(3):885-890.[41] Hosker G, Cody JD, Norton CC. Electrical stimulation for faecal incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(3):CD001310.[42] Wexner SD, Jin HY, Weiss EG, et al. Factors associated with failure of the artificial bowel sphincter: a study of over 50 cases from Cleveland Clinic Florida. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52(9):1550-1557.[43] Qiao FN, Cao ZJ. Jiezhichang Gangmen Waike. 2010;16(5): 54-56. 乔峰妮,曹暂剑.吻合器用于直肠癌不保肛手术中可控制排便人工肛门成形术的理论研究[J].结直肠肛门外科,2010,16(5): 54-56.[44] Gallas S, Leroi AM, Bridoux V, et al. Constipation in 44 patients implanted with an artificial bowel sphincter. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24(8):969-974. [45] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[46] Davies RR, Davies JA. Rabbit gastrointestinal physiology. Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2003;6(1):139-153.[47] Tariq SH. Fecal incontinence in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 2007;23(4):857-869, vii.[48] Jorge JM, Wexner SD. Etiology and management of fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993;36(1):77-97.[49] Rockwood TH, Church JM, Fleshman JW, et al. Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scale: quality of life instrument for patients with fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43(1):9-17.[50] Lehur PA, Zerbib F, Neunlist M, et al. Comparison of quality of life and anorectal function after artificial sphincter implantation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(4):508-513.[51] Wong WD, Congliosi SM, Spencer MP, et al. The safety and efficacy of the artificial bowel sphincter for fecal incontinence: results from a multicenter cohort study. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(9):1139-1153. [52] Shi HF, Yan DT. Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2007; 26(2):43-45. 石浩峰,颜德田.生物反馈式括约肌控制装置[J].北京生物医学工程,2007,26(2):43-45.[53] Nelson RL. Epidemiology of fecal incontinence. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(1 Suppl 1):S3-7.[54] Wald A. Clinical practice. Fecal incontinence in adults. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(16):1648-1655.[55] Karoui S, Savoye-Collet C, Koning E, et al. Prevalence of anal sphincter defects revealed by sonography in 335 incontinent patients and 115 continent patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;173(2):389-392. [56] Yue JZ, Gao QY. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun yu Shijian. 2005; 11(1): 74-75. 岳军忠,高庆云.大便失禁的外科治疗现状[J].中国康复理论与实践,2005,11(1):74-75.[57] Santoro GA, Eitan BZ, Pryde A, et al. Open study of low-dose amitriptyline in the treatment of patients with idiopathic fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43(12):1676-1682.[58] Carapeti EA, Kamm MA, Phillips RK. Randomized controlled trial of topical phenylephrine in the treatment of faecal incontinence. Br J Surg. 2000;87(1):38-42.[59] Tan JJ, Chan M, Tjandra JJ. Evolving therapy for fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007;50(11):1950-1967. [60] Hu NP, Zhan WH. Guowai Yixue Waike Xue Fence. 2001; 28(2):31-33. 胡念平,詹文华.电刺激股薄肌肛门成形术[J].国外医学:外科学分册,2001,28(2):31-33.[61] Galandiuk S, Roth LA, Greene QJ. Anal incontinence-sphincter ani repair: indications, techniques, outcome. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009;394(3):425-433. [62] Norton C. Fecal incontinence and biofeedback therapy. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008;37(3):587-604, viii.[63] Gregorcyk SG. The current status of the Acticon Neosphincter. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2005;18(1):32-37.[64] Ruiz Carmona MD, Alós Company R, Roig Vila JV, et al. Long-term results of artificial bowel sphincter for the treatment of severe faecal incontinence. Are they what we hoped for? Colorectal Dis. 2009;11(8):831-837.[65] Hayden DM, Weiss EG. Fecal incontinence: etiology, evaluation, and treatment. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011; 24(1):64-70.[66] Chittawatanarat K, Koh DC, Seah AA, et al. Artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence in Asian patients. Asian J Surg. 2010;33(3):134-142.[67] Michot F, Lefebure B, Bridoux V, et al. Artificial anal sphincter for severe fecal incontinence implanted by a transvaginal approach: experience with 32 patients treated at one institution. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53(8):1155-1160. [68] Gregorcyk SG. The current status of the Acticon Neosphincter. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2005;18(1):32-37. [69] Madoff RD, Baeten CG, Christiansen J, et al. Standards for anal sphincter replacement. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43(2): 135-141.[70] Li JG, Shi FJ, Xu S, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(48):9011-9014. 李建国,史福军,徐帅,等.智能人工肠内容物感知神经的初步研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(48):9011-9014.[71] Chiarioni G, Whitehead WE. The role of biofeedback in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;5(7):371-382. |
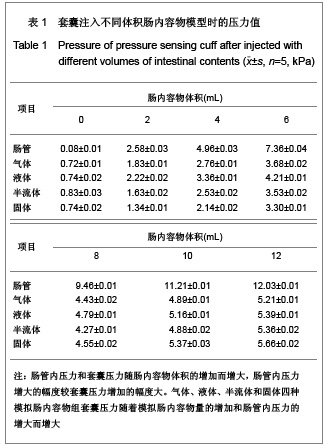
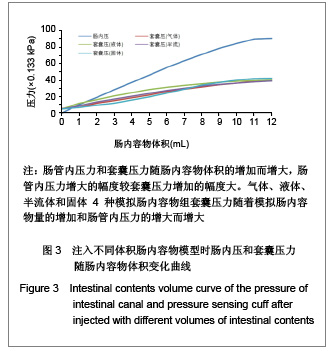

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)