| [1] Richards KA, Hemal AK. Current status and outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy and urinary diversion. Curr Urol Rep.2011;12(2):107-114.[2] Ardelt PU, Woodhouse CR, Riedmiller H, et al. The efferent segment in continent cutaneous urinary diversion: a comprehensive review of the literature. BJU Int.2011.[3] Hautmann RE, Volkmer BG, Schumacher MC, et al. Long-term results of standard procedures in urology: the ileal neobladder. World J Urol.2006;24(3):305-314.[4] Atala A, Bauer SB, Soker S, et al. Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet. 2006;367(9518):1241-1246.[5] Raya-Rivera A, Esquiliano DR, Yoo JJ, et al. Tissue-engineered autologous urethras for patients who need reconstruction: an observational study. Lancet.2011;377 (9772):1175-1182.[6] Yang SX,Song C,Liu Y,et al. Zhonghua Miniao Waike Zazhi. 2003; 24(8):555-557.杨嗣星,宋超,刘勇,等. 尿道细胞外基质的研制[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志,2003,24(8): 555-557.[7] Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, et al. Update of the Clinical Guidelines of the European Association of Urology on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder carcinoma. Actas Urol Esp.2010;34(1):51-62.[8] Kassouf W, Hautmann RE, Bochner BH, et al. A critical analysis of orthotopic bladder substitutes in adult patients with bladder cancer: is there a perfect solution?. Eur Urol.2010; 58(3):374-383.[9] White SE, Malkowicz SB. Management of the male urethra after cystectomy. Urol Clin North Am.2010;37(3):475-479.[10] Somani BK, Nabi G, Wong S, et al. How close are we to knowing whether orthotopic bladder replacement surgery is the new gold standard?--evidence from a systematic review update. Urology.2009;74(6):1331-1339.[11] Drewa T. The artificial conduit for urinary diversion in rats: a preliminary study. Transplant Proc.2007;39(5):1647-1651.[12] Davis NF, Callanan A, Mcguire BB, et al. Evaluation of viability and proliferative activity of human urothelial cells cultured onto xenogenic tissue-engineered extracellular matrices. Urology.2011;77(4):1077.[13] Watanabe E, Yamato M, Shiroyanagi Y, et al. Bladder augmentation using tissue-engineered autologous oral mucosal epithelial cell Sheets grafted on demucosalized gastric flaps. Transplantation.2011;91(7):700-706.[14] Eberli D, Freitas FL, Atala A, et al. Composite scaffolds for the engineering of hollow organs and tissues. Methods.2009; 47(2): 109-115.[15] Pariente JL, Kim BS, Atala A. In vitro biocompatibility assessment of naturally derived and synthetic biomaterials using normal human urothelial cells.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55(1):33-39.[16] Pariente JL, Kim BS, Atala A. In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of naturally derived and synthetic biomaterials using normal human bladder smooth muscle cells. J Urol. 2002;167(4):1867-1871.[17] Mauney JR, Cannon GM, Lovett ML, et al. Evaluation of gel spun silk-based biomaterials in a murine model of bladder augmentation. Biomaterials.2011;32(3):808-818.[18] Chun SY, Lim GJ, Kwon TG, et al. Identification and characterization of bioactive factors in bladder submucosa matrix. Biomaterials.2007;28(29):4251-4256.[19] Rosario DJ, Reilly GC, Ali SE, et al. Decellularization and sterilization of porcine urinary bladder matrix for tissue engineering in the lower urinary tract. Regen Med.2008;3(2): 145-156.[20] Farhat WA, Chen J, Haig J, et al. Porcine bladder acellular matrix (ACM): protein expression, mechanical properties. Biomed Mater.2008;3(2):25015. |
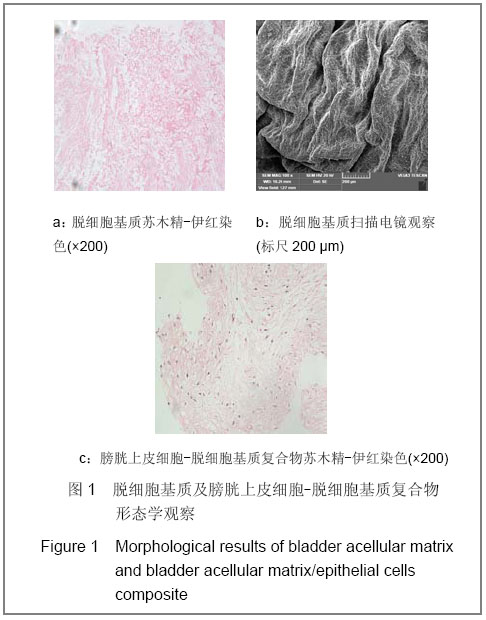
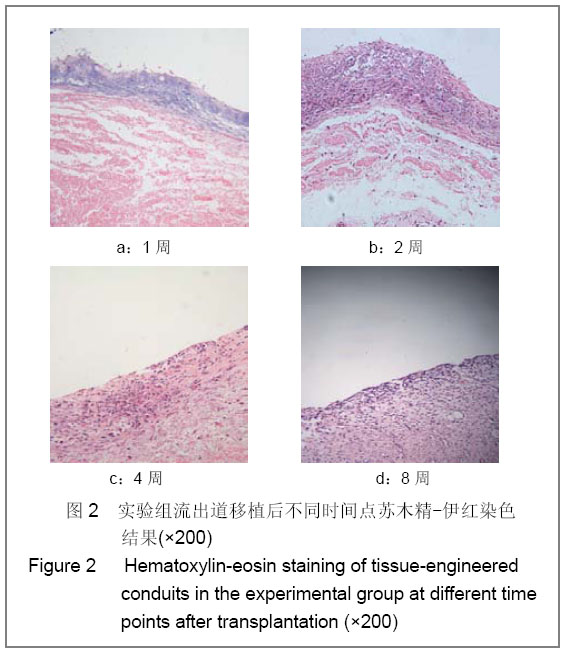
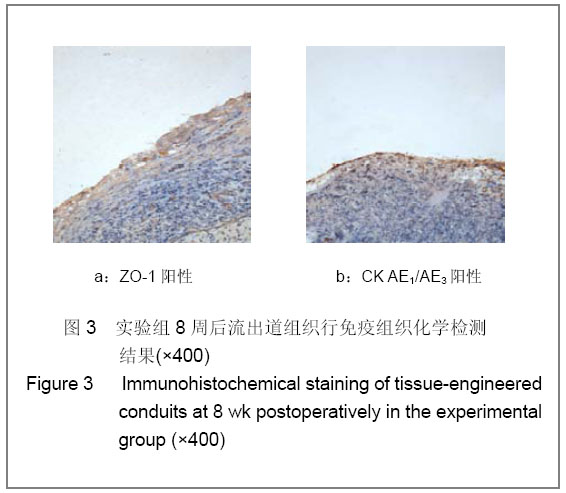
.jpg)