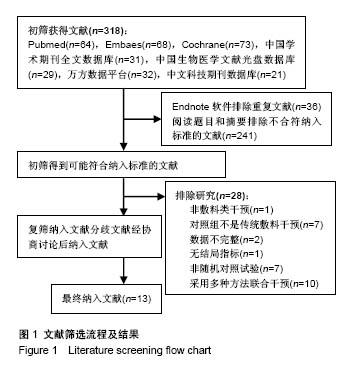
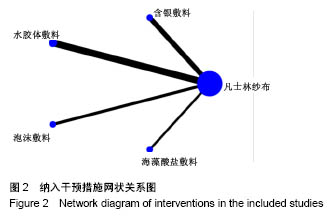
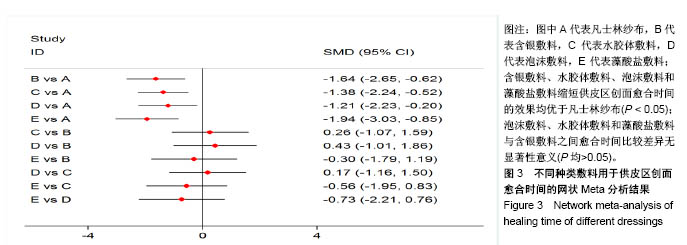
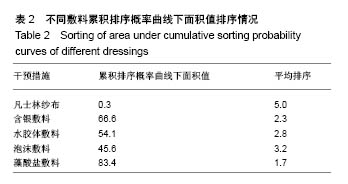
| [1] 尤蓓蓓,袁玲玲.烧伤患者头部供皮区行红光治疗护理的效果观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(46):249.[2] 孙超锋,李跃军,李望舟,等.中厚皮供区创面愈合临床研究[J].兰州大学学报(医学版),2016,42(4):8-13.[3] 田金徽,陈耀龙,杨克虎,等.SR/MA研究进展与挑战[J].兰州大学学报(医学版),2016,42(1):42-47.[4] 曾宪涛,曹世义,孙凤,等.Meta分析系列之六:间接比较及网状分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(5):399-402.[5] 杨云,王继华,朱礼昆,等.藻酸盐敷料在整形外科的应用[J].中外医疗,2010,29(5):108.[6] 田彭,周业平.藻酸盐敷料对瘢痕皮肤供皮区创面愈合的临床效果研究[J].中国全科医学, 2014,17(24):2871-2873.[7] 邬天刚,冯登超.藻酸盐敷料和凡士林纱布对瘢痕皮肤供皮区创面愈合及相关分子表达的影响[J].海南医学院学报, 2016, 22(16):1911-1913.[8] 许腊梅,刘宸.两种敷料用于中厚皮片供皮区创面处理的效果观察[J].现代医学,2015,43(2):207-210.[9] 邱玉友.水胶体敷料治疗头部供皮创面的效果观察[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(12):194-196.[10] 郑捷新,施浩然.多爱肤敷料在中厚皮片供皮区的应用[J].上海第二医科大学学报,1999,19(4):362-363.[11] Brölmann FE,Eskes AM,Goslings JC,et al.Randomized clinical trial of donor-site wound dressings after split-skin grafting.Br J Surg.2013;100(5):619-627.[12] Pak CS, Park DH, Oh TS,et al.Comparison of the efficacy and safety of povidone-iodine foam dressing (Betafoam), hydrocellular foam dressing (Allevyn), and petrolatum gauze for split-thickness skin graft donor site dressing.Int Wound J. 2018. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13043. [Epub ahead of print].[13] 鲍志渊.软聚硅酮泡沫敷料在白癜风表皮移植术供皮区创面的应用[J].中国卫生工程学,2015,14(3):277-278.[14] 李学川,乔亮,黄晓琴,等.吸水性聚氨酯泡沫敷料促进皮肤移植供皮区愈合的疗效观察[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2013, 33(5):663-666.[15] Lohsiriwat V,Chuangsuwanich A.Comparison of the ionic silver-containing hydrofiber and paraffin gauze dressing on split-thickness skin graft donor sites.Ann Plast Surg. 2009; 62(4):421-422.[16] 牟军.纳米银敷料治疗供皮区创面的疗效分析[J].中国现代医生, 2017,55(4):50-53.[17] 冯光,曹卫红.纳米银敷料在中厚皮片供皮区的应用研究[J].感染、炎症、修复,2008,9(1):43-43.[18] 赵玲霞,白倩.烧伤整形植皮患者术后供皮区的护理[J].医学信息, 2016,29(5):148-149.[19] 林元邦,鲁淑英,沈伟嵘,等.湿性敷料在腹部手术术后伤口愈合不良中应用效果的观察[J].感染、炎症、修复,2009,10(3):179-180.[20] 王凤岩,许鑫,胡三莲.密闭湿性敷料、凡士林纱布在供皮区应用效果的研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2017,21(2):105-107.[21] 陈红涛,董彩梅,吕冬,等.藻酸盐敷料在伤口创面护理中的应用进展[J].护理研究,2015,29(3):257-259.[22] 顾其胜,王帅帅,王庆生,等.海藻酸盐敷料应用现状与研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(2):255-258.[23] 苏怡芳,马俊,章左艳,等.银离子藻酸盐敷料在糖尿病合并压疮患者中的应用效果[J].解放军护理杂志,2016,33(4):61-63.[24] 温珊珊.藻酸盐敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡临床观察和护理[J].海峡药学,2017,29(6):191-192.[25] 周艳红,郝彤,李俊杰,等.新型纳米银基抗感染敷料的研制及生物学效应评价[J].军事医学,2016,40(6):497-501.[26] Esteban-Tejeda L, Malpartida F, Esteban-Cubillo A,et al. The antibacterial and antifungal activity of a soda-lime glass containing silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology.2009;20(8): 085103.[27] 刘俊玲,陈彤,刘建云,等.纳米银敷料、银离子敷料、磺胺嘧啶银治疗Ⅱ度烧伤的网状Meta分析[J].国外医学医学地理杂志, 2016,37(3):258-262.[28] 程祥,赵玉云,邵安良,等.含银敷料的表征和银的体外释放实验方法研究及其应用[J].药物分析杂志,2015,25(3):491-499.[29] Doggen K,Van Acker K, Beele H,et al. Implementation of a quality improvement initiative in Belgian diabetic foot clinics: feasibility and initial results.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014; 30(5):435-443.[30] 吴文婷,王艳君,赵文杰,等.防污载银复合材料的研究进展[J].表面技术,2017,46(11):128-137.[31] 陈学情,蒋家璇,任志鸿,等.纳米银的抗菌特性及对多重耐药菌株的抗菌作用[J].微生物学报,2017,57(4):85-95.[32] 刘鑫,任艳,周子军,等.纳米银抗菌机理及应用研究进展[J].安徽农业大学学报,2017,44(4):702-708.[33] 陈炯,韩春茂,张力成,等.纳米银用于Ⅱ度烧伤创面的疗效及安全性评价[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(5):451-455.[34] 郑辉烈,俞慧强,刘勇,等.Meta分析发表偏倚的联合诊断研究[J].现代预防医学,2016,43(7):1153-1155,1161. |
.jpg)

.jpg)