| [1]Khalili AA,Ahmad MR.A Review of Cell Adhesion Studies for Biomedical and Biological Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16(8):18149-18184.[2]Kunutsor SK,Bakker SJ,Dullaart RP.Soluble Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecules May be Protective of Future Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Findings from the PREVEND Prospective Cohort Study. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017; 24(8): 804-818.[3]Garrido-Urbani S, Vonlaufen A, Stalin J,et al. Junctional adhesion molecule C (JAM-C) dimerization aids cancer cell migration and metastasis.Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. 2018;1865(4):638-649.[4]Dimitriadis GK,Kaur J,Adya R,et al.Chemerin induces endothelial cell inflammation: activation of nuclear factor-kappa beta and monocyte-endothelial adhesion. Oncotarget.2018;9(24):16678-16690.[5]Guevara-Pantoja PE,Jimã©Nez-Valdã©S RJ, GarcãA-Cordero JL, et al. Pressure-actuated monolithic acrylic microfluidic valves and pumps.Lab Chip. 2018;18(4): 662-669.[6]Cui X,Liu Y,Hu D,et al.A fluorescent microbead-based microfluidic immunoassay chip for immune cell cytokine secretion quantification.Lab Chip.2018;18(3);522-531.[7]Chen C, Townsend AD, Hayter EA, et al. Insert-based microfluidics for 3D cell culture with analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem.2018;410(22):1-11.[8]Wang W,Li L,Ding M,et al.A Microfluidic Hydrogel Chip with Orthogonal Dual Gradients of Matrix Stiffness and Oxygen for Cytotoxicity Test.Biochip J.2018;12(2):1-10.[9]Honarmandi P,Lee H,Lang MJ,et al. A microfluidic system with optical laser tweezers to study mechanotransduction and focal adhesion recruitment.Lab Chip.2011;11(4):684-694.[10]Thompson TJ, Han B.Analysis of adhesion kinetics of cancer cells on inflamed endothelium using a microfluidic platform.Biomicrofluidics.2018;12(4):042215.[11]Tu L,Li X,Bian S,et al.Label-free and real-time monitoring of single cell attachment on template-stripped plasmonic nano-holes.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):1-11.[12]Hoffmann M,Tserpes K,Moutsompegka E,et al.Determination of adhesion strength of pre-bond contaminated composite-to- metal bonded joints by centrifuge tests.Compos B Eng.2018; 147: 114-121.[13]Kim H, Yamagishi A,Imaizumi M, et al. Quantitative measurements of intercellular adhesion between a macrophage and cancer cells using a cup-attached AFM chip. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017; 155:366-372.[14]Hogan B,Babataheri A,Hwang Y,et al.Characterizing Cell Adhesion by Using Micropipette Aspiration.Biophys J. 2015;109(2):209-219.[15]Jing P,Liu Y,Keeler EG,et al.Optical tweezers system for live stem cell organization at the single-cell level.Biomed Opt Express.2018;9(2):771-779.[16]Fuhrmann A,Engler AJ.The cytoskeleton regulates cell attachment strength.Biophys J. 2015;109(1):57-65.[17]Kim HW, Han S,Kim W,et al.Modulating wall shear stress gradient via equilateral triangular channel for in situ cellular adhesion assay.Biomicrofluidics.2016;10(5):11-25.[18]Li Y,Gao A,Yu L.Monitoring of TGF-β 1-Induced Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation Process by Measuring Cell Adhesion Force with a Microfluidic Device.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016; 178(1):114-125.[19]Lu L, Zheng GX, Yang YS, et al. Measurement of Giardia lamblia, adhesion force using an integrated microfluidic assay.Anal Bioanal Chem.2017;409(5):1-9.[20]Christ KV,Williamson KB,Masters KS,et al.Measurement of single-cell adhesion strength using a microfluidic assay. Biomed Microdevices.2010;12(3):443-455.[21]Mao S,Zhang W,Huang Q,et al.In Situ Scatheless Cell Detachment Reveals Correlation between Adhesion Strength and Viability at Single-Cell Resolution.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;57(1):236-240.[22]Mao S,Zhang Q,Li H,et al.Adhesion analysis of single circulating tumor cells on a base layer of endothelial cells using open microfluidics.Chem Sci.2018;9:7694-7699.[23]Cheng Z,Wu X,Cheng J,et al. Microfluidic fluorescence- activated cell sorting (μFACS) chip with integrated piezoelectric actuators for low-cost mammalian cell enrichment.Microfluid Nanofluidics.2017;21(1):9-19.[24]Kwak B, Lee J, Lee D, et al. Selective isolation of magnetic nanoparticle-mediated heterogeneity subpopulation of circulating tumor cells using magnetic gradient based microfluidic system. Biosens Bioelectron.2017;88:153-158.[25]Pang L, Shen S, Ma C, et al. Deformability and size-based cancer cell separation using an integrated microfluidic device. Analyst.2015;140(21):7335-7346.[26]Ali H,Park CW.Numerical study on the complete blood cell sorting using particle tracing and dielectrophoresis in a microfluidic device.Korea-Aust Rheol J.2016;28(4):327-339.[27]Ung L,Mutafopulos K, Spink P, et al. Enhanced Surface Acoustic Wave Cell Sorting by 3D microfluidic chip design. Lab Chip.2017;17(23):4059-4069.[28]Singh A,Singh A, Suri S, et al. Adhesion strength-based, label-free isolation of human pluripotent stem cells.Nat Methods.2013;10(5):438-444.[29]桑维维,常亚男,李娟.微流控芯片对乳腺癌细胞mda-mb-231的捕获及再培养研究[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2015,35(6):46-53. [30]Zhang Y,Wu M,Han X,et al.High-throughput, label-free isolation of cancer stem cells based on cell adhesion capacity.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2015;54(37):10838-10842.[31]Chen W,Allen SG,Reka AK,et al.Nanoroughened adhesion-based capture of circulating tumor cells with heterogeneous expression and metastatic characteristics. BMC Cancer.2016;16:614-625.[32]Dasanna AK,Schwarz US.Adhesion-based sorting of blood cells: an adhesive dynamics simulation study.Soft Matter. 2018;14(44):9061-9070.[33]Ermis M,Antmen E,Hasirci V.Micro and Nanofabrication methods to control cell-substrate interactions and cell behavior: A review from the tissue engineering perspective. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):355-369.[34]Francesco R,Simone B, Federica F, et al. A micron-scale surface topography design reducing cell adhesion to implanted materials.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):10887-10899.[35]Zahran R,Rosales LJI,Rodríguez Valverde MA,et al.Effect of Hydrofluoric Acid Etching Time on Titanium Topography, Chemistry, Wettability, and Cell Adhesion.PLoS One.2016; 11(11):e0165296.[36]余劭婷,秦金桥,关国平,等.丝素纤维表面改性提高细胞黏附性能[J].生物医学工程学进展,2016, 37(3):144-149.[37]Tang Z,Akiyama Y,Itoga K,et al.Shear stress-dependent cell detachment from temperature-responsive cell culture surfaces in a microfluidic device.Biomaterials. 2012; 33(30): 7405-7411.[38]Hampe A,Li Z,Sethi S,et al.A Microfluidic Platform to Study Astrocyte Adhesion on Nanoporous Gold Thin Films. Nanomaterials.2018;8(7):452-463. [39]Li P,Yu H,Liu N,et al.Visible Light Induced Electropolymerization of Suspended Hydrogel Bioscaffolds in a Microfluidic Chip.Biomater Sci.2018;6(6):1371-1378.[40]Stamp ME,Jötten AM, Kudella PW,et al.Exploring the Limits of Cell Adhesion under Shear Stress within Physiological Conditions and beyond on a Chip.Diagnostics. 2016;6(4): 38-52.[41]Gong X, Yao J, He H, et al.Combination of flow and micropattern alignment affecting flow-resistant endothelial cell adhesion.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;74:11-20.[42]Vanessa K,Christoph G,Ivannikov D,et al. vasQchip: A Novel Microfluidic, Artificial Blood Vessel Scaffold for Vascularized 3D Tissues.Adv MaterTechnol.2018;3(4):1700246.[43]Sharmistha N, Kumar PA, Viswanathan K, et al.Controlled shear flow directs osteogenesis on UHMWPE based hybrid nano-biocomposites in custom designed PMMA microfluidic device.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;1(2):414−435.[44]秦建华,张敏,于浩,等.人体器官芯片[J].中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(12):18-26.[45]Ahn S,Ardoña HAM,Lind JU,et al.Mussel-inspired 3D fiber scaffolds for heart-on-a-chip toxicity studies of engineered nanomaterials. Anal Bioanal Chem.2018;410(24):6141-6154. [46]Khazali AS, Clark AM, Wells A. A Pathway to Personalizing Therapy for Metastases Using Liver-on-a-Chip Platforms. Stem Cell Rev.2017;13(3):364-380.[47]Humayun M,Chow CW,Ewk Y.Microfluidic lung airway-on-a-chip with arrayable suspended gels for studying epithelial and smooth muscle cell interactions. Lab Chip. 2018;18(9):1298-1309.[48]Wilmer MJ,Ng CP,Lanz HL,et al.Kidney-on-a-Chip Technology for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity Screening. Trends Biotechnol.2016;34(2):156-170.[49]Jalili-Firoozinezhad S,Prantil-Baun R,Jiang A,et al.Modeling radiation injury-induced cell death and countermeasure drug responses in a human Gut-on-a-Chip. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9(2):223-236.[50]Kucukal E, Little JA,Gurkan UA. Shear dependent red blood cell adhesion in microscale flow. Integr Biol. 2018;10(4): 194-206.[51]Kim M, Alapan Y, Adhikari A, et al. Hypoxia enhanced adhesion of red blood cells in microscale flow. Microcirculation. 2017;24(5):e12374.[52]Shea DJ,Li YW,Stebe KJ,et al. E-selectin-mediated rolling facilitates pancreatic cancer cell adhesion to hyaluronic acid. FASEB J.2017;31(11):5078-5086.[53]Antoniellis Silveira AA,Dominical VM,Morelli Vital D,et al. Attenuation of TNF-induced neutrophil adhesion by simvastatin is associated with the inhibition of Rho-GTPase activity, p50 activity and morphological changes.Int Immunopharmacol.2018;58:160-165. |
.jpg)
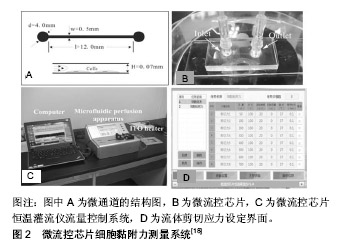
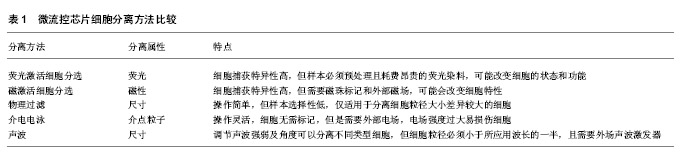
.jpg)
.jpg)