中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3456-3462.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1272
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
上颌窦提升中羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素组织工程骨的成骨效应
刁兆峰1,李晓亮1,艾力麦尔旦•艾尼瓦尔1,林 成2,周 梅1,潘晓玲1,3,李 鹏1
- 1新疆医科大学,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011; 2南方医科大学深圳医院,广东省深圳市 518000;3新疆军区总医院北京路临床部,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830013
Osteogenic effects of hydroxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan/methylcellulose bone for maxillary sinus elevation
Diao Zhaofeng1, Li Xiaoliang1, Ailimaierdan•Aniwear1, Lin Cheng2, Zhou Mei1, Pan Xiaoling1, 3, Li Peng1
- 1Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Shenzhen Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China; 3Beijing Road Clinical Department, Xinjiang Military Region General Hospital, Urumqi 830013, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
组织工程支架材料:对细胞外基质和功能进行仿生,从而构建的材料。支架材料起到一定的支撑和模板作用,为细胞提供寄宿、生长、分化和增殖的场所,从而引导受损组织再生,最终达到修复损伤组织和器官的目的。
上颌窦提升术:该实验采用经兔鼻背部入路的上颌窦外提升术植入支架材料,以观察提升成骨效果,因提升术的运用具备良好的手术视野、便于手术操作的特点,实验中可清楚观察到术中窦黏膜情况,减少了上颌窦损伤和穿通的发生概率,可有效建立上颌窦提升动物模型,增加此类动物模型建立的成功率。
背景:前期实验构建了羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素三维复合支架材料,发现其具有良好的理化性能和生物相容性。
目的:评估可注射性羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素支架复合骨髓间充质干细胞用于兔上颌窦提升的成骨效果。
方法:取24只新西兰大白兔(新疆医科大学动物实验中心提供),每只兔均制作4处上颌窦提升区域,其中3处分别植入可注射性羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素支架与骨髓间充质干细胞复合物(实验组)、可注射性羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素支架(对照组1)、羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙骨粉(对照组2),最后一处不植入任何材料,作为空白对照。术后4,8,12周,取上颌窦提升区域标本,分别进行锥形束CT扫描、苏木精-伊红染色与免疫组织学化染色观察。实验经新疆医科大学第一附属医院实验动物伦理委员会审议批准(批准编号IACUC20170706-02)。
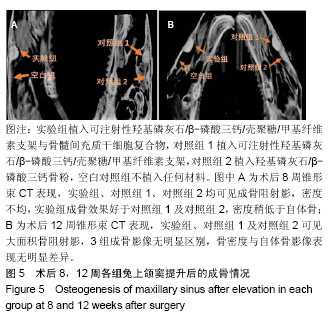
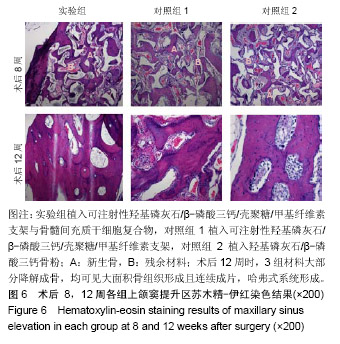
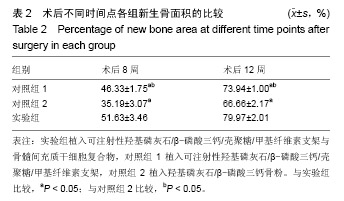
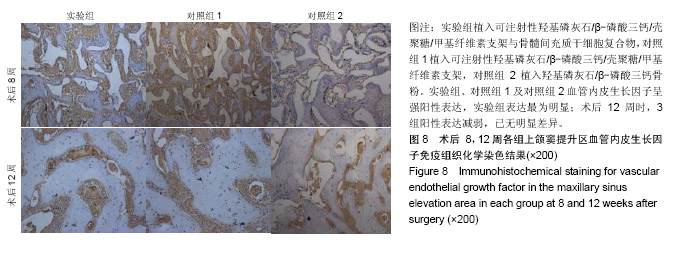
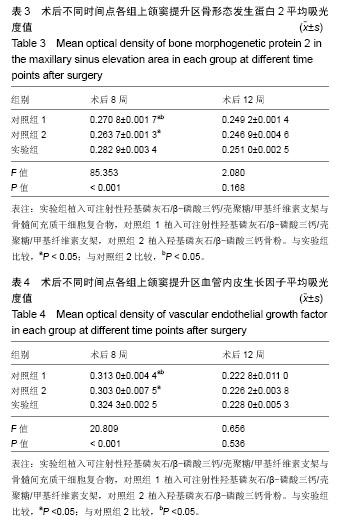
结果与结论:①锥形束CT显示,空白对照组始终无新骨生成,其余3组术后8周时可见新骨生成,且以实验组成骨效果最明显;术后12周时,实验组、对照组1、对照组2成骨效果进一步增强,3组间差异不明显;②苏木精-伊红染色显示,实验组术后8,12周的成骨效果优于对照组1、对照组2(P < 0.05);③免疫组织化学染色显示,实验组术后8周的成骨指标骨形态发生蛋白2、血管内皮生长因子表达均强于对照组1、对照组2(P < 0.05);术后12周时,3组间两指标表达差异不明显(P > 0.05);④结果表明,羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖/甲基纤维素可注射组织工程骨可促进上颌窦提升区域的骨形成。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)