中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (12): 1840-1845.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1110
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨转子间骨折618例患者的流行病学分析
郭金超1,曹 源2,黄俊灵1,马嘉嘉1,马 创1
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院骨科中心显微修复外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830001;2新疆医科大学研究生院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830001
Intertrochanteric femoral fractures: an epidemiological analysis of 618 cases
Guo Jinchao1, Cao Yuan2, Huang Junling1, Ma Jiajia1, Ma Chuang1
- 1Department of Microscope Repairing, Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Graduate School of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
流行病学调查:是指用流行病学的方法进行的调查研究。主要用于研究疾病、健康和卫生事件的分布及其决定因素。通过这些研究将提出合理的预防保健对策和健康服务措施,并评价这些对策和措施的效果。
股骨转子间骨折:指股骨颈基底至小转子水平以上部位所发生的骨折。患者平均年龄比股骨颈骨折高五六岁,90%发生于65岁以上的老年人,70岁以上发病率急剧增加。因转子部血供丰富,极少发生骨折不愈合,但保守治疗死亡率和致残率高,目前以手术治疗为主。
摘要
背景:目前国内外针对乌鲁木齐地区的股骨转子间骨折的流行病学调查鲜有报道。而关于股骨转子间骨折从发病、治疗到近期预后较为完整的流行病学调查仍较少。
目的:分析股骨转子间骨折住院患者的流行病学分布特征,为开展防治策略研究提供科学依据。
方法:回顾性分析新疆医科大学第一附属医院从2007年1月至2017年12月收治的以股骨转子间骨折为主要诊断的618例患者病历资料,采集患者个人特征、致伤时间、致伤原因、受伤到手术的时间、治疗方式、术中指标、住院时间、住院费用及术后6个月死亡率等信息,并进行流行病学特征描述。应用SPSS 22.0软件对数据进行统计分析。
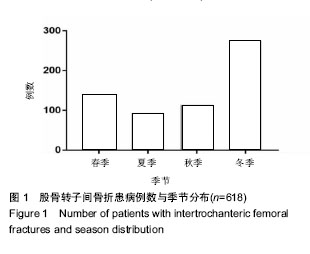
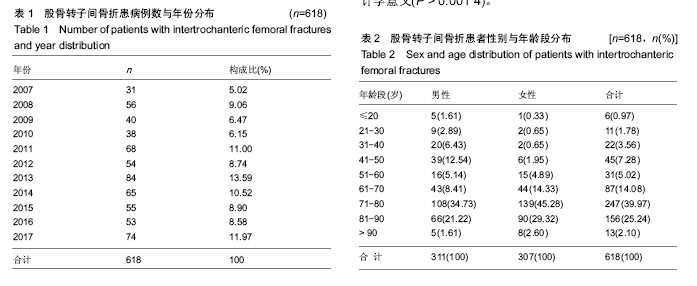
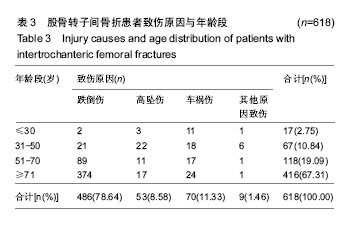
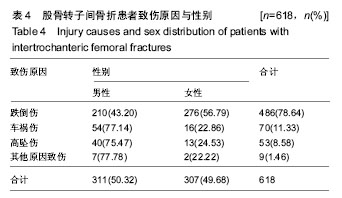
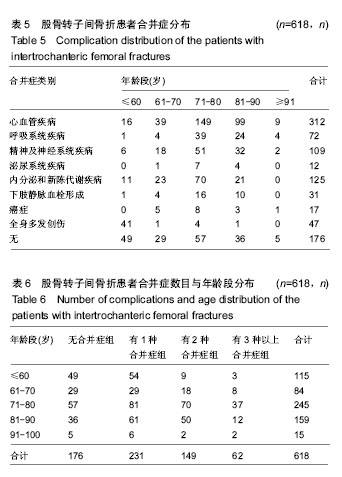
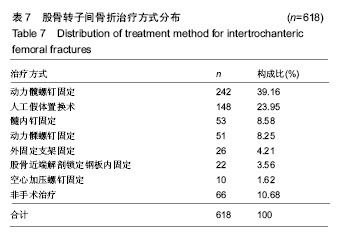
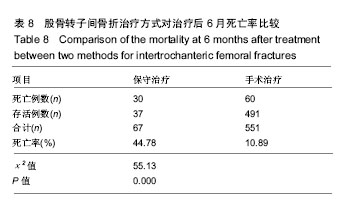
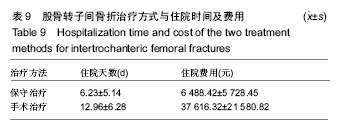
结果与结论:①患者年龄、性别差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),≥61岁的患者最多,占81.39%,左侧多于右侧(1.04∶1),男性患者比例稍高(男女比例为1.01∶1);②患病例数随年份增加而增多(P < 0.05),致伤时间的季节分布差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),冬季例数最多(44.5%);③乌鲁木齐地区患者例数最多,共300例(48.54%);④致伤原因分布差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),跌倒伤最高,占78.64%,年龄和性别与致伤原因分布的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);⑤各年龄段患者受伤至手术时间分布差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);⑥主要采用手术治疗,占89.32%;手术治疗后6个月死亡率显著低于保守治疗的患者(P < 0.05);⑦结果提示,股骨转子间骨折住院患者在年龄、性别、地区分布、致伤原因、致伤时间、致伤到手术时间、治疗方式及治疗后6个月死亡率等方面有一定的分布规律,应进一步深入开展防治策略研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5537-6019(郭金超)
中图分类号:
.jpg)