中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3659-3664.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0270
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
拇外翻微创截骨联合“8”字绷带外固定的生物力学分析
李晏乐1,常 程2,岳肖华1,白子兴1,孙家琦1,丛 燕3,温建民1,孙卫东1
- 1中国中医科学院望京医院骨关节二科,北京市 100102;2山西中医药大学,山西省太原市 030619;3北京社会管理职业学院,北京市 101601
Biomechanical study of minimally invasive osteotomy with 8-shaped bandage external fixation of hallux valgus
Li Yan-le1, Chang Cheng2, Yue Xiao-hua1, Bai Zi-xing1, Sun Jia-qi1, Cong Yan3, Wen Jian-min1, Sun Wei-dong1
- 1Second Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China; 2Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 3Beijing Vocational College of Social Management, Beijing 101601, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
拇外翻微创截骨:采用削磨钻于第一跖骨头颈部斜形截骨,结合中医整复骨折畸形手法治疗拇外翻的手术方法。该方法切口小,操作简便,无需内固定,治疗后行“8”字绷带外固定、配合中药内服外用及康复锻炼等,是目前治疗拇外翻较好的方法。
主、被动功能锻炼:主动功能锻炼是指患者主动进行足趾及踝关节的跖屈、背伸,活动跖趾及趾间关节,重点以第一跖趾关节为主;被动功能锻炼指患者一手紧握截骨端,维持截骨端位置不动,另一手握住第一跖趾关节远端,做关节的屈伸活动。该方法能有效防止关节粘连,恢复关节功能,预防治疗后并发症的发生,临床应引起足够重视。
摘要
背景:拇外翻是临床常见足部畸形之一,严重影响患者生活质量,传统手术治疗采取大切口,直视下矫形手术,患者痛苦大,恢复慢。随着微创技术的进步与发展,中西医结合微创治疗拇外翻在临床应用广泛,具有切口小,恢复快,能够尽早下地等优点。
目的:测量拇外翻微创截骨治疗后“8”字绷带外固定患者行走、站立及主被动功能锻炼时截骨端周围压力。
方法:对1例拇外翻微创治疗后4周的24岁女性患者,运用SPI FREE FORM 32通道单点压力测量系统测量患者在行走、站立、主动跖屈、主动背伸、被动跖屈与被动背伸6种状态下“8”字绷带外固定拇外翻截骨端周围的压力参数。
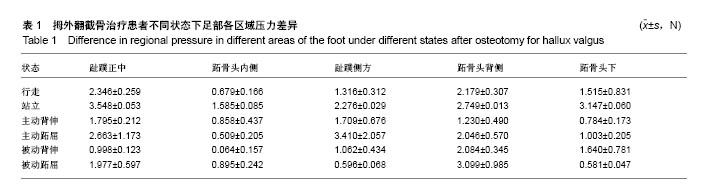
结果与结论:通过对拇外翻治疗后“8”字绷带外固定下不同区域的压力分析,趾蹼正中始终保持较大的压力;除站立状态下,跖骨头背侧压力均大于跖骨头下压力;除被动跖屈状态下,趾蹼侧方压力均大于跖骨头内侧压力。提示拇外翻微创截骨治疗后“8”字绷带外固定能维持截骨远端跖屈位及拇趾中立位,有效保持截骨端的稳定,有利于骨折愈合。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5511-4385(李晏乐)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)