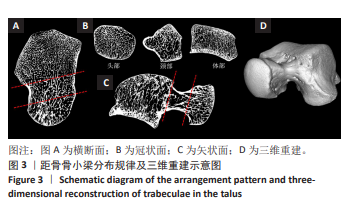
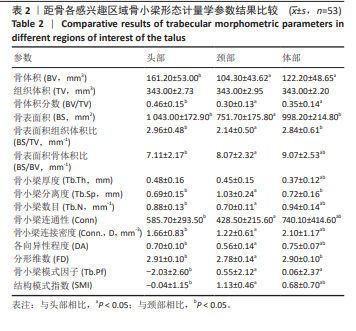
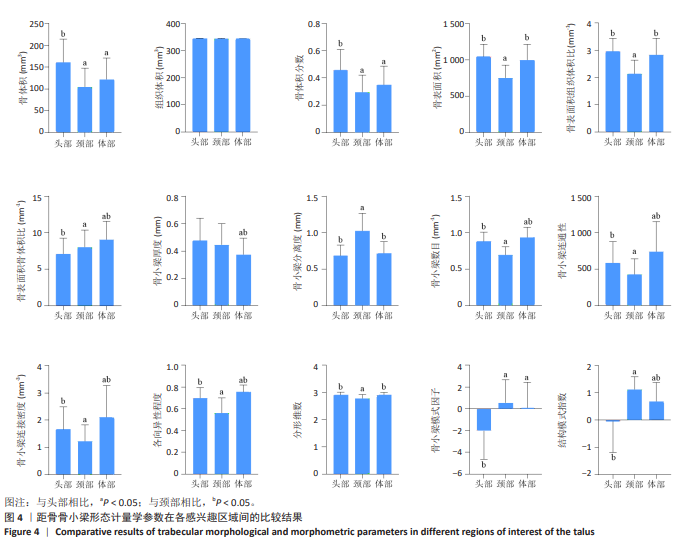
[1] HEGAZY AA, HEGAZY MA. Talus bone: Unique anatomy. Int J Cadav Stud Anat Variat. 2022;3(2):52-55.
[2] 刘洪达,闫荣亮,张波,等.距骨骨折治疗研究进展[J].足踝外科电子杂志,2018,5(1):56-58.
[3] BARBONE GE, BRAVIN A, MITTONE A, et al. High-Spatial-Resolution Three-dimensional Imaging of Human Spinal Cord and Column Anatomy with Postmortem X-ray Phase-Contrast Micro-CT. Radiology. 2021;298(1):135-146.
[4] 续开亮,孟昊业,汪爱媛,等.骨质疏松性头颈型股骨颈骨折股骨头的显微CT观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2024,30(8):706-710+726.
[5] EL-GIZAWY AS, MA X, PFEIFFER F, et al. Characterization of microarchitectures, stiffness and strength of human trabecular bone using micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT) scans. BioMed. 2023;3(1):89-100.
[6] RIBEIRO AKC, DE FREITAS RFCP, DE CARVALHO IHG, et al. Flexural strength, surface roughness, micro-CT analysis, and microbiological adhesion of a 3D-printed temporary crown material. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(5):2207-2220.
[7] 李晶,任晓琦,乔玮,等.一种新型可塑形骨填充材料的制备及骨修复能力研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(3):302-307.
[8] SHEVROJA E, CAFARELLI FP, GUGLIELMI G, et al. DXA parameters, Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD), in fracture risk prediction in endocrine-mediated secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine. 2021;74(1):20-28.
[9] CHU L, HE Z, QU X, et al. Different subchondral trabecular bone microstructure and biomechanical properties between developmental dysplasia of the hip and primary osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2019;22:50-57.
[10] ALMHDIE-IMJABBAR A, PODSIADLO P, LJUHAR R, et al. Trabecular bone texture analysis of conventional radiographs in the assessment of knee osteoarthritis: review and viewpoint. Arthritis Res. 2021; 23(1):1-13.
[11] YU YE, HU YJ, ZHOU B, et al. Microstructure Determines Apparent-Level Mechanics Despite Tissue-Level Anisotropy and Heterogeneity of Individual Plates and Rods in Normal Human Trabecular Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(9):1796-1807.
[12] KRAUSE M, RUPPRECHT M, MUMME M, et al. Bone microarchitecture of the talus changes with aging. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(11): 3663-3771.
[13] 范峥睿,马剑雄,赵兴文,等.基于高分辨X线及Micro-CT的距骨内骨小梁空间结构研究[J].中华医学杂志,2021,101(37):2982-2987.
[14] KAROBARI MI, BATUL R, KHAN M, et al. Micro computed tomography (Micro-CT) characterization of root and root canal morphology of mandibular first premolars: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):1.
[15] MOLINO G, MONTALBANO G, PONTREMOLI C, et al. Imaging techniques for the assessment of the bone osteoporosis-induced variations with particular focus on micro-ct potential. Applied Sciences. 2020;10(24):8939.
[16] YANG X, WANG Q, YAN C, et al. A dual-functional strontium-decorated titanium implants that guides the immune response for osseointegration of osteoporotic rats. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;233:113643.
[17] AKHTER MP, RECKER RR. High resolution imaging in bone tissue research-review. Bone. 2021;143:115620.
[18] GIANAKOS AL, YASUI Y, FRASER EJ, 等.不同骨髓刺激技术对人距骨软骨下骨的影响:一项Micro-CT评价研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2017,9(2):122.
[19] 李彦璋,王鼎予,方璇,等.microCT重建距骨骨内微小动脉三维结构的临床解剖学研究[J].生物医学转化,2021,2(1):95-100.
[20] 陈兴明,梁振华.低剂量CT扫描技术在距骨骨折的应用价值研究[J].佛山科学技术学院学报(自然科学版),2019,37(6):54-57.
[21] 何锦泉.距骨数字化三维形态学特征研究及临床应用[D].天津: 天津医科大学,2017.
[22] HEGAZY MA, KHAIRY HM, HEGAZY AA, et al. Talus bone: normal anatomy, anatomical variations and clinical correlations. Anat Sci Int. 2023;98(3):391-406.
[23] SCHWARTZ AM, RUNGE WO, HSU AR, et al. Fractures of the Talus: Current Concepts. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2020;5(1):2473011419900766.
[24] ZHANG H, FLETCHER AN, SCOTT DJ, et al. Avascular Osteonecrosis of the Talus: Current Treatment Strategies. Foot Ankle Int. 2022;43(2): 291-302.
[25] KADAKIA RJ, AKOH CC, CHEN J, et al. 3D Printed Total Talus Replacement for Avascular Necrosis of the Talus. Foot Ankle Int. 2020;41(12): 1529-1536.
[26] LORENTZON M. The Importance and Possible Clinical Impact of Measuring Trabecular and Cortical Bone Microstructure to Improve Fracture Risk Prediction. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(5):831-832.
[27] ÖHMAN-MÄGI C, HOLUB O, WU D, et al. Density and mechanical properties of vertebral trabecular bone-A review. JOR Spine. 2021; 4(4):e1176.
[28] CHAVASSIEUX P, CHAPURLAT R. Interest of Bone Histomorphometry in Bone Pathophysiology Investigation: Foundation, Present, and Future. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:907914.
[29] DING M, OVERGAARD S. 3-D microarchitectural properties and rod- and plate-like trabecular morphometric properties of femur head cancellous bones in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;28:159-168.
[30] BARRETT JM, MCKINNON C, CALLAGHAN JP. Cervical spine joint loading with neck flexion. Ergonomics. 2020;63(1):101-108.
[31] 钟毅征,黄培镇,蔡群斌,等.影响骨小梁微有限元模型最大应力的骨微结构指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1313-1318.
[32] MAQUER G, MUSY SN, WANDEL J, et al. Bone volume fraction and fabric anisotropy are better determinants of trabecular bone stiffness than other morphological variables. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6): 1000-1008.
[33] 郭新路.骨小梁结构形态学参数分析与仿生重建[D].大连:大连理工大学,2018.
[34] 吴沛泽,罗守华,陈功,等.基于MicroCT的骨小梁参数测量系统的应用效果分析[J].中国医疗设备,2016,31(4):45-48+39.
[35] XIONG Z, ROUQUIER L, CHAPPARD C, et al. A New Microarchitecture-Based Parameter to Predict the Micromechanical Properties of Bone Allografts. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(9):3349.
[36] 文才,周黄君,叶思娴,等.口腔种植骨愈合期内骨小梁分形维度化的初步研究[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(4):335-339.
[37] CARVALHO BF, DE CASTRO JGK, DE MELO NS, et al. Fractal dimension analysis on CBCT scans for detecting low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Imaging Sci Dent. 2022;52(1):53-60.
[38] BANEFELT J, TIMOSHANKO J, SÖRESKOG E, et al. Total Hip Bone Mineral Density as an Indicator of Fracture Risk in Bisphosphonate-Treated Patients in a Real-World Setting. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(1):52-58.
[39] 吴成爱,阎国强,李宁,等.Micro-CT观察重组人甲状旁腺素在骨折愈合过程中的作用[J].中国实验动物学报,2017,25(4):350-355.
[40] 王红涛.距骨骨折的基础研究及临床治疗进展[J].医学理论与实践, 2017,30(1):30-31+33. |