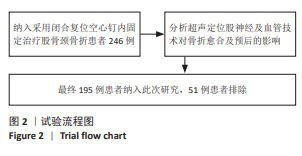
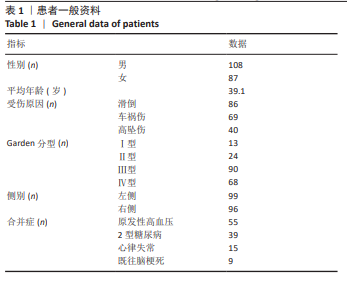
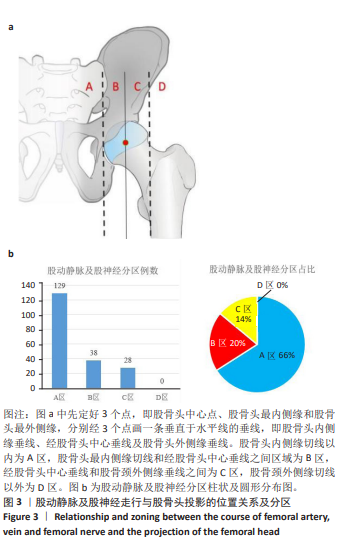
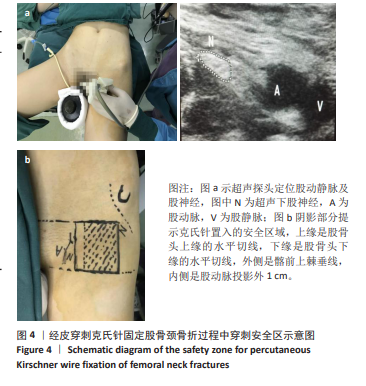
[1] 王凤丽,徐咏梅,李高玉,等.股骨颈系统与空心螺钉固定股骨颈骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(24):2221-2225.
[2] LIM EJ, KIM BS, KIM CH. Parallel and non-parallel cannulated screw fixation complications in femoral neck fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(6):103005.
[3] 吴升辉,缪语,朱晓中,等.股骨颈骨折对局部血供的损伤及评估:解剖基础及其临床运用进展[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(3):294-298.
[4] KONARSKI W, POBOŻY T, ŚLIWCZYŃSKI A, et al. Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head-Overview and Current State of the Art. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(12):7348.
[5] LIM EJ, KIM BS, KIM M, et al. Open reduction versus closed reduction in internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fracture in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):49.
[6] REN B, LV X, MA Q. Fine-tuning reduction of femoral neck fracture with crossed Kirschner wires. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(11):5037-5038.
[7] GARDEN RS. Malreduction and avascular necrosis in subcapital fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971;53(2): 183-197.
[8] ELKHOLY AR, REZK EM, SHABAAN N, et al. The role of preoperative ultrasound in the management of peripheral nerve injuries. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2024;236:108083.
[9] GAO Z, HAU WK, LU M, et al. Automated Framework for Detecting Lumen and Media-Adventitia Borders in Intravascular Ultrasound Images. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(7):2001-2021.
[10] ZHAO S, GAO Z, ZHANG H, et al. Robust Segmentation of Intima-Media Borders With Different Morphologies and Dynamics During the Cardiac Cycle. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2018;22(5):1571-1582.
[11] YU S, XU X, PANDEY NR, et al. A safe percutaneous technique for the reduction of irreducible femoral neck fractures using ultrasound localization of the femoral vascular and nervous structures at the hip. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(15):e15163.
[12] CHU K, CHENG G, YU GZ, et al. Inconsistency of Bone Mineral Density Between Femoral Head and Proximal Femur After Femoral Neck Fracture Surgery Indicates Great Possibility of Femoral Head Necrosis. Orthopedics. 2021;44(2):e223-e228.
[13] LIU Y, LIANG H, ZHOU X, et al. Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis of Femoral Head Necrosis After Long-Term Internal Fixation for Femoral Neck Fracture. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(6):1186-1192.
[14] 王伯珉,杨永良,贾宏磊,等.股骨颈骨折的手术治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2022,24(7):539-543+549.
[15] ZHOU X, JI H, GUO J, et al. Modified osteotomy of posterolateral overhanging part of the trochanter via posterior approach for hip arthroplasty: an anatomical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):119.
[16] 吴红斌.股直肌、缝匠肌皮瓣移位修复腹壁缺损的应用解剖学[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,1989(3):171-174+191.
[17] IKE H, BODNER RJ, LUNDERGAN W, et al. The Effects of Pelvic Incidence in the Functional Anatomy of the Hip Joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(11):991-999.
[18] GONZÁLEZ BLUM C, RICHTER R, FUCHS R, et al. An interprofessional teaching approach for medical and physical therapy students to learn functional anatomy and clinical examination of the lower spine and hip. Ann Anat. 2020;231:151534.
[19] KURODA Y, RAI A, SAITO M, et al. Anatomical variation of the Psoas Valley: a scoping review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):219.
[20] ZHOU W, SANKAR WN, ZHANG F, et al. Evolution of concentricity after closed reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(5):618-626.
[21] HUANG C, TAN H, KERNKAMP WA, et al. Effect of altered proximal femoral geometry on predicting femoral stem anteversion in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):420.
[22] TU LA, WEINBERG DS, LIU RW. The association between femoral neck shaft angle and degenerative disease of the hip in a cadaveric model. Hip Int. 2022;32(5):634-640.
[23] 徐高翔,唐佩福.股骨颈前倾角测量方法的回顾与展望[J].解放军医学院学报,2020,41(1):97-100.
[24] 孙蕴,贺丽英,马兆坤,等.Ward三角区再研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(6):706-710+717.
[25] BARTONÍČEK J, ALT J, NAŇKA O. Internal architecture of the proximal femur: calcar femorale or Adams’ arch?. Int Orthop. 2023;47(7): 1871-1877.
[26] 党瑞山,陈尔瑜,蔡国君,等.股骨距的应用解剖[J].解剖学杂志, 2001,24(6):587-590.
[27] 高令军,裘世静.股骨距的三维结构和显微结构特征及其力学意义[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(2):109-112.
[28] GREENEWAY GP, PAGE PS, AMMANUEL SG, et al. Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve transposition. Neurosurg Focus Video. 2023;8(1):V8.
[29] BECCIOLINI M, PIVEC C, RIEGLER G. Ultrasound of the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: A Review of the Literature and Pictorial Essay. J Ultrasound Med. 2022;41(5):1273-1284.
[30] KONG L, ZUO R, WANG M, et al. Silencing MicroRNA-137-3p, which Targets RUNX2 and CXCL12 Prevents Steroid-induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Facilitating Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(4):655-670.
[31] AL FALEH AF, JAWADI AH, SAYEGH SA, et al. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: Assessment following developmental dysplasia of the hip management. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2020;14(1):20-23.
[32] MEI J, QUAN K, WANG H, et al. Total cross-sectional area of the femoral neck nutrient foramina measured to assess arterial vascular beds in the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):439.
[33] LEI P, DU W, LIU H, et al. Free vascularized iliac bone flap based on deep circumflex iliac vessels graft for the treatment of osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):397.
[34] YOSHIMATSU H, YAMAMOTO T, HAYASHI A, et al. Use of the transverse branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery as a landmark facilitating identification and dissection of the deep branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery for free flap pedicle: Anatomical study and clinical applications. Microsurgery. 2019;39(8):721-729.
[35] 许本柯,徐达传,王兵,等.股骨头血供特点及临床意义[J].解剖学杂志,2007,30(3):371-373.
[36] WANG P, WANG C, MENG H, et al. The Role of Structural Deterioration and Biomechanical Changes of the Necrotic Lesion in Collapse Mechanism of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(5):831-839.
[37] WANG Y, MA JX, YIN T, et al. Correlation Between Reduction Quality of Femoral Neck Fracture and Femoral Head Necrosis Based on Biomechanics. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):318-324.
[38] GREER RB 3RD. Wolff’s Law. Orthop Rev. 1993;22(10):1087-1088.
[39] 许新忠, 吴钟汉, 余水生, 等. 斯氏针置入股骨头不同方式的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1313-1317.
[40] 于潇杰,宋修恩,荣晓玲.CT与MRI对不同分型股骨颈骨折的诊断效能比较[J].医学影像学杂志,2024,34(5):165-168.
[41] DONG Y, LUO C, ZHANG N, et al. [Correlation between combined deflection angle classification adduction typing and complications after internal fixation of adduction femoral neck fracture]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024;38(4):405-411. |